![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
adaptive immune defenses in eye
|
IgA (tears), IgG (tears), activated T and B cells
|
|
|
immune privilege
|
suppressed immune responses; protects from inflammatory immune responses which could potentially damage sensitive areas (brain, testes, fetus, eye)
|
|
|
immune privilege in eye mechanism
|
Avascular cornea; limited lymphatic drainage; low/absent MHC expression; local production of anti-inflammatory neuropeptides, cytokines (TGF-b) and other anti-inflammatory molecules (IL-1 receptor antagonist); high expression of complement regulatory proteins; expression of FasL by eye tissues
Il-1R antagonist; binds to IL-1R receptor not letting it signal downreg of complement FasL expressed by eye tissues low/absent MHC expression |
|
|
FasL:fas interaction
|
activates caspase-8 in Fas-expressing immune cells induces apoptosis;
immune cells contact eye tissue which may have FasL = apoptosis |
|
|
Immune privilege and corneal transplantation
|
immune privilege facilitates this; since normal cornea has noblood supply immune cells can't arrive and theres no MHC antigens to act as targets
mcc of graft failure is rejection; rejection by CD4+ T cells does occur bottom line = immune privilege delays but does not prevent rejection |
|
|
5 mechianms fo rimmune privilege in eye
|
limited lymphatic drainage; low/absent MHC; anti-inflammatory neuropeptides; cytokines TGF-B and IL-!Ra; presence of coplement regulatory proteins; FasL expression
|
|
|
why antibiotic prednisolone drops given?
|
empirical tx for post surgical infection/inflammation
|
|
|
why give cyclosporine?
|
inhibis T cell activation (rejection caused by activated T cells)
|
|
|
Amphotericin B
|
antifungal
|
|
|
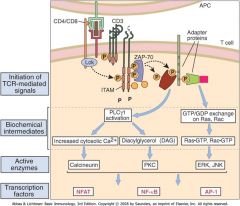
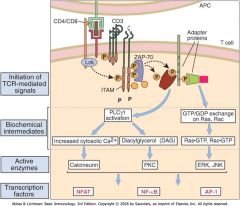
Cyclosporine inhibits calcineurin (dephosphorylates/activates NFAT); dont activate NFAT and is a huge player in transplantation medicine
|
|
|
hypersensitivities in conjunctivitis
|
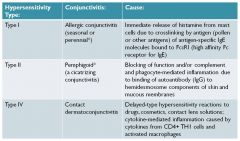
|
|
|
Pemphigoid
|
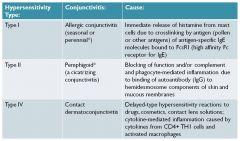
autoantibody against skin hemidesmosome can cause conjunctivitis
|
|
|
FCRI is a high affinity receptor on Mast Cells, how does this affect IgE levels
|
serum IgE does not need to be high for IgE to bind FC-gamma-RI
|
|
|
ankylosis spondylitis
|
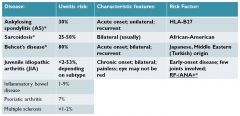
|
|
|
sarcoidosis uveitis
|
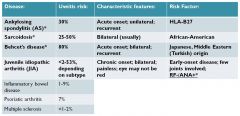
|
|
|
behcets disease
|
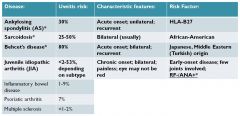
|
|
|
juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA)
|
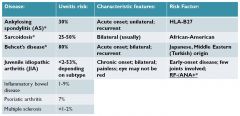
|
|
|
lens induced uveitis
|
trauma or cataract extraction (especially in the presence of bacteria* like Propionibacterium acnes) may initiate an autoimmune reaction
bacteria activates PRR which activates T cells for autoimmune response to own tissue infection causes autoimmune dz |
|
|
Sympathetic ophthalmia:
|
- penetrating injury (or surgery) to one eye sets up an autoimmune reaction to an ocular antigen that can damage both eyes
|
|
|
hypopyon
|
neutrophillic pus that settles out in the anterior chamber; not specific; can be caused by anything causing inflammation in the anterior chamber
|
|
|
bahcets disease
|
vasculitis triad; mouth ulcers, genital ulers, eye inflammation
|
|
|
etanercept
|
synthetic TNF receptor-like molecule; sucks up TNF
|
|
|
anakinra
|
IL-1 R antagonist
|
|
|
most likely cause of immune mediates scleritis (9)
when you think scleritis think vasculitis |
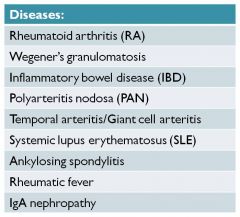
1/3 is RA
|
|
|
most common feature of idseases that cause immune mediates scleritis
|
immune mediated systemic vasculitis
|
|
|
anakinra and immune privilege in theey have in common
|
IL-1Ra
|

