![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Unilateral Renal Agenesis |
Only having 1 kidney at birth Congenital abnormality |
|
|
Supernumerary Kidney |
Having 3 kidneys at birth 3rd kidney is usually smaller than normal |
|
|
Hypoplastic Kidney |
"mini-kidney" anatomy and function are the same just smaller in size
not the same as "atrophic kidney" which becomes small due to inadequate blood supply |
|
|
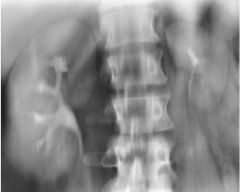
Compensatory Hypertrophy Acquired condition Large kidney preforms work for two kidneys Usually due to inability of other kidney or renal genesis Hypoplastic kidney Delayed/prolonged nephrogram |
|
|
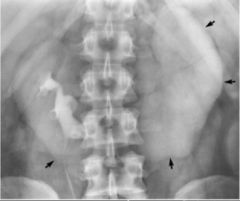
Horseshoe Kidney Most common fusion anomaly Kidneys joints medially at lower poles Prolonged nephrogram left Delayed calcyleal left Obstructive stone |
|
|
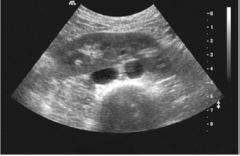
Horseshoe Kidney Most common fusion anomaly Kidneys joined at lower poles Tranverse US Flank pain Stone UVJ |
|
|
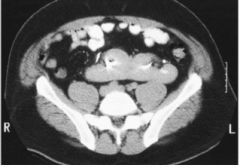
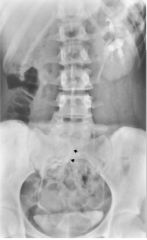
Horseshoe Kidney Most common fusion anomaly Both kidneys improperly positioned and lower poles joined creating horseshoe shape w/Con |
|
|
Ectopic Kidney (Intra-thoracic Kidney) Kidney notpositioned normally within abdomen Kidney in pelvis = pelvic kidney |
|
|
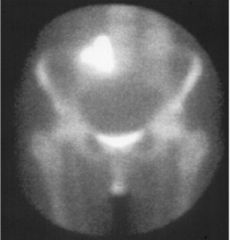
Ectopic Kidney (Pelvic Kidney) Kidney notpositioned normally within abdomen
Kidney in pelvis = Pelvic Kidney |
|
|
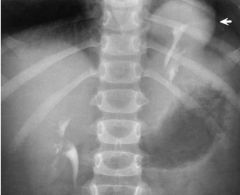
Ectopic Kidney (Intra-thoracic Kidney) Kidney notpositioned normally within abdomen
Kidney above diaphragm = Intra-thoracic Kidney |
|
|
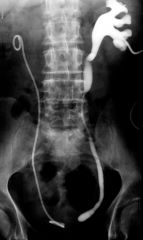
Simple Ureterocele Stenosis of ureter orifice -> urine backs up -> increased pressure -> dilation distal -> ureter prolapses into bladder Ureterocele FILLED with contrast: Round contrast filled density with lucent outline in contrast filled bladder Ureterocele NOT filled with contrast: Appears as radiolucent mass (filling defect in contrast filled bladder) Cobrahead sign
|
|
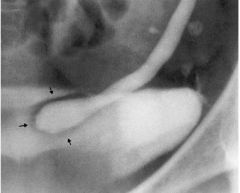
|
Simple Ureterocele Stenosis of ureter orifice -> urine backs up -> increased pressure -> dilation distal -> ureter prolapses into bladder Ureterocele FILLED with contrast: Round contrast filled density with lucent outline in contrast filled bladder
