![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
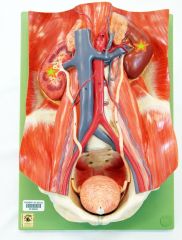
|
Kidneys - perform excretory functions of urinary system - produce urine |
|
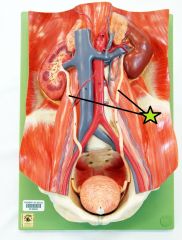
|
Ureters - transports urine to urinary bladder |
|
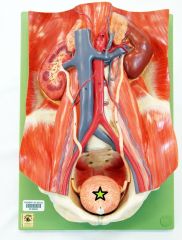
|
Urinary Bladder - temporarily stores urine |
|
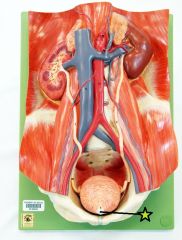
|
Urethra - conducts urine to exterior - for males transports semen |
|
|
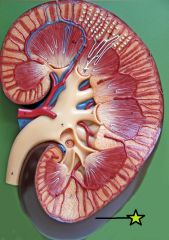
Capsule - outer surface of the kidney - maintains shape and provides mechanical protection |
|
|
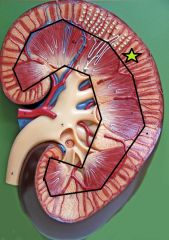
Renal Cortex - outer layer of the kidney |
|
|
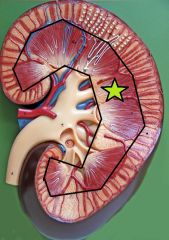
Renal Medulla - composed of 6-18 renal pyramids |
|
|
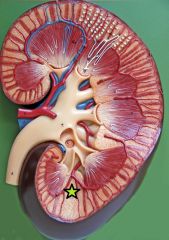
Renal Column - bands of cortical tissue separating adjacent renal pyramids |
|
|
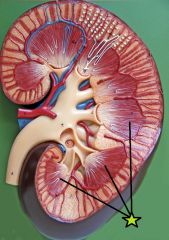
Renal Pyramid - base faces cortex - renal papilla (tip) projects into renal sinus |
|
|
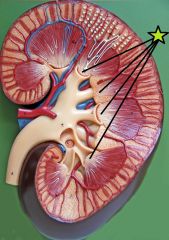
Renal Papilla - converging tip of the renal pyramid |
|
|
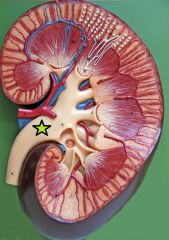
Renal Pelvis - large funnel shaped chamber formed by converging major calyces |
|
|
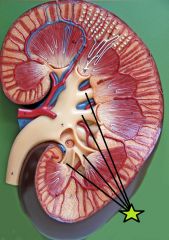
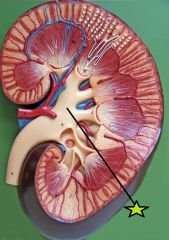
Minor Calyx - cup shaped drain in which renal papilla discharge urine into |
|
|
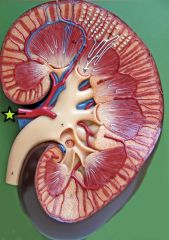
Major Calyx - formed by the convergence of 4-5 minor calyces |
|
|
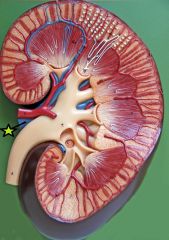
Renal Artery - supplies blood to the kidney from abdominal aorta - branches into segmental arteries |
|
|
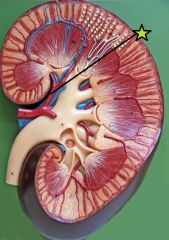
Renal Vein - drain kidney - interlobar veins converge to form |
|
|
Segmental Artery - diverge from renal artery - further divide into interlobar arteries |
|
|
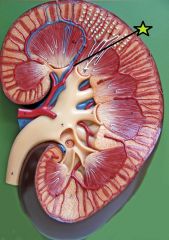
Interlobar Artery - diverge from segmental arteries - extend thru renal columns between renal pyramids - supplies blood to arcuate arteries |
|
|
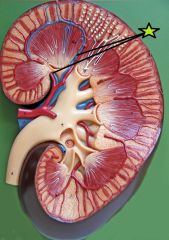
Interlobar Vein - drain into renal vein - drain arcuate veins |
|
|
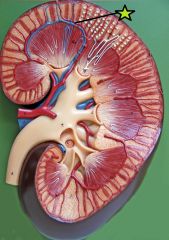
Arcuate Artery - arise from interlobar arteries - parallel boundary between cortex and medulla - diverge to cortical radiate arteries (interlobular) |
|
|
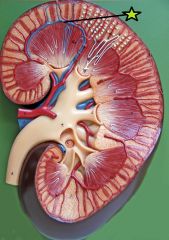
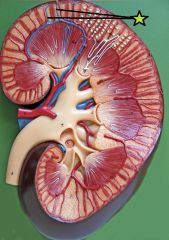
Arcuate Vein - parallel boundary between cortex and medulla - collect blood from interlobular veins - drain into interlobar veins |
|
|
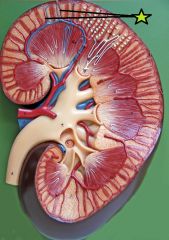
Interlobular Vein - collect blood from nephron venules - drain into arcuate vein |
|
|
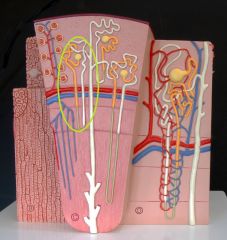
Cortical Radiate Arteries (Interlobular Arteries) - diverge from arcuate artery - branch to afferent arterioles - supply nephrons |
|
|
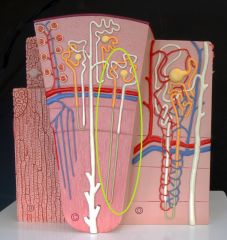
Cortical Nephron - 85% of all nephrons - located w/in superficial cortex - short nephron loop - perform most of reabsorptive and secretory fxns |
|
|
Juxtamedullary Nephron - 15% of all nephrons - located closer to medulla - long nephron loop - create conditions necessary for the production of concentrated urine |
|
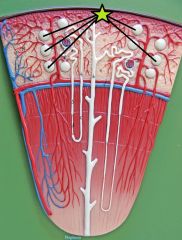
|
Bowman's Capsule - glomerular capsule - outer wall: capsular (parietal) epithelium - separated by capsular space - inner layer: covers glomerular capillaries |
|

