![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe an actinic keratosis.
|
Flat, scaly, with underlying erythema
Small size, lack of strong pigmentation Confined to epidermis Progresses to a white scale or rough spot Poorly demarcated Most common on face/scalp and dorsum of hands |
|
|
Which UV light is most responsible for melanoma?
|
Used to think UVA, but now think UVB
|
|
|
What skin cancer has a pearly or waxy appearance?
|
Basal cell carcinoma
|
|
|
What is the most common type of skin cancer?
|
Basal cell carcinoma
|
|
|
Describe a squamous cell carcinoma.
|
Reddish, scaly lesions
Indistinct borders; may bleed easily May have ulcerated center Potential for rapid growth May develop keratin "horn" |
|
|
What is the percentage of metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma?
|
2-6%
|
|
|
What are the complications of basal cell carcinoma?
|
Direct structural or functional damage
Loss of tissue Scarring |
|
|
What layers of skin does UVA penetrate?
|
deep dermis
however, not as effective as UVB in causing biological change |
|
|
What layers of skin does UVB penetrate?
|
Penetrates epidermis to upper dermis
|
|
|
Which UV is responsible for most biological changes?
|
UVB
|
|
|
How long does it take for UVB to redden skin?
|
6 hours
|
|
|
How long does it take for UVB to darken skin?
|
48-72 hours
|
|
|
What skin lesion is considered an early stage of squamous cell carcinoma?
|
Actinic keratosis
|
|
|
What is the treatment for an isolated actinic keratosis?
|
cryotherapy
|
|
|
What is the treatment for multiple actinic keratoses?
|
topical 5-fluorouracil cream BID for 3 wks
may also use tretinoin, chemical peels, imiquimod, diclofenac |
|
|
Describe a basal cell carcinoma.
|
75-80% of non-melanocytic skin cancers
Pearly, waxy surface May be nodular with central depressed ulcer May resemble dermatitis - red, scaly, wrinkled plaque Morpheaform - look like scars, indurated |
|
|
What is the histology of basal cell carcinoma?
|
islands of basophilic keratinocytes
|
|
|
Which UV light is most responsible for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma
|
UVB
|
|
|
What type of genetic disease is basal cell nevus syndrome?
|
Autosomal dominant
|
|
|
Other than skin manifestations, what are the other signs of basal cell nevus syndrome?
|
Large cysts that can break jaw
Wideset eyes Prominent brow Medullablastomas in kidney Brain tumors |
|
|
What is the histology of squamous cell carcinoma?
|
pleomorphic keratinocytes
|
|
|
What transplant recpients are at greatest risk for failed treatment of squamous cell carcinoma?
|
Heart (most)
Kidney Liver |
|
|
What is the 5 year recurrence percentage for large squamous cell carcinomas?
|
70%
|
|
|
Which UV light causes direct damage?
|
UVB
|
|
|
What is the 5 year recurrence percentage for primary squamous cell carcinomas?
|
8%
|
|
|
What is the 5 year recurrence percentage of lip/ear squamous cell carcinomas?
|
10-25%
|
|
|
At what rate do squamous cell tumors larger than 2 cm metastasize?
|
30%
|
|
|
What are the high risk areas of the body for squamous cell carcinoma?
|
Lips, mucosa, ears
Hands, scalp, forehead, temple, eyelid, nose Penis, scrotum, anus Nail folds |
|
|
What treatment is suitable for in situ squamous cell carcinoma?
|
Electrodessication
Curettage |
|
|
What excision size is suitable for a squamous cell carcinoma smaller than 2 cm and in a low risk site?
|
Excision with 4 mm margin
|
|
|
What excision size is suitable for squamous cell carcinomas larger than 2 cm or in a high risk site?
|
Excision with 6 mm margin
|
|
|
What are the ABCDEs of melanoma?
|
Asymmetry
Border irregularity Color variation Diameter Evolving |
|
|
Where does lentigo maligna melanoma usually occur?
|
on the face
|
|
|
What layer of skin does nodular melanoma start in, and what is the prognosis?
|
deep in dermis
poor prognosis; by the time it is seen on the surface of the skin it's probably metastasized |
|
|
What melanoma appears on the volar hands and feet?
|
Acral-Lentiginous Melanoma
|
|
|
What is the average number of moles for a 40-year-old person?
|
50
|
|
|
What is the current term for benign juvenile melanoma?
|
Spitz nevus
|
|
|
What are the most common forms of chemotherapy used for palliative treatment of metastatic melanoma?
|
DTIC, thalidomide, temozolomide (MTIC)
|
|
|
What does TNM stand for?
|
Tumor
Nodes Metastasis |
|
|
What Clark level describes penetration of the lesion into the lower dermis?
|
Level 4
|
|
|
What does the "a" stand for in this staging?
T2a |
a = not ulcerated
|
|
|
In staging a melanoma, what would M1B mean?
|
Metastases to the lung
|
|
|
In staging a melanoma, what would M1A mean?
|
distant metastases to the skin or subcutaneous tissue or distant lymph nodes
|
|
|
In staging a melanoma, what would M1C mean?
|
Metastases to other organs or distant site with elevated LDH
|
|
|
In staging a melanoma, what does N2A mean?
|
Melanoma has spread to 2 lymph nodes
A = means melanoma can be seen only under microscope |
|
|
In staging a melanoma, what does N1B mean?
|
Metastasis to one lymph node
B = melanoma is visible to naked eye |
|
|
In staging a melanoma, what does N4C mean?
|
Melanoma has spread to 4 or more lymph nodes
C = melanoma can be seen in nearby skin or can be found in lymphatic channels |
|
|
Which UV light causes indirect damage?
|
UVA
|
|
|
What does Clark level 5 indicate?
|
Lesion has invaded subcutaneous tissue
|
|
|
What does Clark level 1 indicate?
|
Lesion confined to epidermis
|
|
|
Which Clark level would indicate that a lesion has begun to invade the dermis?
|
Level 2
|
|
|
What does Clark level 3 indicate?
|
Lesion involves most of the upper dermis
|
|
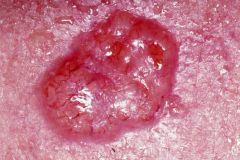
What is this?
|
Basal cell carcinoma
|
|
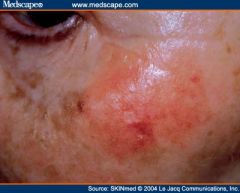
What is this?
|
Amelanotic lentigo maligna melanoma
|
|
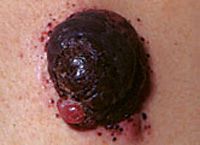
What is this?
|
Nodular melanoma
|
|
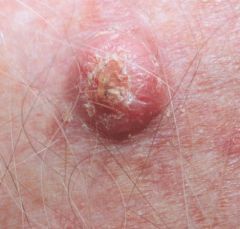
What is this?
|
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
Which UV light penetrates deeper?
|
UVA
|