|
|
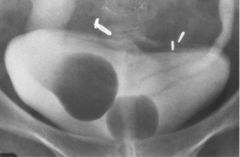
|
Simple Ureterocele Stenosis of ureter orifice -> urine backs up -> increased pressure -> dilation distal -> ureter prolapses into bladder Ureterocele NOT filled with contrast: Appears as radiolucent mass (filling defect in contrast filled bladder)
|
|
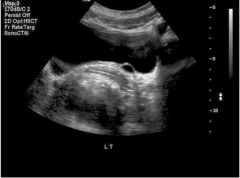
|
Simple Ureterocele Stenosis of ureter orifice -> urine backs up -> increased pressure -> dilation distal -> ureter prolapses into bladder Dilation |
|
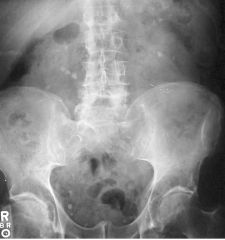
|
Kidney Stones (Renal Calculus) Consolidation of material usually in kidney Calcium Common sites: UPJ /UVJ Hematuria Flank pain radiating toward groin Phleboliths |
|
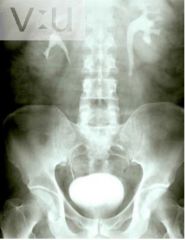
|
Kidney Stones (Renal Calculus)
|
|
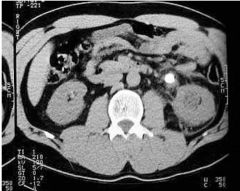
|
Kidney Stones (Renal Calculus)
|
|
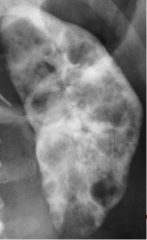
|
Polycystic Kidney Disease (Inherited) Extretory urography Caused by chronic compression of nephrons due to hypertension Lobulated enlargement of kidney Progressive loss of function Crescent shape to kidney Multiple Cysts (swiss-cheese pattern) Delayed/prolongs nepgrogram |
|
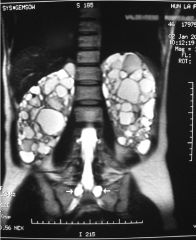
|
Polycystic Kidney Disease (Inherited) Caused by chronic compression of nephrons due to hypertension Lobulated enlargement of kidney Progressive loss of function Crescent shape to kidney Multiple Cysts (swiss-cheese pattern) Thinning of renal parenchyma |
|
|
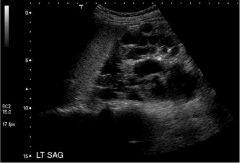
Polycystic Kidney Disease (Inherited) Caused by chronic compression of nephrons due to hypertension progressive loss of function Enlarged kidney Cysts Destruction of renal parenchyma US = screening tool
|
|
|
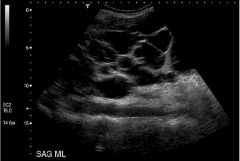
Polycystic Kidney Disease (Inherited) Caused by chronic compression of nephrons due to hypertension progressive loss of function Enlarged kidney Cysts Destruction of renal parenchyma US = screening tool |
|
|
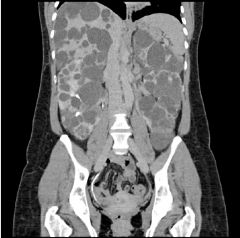
Polycystic Kidney Disease (Inherited) Caused by chronic compression of nephrons due to hypertension progressive loss of function Lobulated enlargement of kidney Progressive loss of function Crescent shape to kidney Multiple Cysts (swiss-cheese pattern) Thinning of renal parenchyma IV con |
|
|
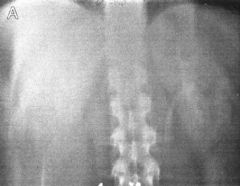