|
Capsular (parietal) Epithelium - outer wall of the capsule |
|

|
Podocytes (visceral) Epithelium - covers glomerular capillaries - specialized cells |
|

|
Proximal Convoluted Tubule - 1st part of the renal tube - absorbs organic nutrients, ions, and plasma proteins from filtrate |
|
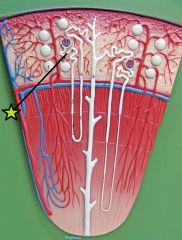
|
Proximal Convoluted Tubule - 1st part of renal tube - absorbs organic nutrients, ions and plasma proteins from filtrate |
|

|
Nephron Loop (Loop of Henle) - thick segs closest to cortex, thin segs w/in deeper medulla - descending & ascending limb - reabsorption |
|
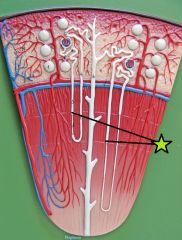
|
Nephron Loop (Loop of Henle) - thick segs closest to cortex, thin segs w/in deeper medulla - descending & ascending limb - reabsorption |
|

|
Distal Convoluted Tubule - end of ascending limb - secretion, absorption |
|
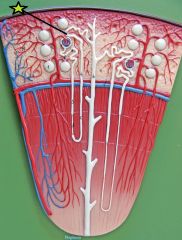
|
Distal Convoluted Tubule - end of ascending limb - secretion, absorption |
|
|
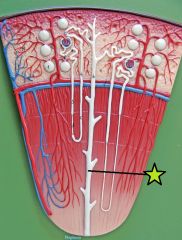
Collecting Duct - collects tubular fluid from distal convoluted tubules - final adjustment to osmotic concentration and volume |
|

