![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Superior Angle |
|
|
|
Inferior Angle |
|
|
|
Glenoid Cavity/ Fossa |
|
|
|
Vertebral (Medial) Border |
|
|
|
Axillary (Lateral Border) |
|
|
|
Superior Border of the Scapula |
|
|
|
Acromion |
|
|
|
Supraspinous Fossa |
|
|
|
Infraspinous Fossa |
|
|
|
Subscapular Fossa |
|
|
|
Supraglenoid Tubercle |
|
|
|
Infraglenoid Tubercle |
|
|
|
Coracoid Process |
|
|
|
Scapular Notch |
|
|
|
Neck of Scapula |
|
|
|
Acromial End of Clavicle |
|
|
|
Sternal End of Clavicle |
|
|
|
Anterior Border of Clavicle |
|
|
|
Trapezoid Line/Ridge of Clavicle |
|
|
|
Conoid Tubercle |
|
|
|
Costal Tuberosity |
|
|
|
Manubrium |
|
|
|
Body of Sternum |
|
|
|
Xiphoid Process |
|
|
|
Rib Facets |
|
|
|
Sternal Angle |
|
|
|
Head of Humerus |
|
|
|
Anatomical Neck of Humerus |
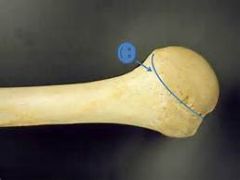
|
|
|
Surgical Neck of Humerus |
|
|
|
Greater Tubercle of Humerus |
|
|
|
Lesser Tubercle of Humerus |
|
|
|
Intertubercular (Bicipital) Groove |
|
|
|
Deltoid Tuberosity |
|
|
|
Lateral Epicondyle of Humerus |
|
|
|
Medial Epicodyle of Humerus |
|
|
|
Lateral Supracondylar Ridge of Humerus |
|
|
|
Medial Supracondylar Ridge of Humerus |
|
|
|
Capitulum |
|
|
|
Trochlea |
|
|
|
Radial Groove |
|
|
|
Olecranon Fossa |
|
|
|
Coronoid Fossa |
|
|
|
Radial Fossa |
|
|
|
Olecranon |
|
|
|
Trochlear Notch |
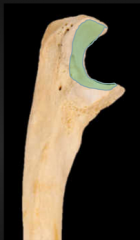
|
|
|
Coronoid Process |
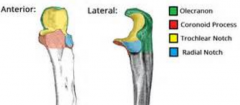
|
|
|
Ulnar Tuberosity |
|
|
|
Radial Notch |
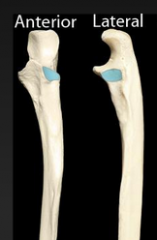
|
|
|
Head and Styloid Process of Ulna |
|
|
|
Ulnar notch of Radius |
|
|
|
Interosseous Membrane |
|
|
|
Dorsal (Lister's) Tubercle |
|
|
|
Scaphoid (navicular) |
|
|
|
Lunate |
|
|
|
Triquetrum |
|
|
|
Pisiform |
|
|
|
Trapezium |
|
|
|
Trapezoid |
|
|
|
Capitate |
|
|
|
Hamate |
|
|
|
Metacarpals |
|
|
|
Phalanges |
|
|
|
Head of Radius |
|
|
|
Radial (Bicipital) Tuberosity |
|
|
|
Spine of Scapula |
|
|
|
Styloid Process of Radius |
|
|
|
Phalanx of the Little Finger |
|
|
|
Phalanx of the Thumb |
|
|
|
Metacarpal of the Little Finger |
|
|
|
Metacarpal of the Thumb |
|

