![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
The Chavín were a civilization that developed in the northern Andean highlands of Peru from 900 BC to 200 BC. They extended their influence to other civilizations along the coast.
Inspired other civilazations to increase trade and religion |
|

Olmec |
The Olmec were the first 'major' civilization in Mexico following a progressive development in Soconusco
First major civilization to use messengers by foot. |
|

Zapotec |
A member of an American Indian people living in and around Oaxaca in southern Mexico.
Ancient tribe responsible for the early agriculture. |
|

Aztec |
A member of the American Indian people dominant in Mexico before the Spanish conquest of the 16th century.
They controlled almost 40% of Southern America at it's peak. |
|

Montezuma |
Moctezuma I, also known by a number of variant spellings including Montezuma, Moteuczoma, Motecuhzoma and referred to in full by early Nahuatl texts as Motecuhzoma Xocoyotzin, was the ninth tribal leader.
Died by disease even though he was to liking of the spanish people. |
|

Tribute System |
The Imperial tributary system of China was the network of trade and foreign relations between China and China's "tributaries" whose ideals in one form or another, for millennia, drove much of East Asian affairs.
Was the first ever official trading system between countries. |
|

Tenochtitlan |
The capital of the Aztec empire: founded in 1325; destroyed by the Spaniards in 1521; now the site of Mexico City.
If not for the horseback of the spanish, the aztec's could have taken over Spain because of there numerous numbers. |
|

Lake Texcoco |
Lake Texcoco was a natural lake formation within the Valley of Mexico. The Aztecs built the city of Tenochtitlan on an island in the lake.
It was a major hotspring for travelers and tourists during the times. |
|

Inca |
The Inca Empire or Inka Empire was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America.
Largest known empire in the world besides Europe, they had vast military powers but were destroyed by diseased and flooding. |
|

Quipu |
An ancient Inca device for recording information, consisting of variously colored threads knotted in different ways.
Used for a writing system, and could be considered a storage system of sorts. |
|

Maya |
A member of a Mesoamerican Indian people inhabiting southeast Mexico, Guatemala, and Belize, whose civilization reached its height around a.d. 300-900. The Maya are noted for their architecture and city planning, their mathematics and calendar, and their hieroglyphic writing system.
They were considered a strong military force, but dissapeared in less than a month which is mysterious. |
|

Chichen Itza |
A village in Yucatán state in Mexico: site of important Mayan ruins.
Known for their brutality and tribute system. |
|

Hieroglyphics |
Writing consisting of hieroglyphs.
The Ancient Egyptians used no punctuation (like full stops, commas or question marks) and they didn’t put any spaces between their words. |
|

Yucatan Peninsula |
A mix of beaches, jungles and history.
The Yucatan Peninsula is a mix of beaches, jungles and history that has become a magnet for tourism |
|

Henry the Navigator |
Prince of Portugal who established an observatory and school of navigation and directed voyages that spurred the growth of Portugal's colonial empire.
Was an early age explorer among others and used advanced geography. |
|

Christopher Columbus |
Prince Henry (Henrique) the Navigator (1394-1460) was a Portuguese royal prince, soldier, and patron of explorers.
Henry sent many sailing expeditions down Africa's west coast, but did not go on them himself. |
|

Vasco de Gama |
Vasco da Gama was the first person to sail directly from Europe to India.
Explorer Vasco da Gama was born in Sines, Portugal, around 1460. In 1497, he was commissioned by the Portuguese king to find a maritime route to the East. |
|

Magellan |
Ferdinand. Portuguese name Fernão de Magalhães. ?1480–1521, Portuguese navigator in the service of Spain.
First sailor to die and never be found under spain's supervision. |
|

Conquistador |
a conqueror, especially one of the Spanish conquerors of Mexico and Peru in the 16th century.
The main spanish explorers killed off the Incas, Mayans and the Aztecs. |
|

Hernan Cortez
|
Spanish conquistador who defeated the Aztecs and conquered Mexico (1485-1547)
He was born in 1485 |
|

Francisco Pizarro |
Spanish explorer and conqueror of the Inca Empire of Peru (1531–1533). He founded the city of Lima in 1535.
He rose from nothing to fame and fortune. |
|

God, Gold, Glory |
"God, glory and gold" was the phrase used by Spanish conquistadors who came to the New World. They came to claim the land in the name of the church, but they also wanted to be famous heroes for doing so. Most of all, they thought they would discover wonderful cities of gold, and they wanted to claim the riches for the church and for themselves.
A lot of Spanish Conquistadors used this term. |
|

Treaty of Tordesillas |
Agreement signed at Tordesillas, Spain, by which Spain and Portugal divided the non-Christian world into two zones of influence. In principle the treaty followed the papal bull issued in1493 by Pope Alexander VI, which fixed the demarcation line along a circle passing 100 leagues W of the Cape Verde Islands and through the two poles. This division gave the entire New World to Spain and Africa and India to Portugal.However, the Treaty of Tordesillas shifted the demarcation line to a circle passing 370 leagues W of the Cape Verde Islands and thus gave Portugal a claim to Brazil. There was little geographic knowledge at the time the treaty wassigned, and it remains controversial whether the Portuguese then knew of the existence of Brazil.
This was written in 1494. |
|

Encomienda System |
A system, instituted in 1503, under which a Spanish soldier or colonist was granted a tract of land or a village together with its Indian inhabitants. |
|
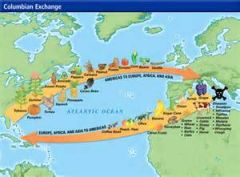
Columbian Exchange |
The Columbian Exchange was a widespread exchange of animals, plants, culture, human populations, communicable disease, and ideas between the American and Afro-Eurasian hemispheres following the voyage to the Americas by Christopher Columbus in 1492.
The term was coined in 1972 by Alfred W. Crosby, a historian at the University of Texas at Austin, in his eponymous work of environmental history. |
|
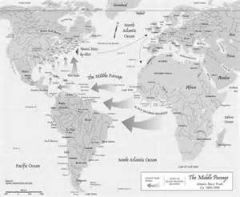
Middle Passage |
The part of the Alantic Ocean between the west coast of Africa and the West Indies. It's the longest part of the journey formerly made by slave ships.
The first known use of this passage was in 1788. |
|
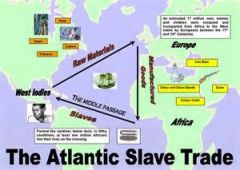
Trans-Alantic Slave Trade |
The Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade began
It was a trade which |
|
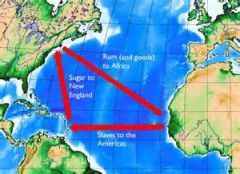
Triangular Trade |
A pattern of colonial commerce in which slaves were bought on the African Gold Coast with New England rum and then traded in the West Indies for sugar or molasses, which was brought back to New England to be manufactured into rum.
A ship leaving Africa for America would contain hundreds of enslaved people, tightly packed in horrific conditions for the journey to their new "home." |
|

Mercantalism |
The theory and system of political economy prevailing in Europe after the decline of feudalism, based on national policies of accumulating bullion, establishing colonies and a merchant marine, and developing industry and mining to attain a favorable balance of trade.
Mercantilism was the dominant school of thought in Europe throughout the late Renaissance and early modern period (from the 15th to the 18th century). |
|
Colonies |
A territory settled on.
Middle Colonies - Pennsylvania Colony: The King of England granted the Quaker William Penn 45,000 square miles of land that was named Pennsylvania |