|
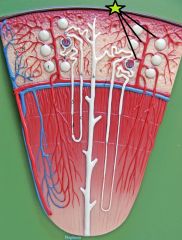
Afferent Arteriole - branch from cortical radiate arteries - supply individual nephrons |
|
|
Afferent Arteriole - branch from cortical radiate arteries - supply individual nephrons |
|
|
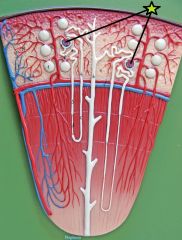
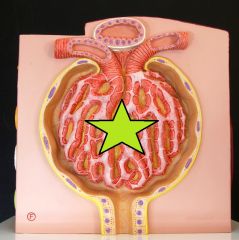
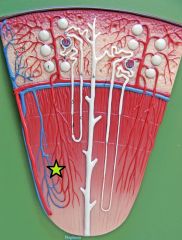
Glomerulus - capillary network w/in renal corpuscule - blood arrives via afferent arteriole and exit via efferent arteriole - filtration across the walls produces a filtrate that passes on to proximal convoluted tubule |
|
|
Glomerulus - capillary network w/in renal corpuscule - blood arrives via afferent arteriole and exit via efferent arteriol - filtration across the walls produce a filtrate that passes on to proximal convoluted tubule |
|

|
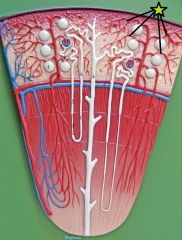
Efferent Arteriole - departs glomerulus into peritubular capillaries |
|
|
Efferent Arteriole - departs glomerulus into peritubular capillaries |
|
|
Peritubular Capillaries - receives blood from efferent arteriole - surround renal tubules - drain into venules that lead to interlobular veins |
|
|
Vasa Recta |
|
|
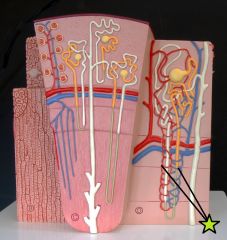
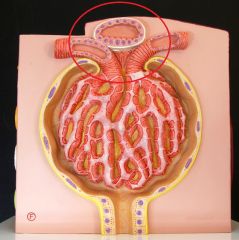
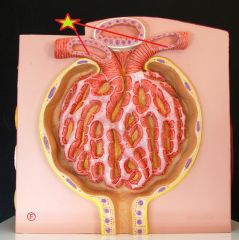
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus - endocrine structure which seceretes renin and erythropoietin - regulates blood volume and BP |
|
|
Juxtaglomerular Cells |
|
|
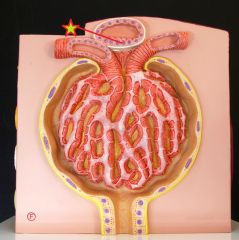
Macula Densa |
|
|
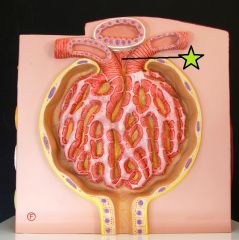
Extraglomerular Mesangial Cells |
|
|
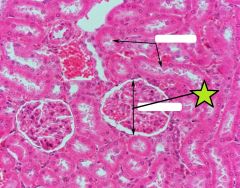
Renal Corpuscle |
|
|
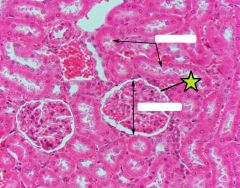
Bowman's Capsule |
|
|
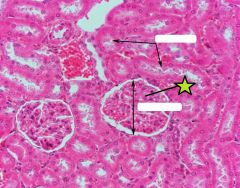
Glomerulus |
|
|
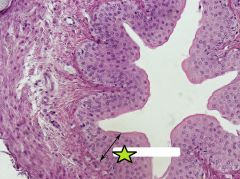
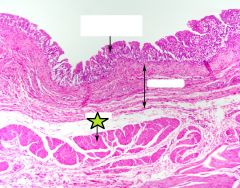
Transitional Epithelium of Ureter |
|
|
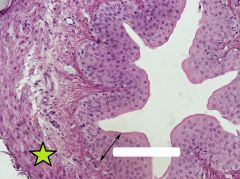
Smooth Muscle of Ureter |
|
|
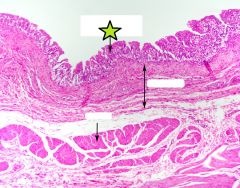
Transitional Epithelium of Urinary Bladder |
|
|
Smooth Muscle of Urinary Bladder |

