![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
List the 9 most known planets in our solar system in order |
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Pluto |
|
|
|
Define celestial bodies |
All bodies we can observe from earth |
|
|
|
Define astronomical bodies |
Astronomical bodies refer to all bodies in space , this is different from celestial bodies because we can not observe all of space from earth, astronomical refers to everything |
|
|
|
Define constellation |
A constellation is a group of stars that viewed from Earth, resembles a form |
|
|
|
Define asterisms |
Asterisms are smaller recognizable star patterns within a large constellation |
|
|
|
What is the summer solstice? |
In the northern hemisphere, it occurs around June 21 as the longest period of daytime of the year and marks the beginning of summer |
|
|
|
What is the winter solstice? |
It is the shortest day of the year and represents the start of winter around December 21. In the southern hemisphere the dates are reversed for the summer and winter solstice |
|
|
|
What is an equinox? When are the vernal and autumnal equinoxes? |
An equinox is when the hours of daylight and of night are equal. There are two types of equinox Vernal or spring around March 21 and autumnal around September 22 |
|
|
|
What is Polaris? |
Polaris is the north star, it doesn't appear to move like most starts because it is above the earth you can see it at the tip of the Little Dipper's handle |
|
|
|
What is the Geocentric Model |
A model of the universe used long ago that states that the Earth is the center of everything and everything orbits around us |
|
|
|
What is the Heliocentric Model? |
This is the accepted model of the solar system that states that the Sun is the center of our solar system and all the planets orbit around it
|
|
|
|
Nebula |
Vast clouds of gas and dust, they are the birthplace of stars |
|
|
|
Describe a solar eclipse? |
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon lies directly between Earth and the Sun, blocking all or part of the Sunlight to viewers in Earth (see hint for visualization) |

|
|
|
Define a lunar eclipse? |
A lunar eclipse is when the Earth blocks out the Sun's light on the Moon, making the Moon briefly disappear (see hint for visualisation) |

|
|
|
Define plasma |
Plasma is the fourth state of matter made up of freely moving charged particles |
|
|
|
What is the tilt of the Earth? |
23.5 degrees |
|
|
|
What is a sunspot? |
A sunspot is a region on the Sun's surface that is cooler than the surrounding areas |
|
|
|
What is a solar prominence? |
A solar prominence is a large, curved, low energy, bright stream of particles. It may last for several hours of weeks (see hint for visualization) |
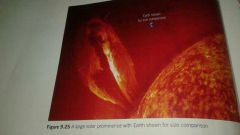
|
|
|
What is a solar flare? |
A solar flare is a high energy massive explosion at the surface of the Sun. An extremely powerful type of solar flare is called a coronal mass ejection. |
|
|
|
What is solar wind? |
Solar wind is the constant flow of particles streaming out of the Sun's surface in all directions |
|
|
|
Name the types of stars and their surface temperatures |
A yellow star had a surface temperature of around 6000 degrees Celsius. A red star has a surface temperature of around 3000 degrees Celsius A blue star has a surface temperature between 20 000 and 35 000
|
|
|
|
What are the aurora borealis and aurora australis? Where do they come from? |
The aurora borealis are the Northern Lights and the aurora australis are the Southern Lights. The both appear when the solar winds penetrates the Magnetosphere and the Earth's magnetic field sends it to the poles where it heats up the air molecules making it glow |
|
|
|
How long is a lunar cycle? |
27 days, 7 hours, 43 minutes. |
|
|
|
How was the Moon likely formed? |
Scientist believe a large object, nearly the size of Mars crashed into the Earth. Earth survived but the other object was destroyed, the gravitational pull of the Earth kept the rubble and debris and it compacted into the Moon. |
|
|
|
Define galaxy |
A large group of solar systems are held together in one galaxy |
|
|
|
What galaxy are we in? |
The Milky way galaxy |
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of galaxies? |
Spiral, Elliptical and Irregular |
|
|
|
What is the closest galaxy to our galaxy? |
Andromena galaxy |
|
|
|
What are spiral galaxies? |
Spiral galaxies are named for the spiral-shaped arms. About half of spiral galaxies including the Milky way have what looks like a bar across them this are called barred spiral galaxies. (See hint for visualization) |
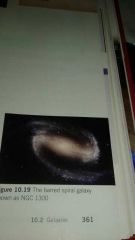
|
|
|
What are elliptical galaxies? |
Elliptical galaxies have shapes ranging from spherical to football-shaped (see hint for visualization) to pencil-shaped.This galaxies are the result of two or more galaxies merging to make a bigger galaxy. |

|
|
|
What is a new moon? |
It is when the Moon lies between Earth and the Sun, none of the sunlight reaches the side that is facing the Earth |
|
|
|
What are irregular galaxies? |
Galaxies without a regular shape, this may be because a galaxy collided with another one or got to close |
|
|
|
What do scientists believe would happen without a moon |
Scientist believe that without a moon, life would not be able to sustain, there would be extreme temperatures ranging from 100 degrees Celsius to -80, Earth would not be able to sustain it's tilt so the Earth would wobble, which would cause extreme environmental changes like snow in deserts and flooding of coasts. Some animals and plants would not know when to mate and that would disturb the food chain. We would be vulnerable to much more asteroid strikes. Basically it would be bad.
|
|
|
|
Nebula theory |
The theory that explains the formation if the solar system and other starand planets systems from nebulae |
|