Polycystic Kidney Disease (Inherited) Caused by chronic compression of nephrons due to hypertension progressive loss of function ·Excretory Urography o Enlarged kidney o Lobulated contour o Cresent shape o “swiss cheese” pattern of multiple cysts o Cysts may have calcifications o Delayed/Prolonged nephrograms |
|
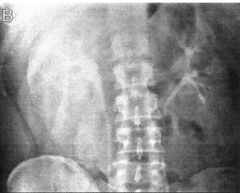
|
Polycystic Kidney Disease (Inherited) Caused by chronic compression of nephrons due to hypertension progressive loss of function Excretory Urography o Enlarged kidney o Lobulated contour o Cresent shape o “swiss cheese” pattern of multiple cysts o Cysts may have calcifications
o Delayed/Prolonged nephrograms |
|
|
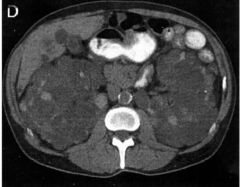
Polycystic Kidney Disease (Inherited) Caused by chronic compression of nephrons due to hypertension progressive loss of function o Enlarged kidneys o Multiple cysts o Thinning of renal parenchyma o PO Contrast |
|
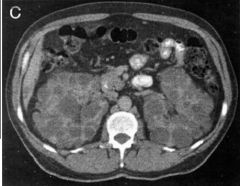
|
Polycystic Kidney Disease (Inherited) Caused by chronic compression of nephrons due to hypertension progressive loss of function o Enlarged kidneys o Multiple cysts o Thinning of renal parenchyma o PO Contrast
|
|
|
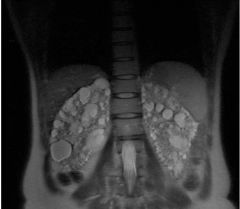
Polycystic Kidney Disease (Inherited) Caused by chronic compression of nephrons due to hypertension progressive loss of function o Enlarged kidneys o Multiple cysts o Thinning of renal parenchyma T2 |
|
|
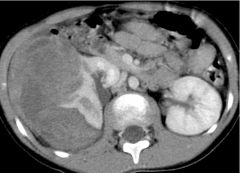
Wilm's Tumor (Nephroblastoma) Common in infants/children Lesions asris from embryonic renal tissue Tumor w/ medullary origins Malignant Large palpable mass Displaced kidney Distorted collecting systems IV Con
|
|
|
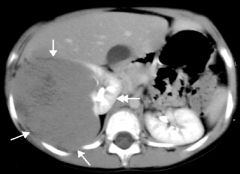
Wilm's Tumor (Nephroblastoma) Common in infants/children Lesions asris from embryonic renal tissue Tumor w/ medullary origins Malignant Large palpable mass Displaced kidney Distorted collecting systems IV Con |
|
|
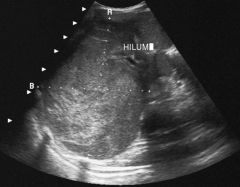
Wilm's Tumor (Nephroblastoma) Common in infants/children Tumor of adrenal medullary origin, arise from embryonic renal tissue Malignant Large palpable mass Displaced kidney Distorted collecting systems Distinguishes tumor from hydronephrosis Large complex mass Kidney hilum displaced medially |
|
|
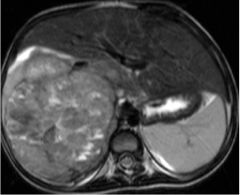
Wilm's Tumor (Nephroblastoma) Common in infants/children Tumor of adrenal medullary origin, arise from embryonic renal tissue Malignant Large palpable mass Displaced kidney MRI T2 Distorted collecting systems |
|
|
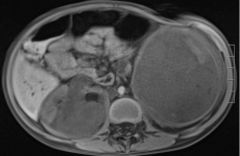
Wilm's Tumor (Nephroblastoma) Common in infants/children Tumor of adrenal medullary origin, arise from embryonic renal tissue Malignant Large palpable mass Displaced kidney MRI T1 |
|
|
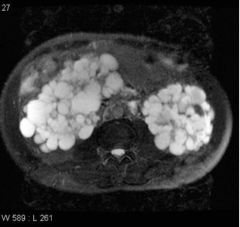
Polycystic Kidney Disease (Inherited) Caused by chronic compression of nephrons due to hypertension o Enlarged kidneys o Multiple cysts o Thinning of renal parenchyma T2 |
|
|
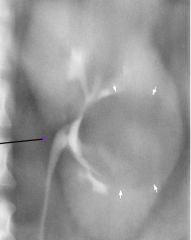
Simple Cyst Nephrotomogram fluid filled cyst elevates adjacent edges of cortex Benign = smooth borders Thin radiopaque rim |
|
|
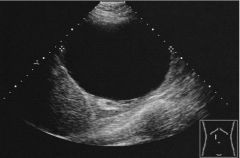
SImple Cyst Anechoic lesions Well defined wall Distinguish simple cyst vs solid mass Benign |
|
|
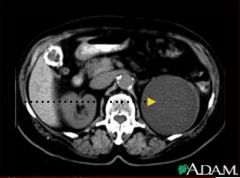
SImple Cyst Fluid Filled Cyst Benign CT PO Con Gallstones Aortic Calcifications Uniform attentuation near water Hypodense mass |
|
|
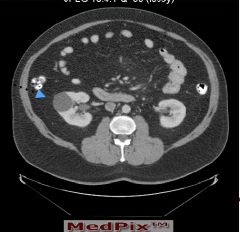
Simple Cyst Fluid Filled cyst Benign CT PO/IV con Simple cyst apparent Hypodense mass |
|
|
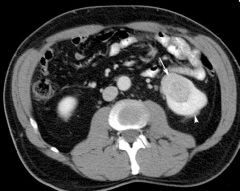
Simple Cyst Fluid Filled cyst Benign CT PO/IV con Simple cyst apparent Hypodense mass |
|
|
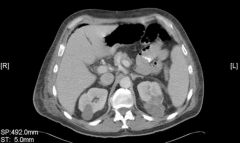
Simple Cyst Fluid Filled cyst Benign & Malignant CT PO/IV con Simple cyst apparent Hypodense mass |
|
|
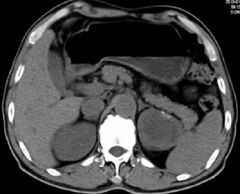
Simple Cyst Fluid Filled cyst MASS Non Con Density in left kidney |
|
|
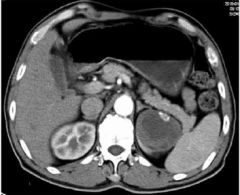
Simple Cyst Fluid filled cyst MASS ARTERIAL PHASE Filling defect left kidney Nothing filling left kidney IV Con |
|
|
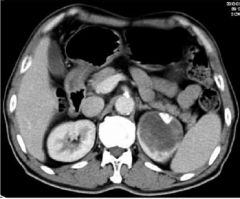
Simple Cyst Fluid filled cyst MASS NEPHROGRAPHIC PHASE Filling defect left kidney Nothing filling left kidney IV Con |
|
|
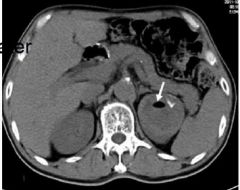
Simple Cyst Fluid filled cyst MASS NON CON Filling defect left kidney Nothing filling left kidney Low density mass in left |
|
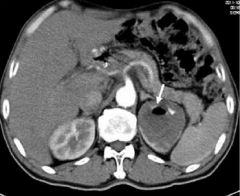
|
Simple Cyst Fluid filled cyst MASS ARTERIAL PHASE Filling defect left kidney Nothing filling left kidney Low density mass in left |
|
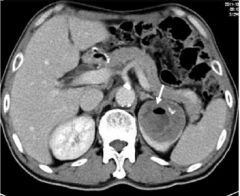
|
Simple Cyst Fluid filled cyst MASS NEPHROGRAPHIC PHASE Filling defect left kidney Nothing filling left kidney Low density mass in left |

