![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How much time does each healing phase take to complete?
|
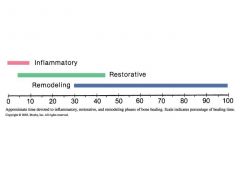
10% - Inflammatory
25% - Restorative 70% - Remodeling (Inflammatory & Restorative overlap by approx. 5%) (Restorative & Remodeling overlap by approx. 15%) |
|
|
What healing phase is most common for bone re-injury?
|
During the remodeling phase because the brace/cast is usually off by that time & the child may overdo it.
|
|
|
What are the affects of immobilization?
|
*Sensory deprivation leads to
isolation and helplessness *Language delay *Gross motor delay *Social delay - limited interaction out of their normal routine (confined to bed, hospital or home) *Behavioral issues: depression, aggression, anger |
|
|
Plan of care for the immobilized child.
|
* Make sure child is well medicated
* Transport child by stretcher, stoller, wagon, etc... from confines of room to provide for mobilization despite restrictions. * Change position of bed in room to alter monotony of immobilization |
|
|
Plan of care for the immobilized child (con't)
Ndx: Impaired physical mobility |
* Instruct child in use of assisstive devices to facilitate independent mobility
* Encourage activities that require mobilization. * Promote own care as much as possible * Give child choices throughout the day. |
|
|
Plan of care for the immobilized child (con't)
Ndx: Risk for impaired skin integrity |
* Use pressure reducing devices to promote skin integrity.
* Change position in bed frequently (unless contraindicated) to prevent dependent edema & stimulate circulation * Protect pressure points on body. * Make sheets smooth * Gently massage only healthy skin w/lubricant to keep skin soft. |
|
|
Stages of bone healing
Stage 1: Hematoma formation Card 1 of 3 |
Imapact:
* Fracture * Injury to soft tissue * Periosteal tissue torn * Vessels rupture |
|
|
Stages of bone healing
Stage 1: Hematoma formation Card 2 of 3 |
3-5 minutes:
--Bleeding from bone and tissues into area between and around bone fragmnets |
|
|
Stages of bone healing
Stage 1: Hematoma formation Card 3 of 3 |
First 24 hours:
--Hematoma forms and clots --Fibrin assists in clotting periosteal membrane to aid in repair --Clot provides fibrin network for cellular invasion --Granulation tissue forms by fibroblasts and new capilaries --Osteoblastic activity stimulated |
|
|
Stages of bone healing
Stage 2: Celular proliferation Card 1 of 3 |
After 24 hours:
--Blood supply increases, bringing available Ca, phos & fibroblast --Cells proliferate at ends of bone fragments and differentiate into cartilage & connective tissue |
|
|
Stages of bone healing
Stage 2: Celular proliferation Card 2 of 3 |
Next few days:
--Hematoma becomes granulation tissue, which forms into a framework for bone-forming substances --Fibroblasts convert to osteoblasts(bone forming cells) |
|
|
Stages of bone healing
Stage 2: Celular proliferation Card 3 of 3 |
2-3 days:
--Halisteresis (softening of bone ends) 1/8 to 1/4 inch and absorption of bone cells. |
|
|
Stages of bone healing
Stage 3: Callus formation Card 1 of 3 |
6-10 days:
--Fibroblasts form in granulation tissue --Form bone in areas adjacent to surfacce of bone shaft --Form carilage at surfaces more distal to blood supply |
|
|
Stages of bone healing
Stage 3: Callus formation Card 2 of 3 |
6-10 days (con't):
--Provisional callus develops --Bridging fracture ends --Holds bone together but will not support body weight |
|
|
Stages of bone healing
Stage 3: Callus formation Card 3 of 3 |
14-21 days:
--True cllus develops, seen on radiographs --Forms more than needed, but with remodeling, excess callus absorbs --Cartilage differentiates to bone tissue |
|
|
Stages of bone healing
Stage 4: Ossification Card 1 of 3 |
3-10 weeks:
--Callus forms into bone, which grows beneath periosteum of fragments --Fuses fracture defect by knitting fragments together --Also called the union stage |
|
|
Stages of bone healing
Stage 5: Consolidation and Remodeling |
After 9 months:
--Bone marrow cavity restored --Compact bone formed according to stress patterns --Remodeling according to Wolff's law - Fracture line always visible on x-rays |
|

Identify the fracture
|
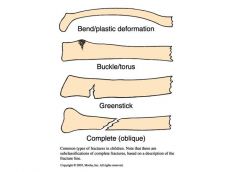
Greenstick
Complete (oblique) Buckle/torus Bend/plastic |
|
|
Name some fracture complications.
|
--ORIF used to prevent complications and to prevent limb shortening
--Compartment syndrome --Infection --Neurovascular compromise --Movement and function is compromised to the area |
|
|
Describe the nursing care of casts.
|
--Monitor for edema, in case the affected limb swells beyond the limits of the cast.
--The five P’s of ischemia. * Pain, especially w/passive ROM * Pallor * Pulselessness (a dismal and late sign) * Paresthesia * Paralysis --Check for foul smells or “hot spots” on the cast that could indicate infection --Handle wet cast w/palms of hands to avoid dimpling and creating pressure points within the cast. |
|
|
Describe the purpose of Buck's traction.
|
--A type of skin traction with the legs in an exteded position.
--Used primarily for short-term immobilization, such as pre-op management of a child w/a dislocated hip --Used for correcting contractures or bone deformaties (Legg-Calve) --Pull straight down towards end of bed |
|
|
Describe the purpose of Dunlop's traction.
|
--The arm is suspended horizontally, using either skin or skeletal attachment.
--To realign a broken humerus |
|
|
Describe the purpose of Russell's traction.
|
--Uses skin tractions on the lower leg and a padded sling under the knee.
--This combination of pulls allows realignment of the lower extremity & immobilizes the hip & knee in a flexed position. |
|
|
What are the nursing interventions for muscle spasms?
|
--Use of antispasmodics: drug of choice is valium for relief of muscle spasms in acute fractures.
--Can even premedicate for spasms. Very painful. --Assess for lack of pain relief after pain meds- it may be spasms. |
|
|
What is the interdisciplinary approach to long-term care of the immobilized child?
|
--Physical Therapist
--Occupational Therapist to assisst w/ADL's --Child life specialist --Child psychologist |
|
|
What is the interdisciplinary approach to long-term care of the immobilized child's family?
|
--Home visits by social worker to determine needs of immobilized child.
--Info on respite care --Indiv. & group counseling --Parent support groups |
|
|
Develop a teaching plan for adolescent girls re: Scoliosis prevention.
|
--Early detection is key
--Healthy diet balanced in vitamins & minerals most importantly Ca & magnesium. --Bone strengthening exercises to build bone density. --Bracing when appropriate |
|
|
What is post-op nursing care for a child who has had a spinal fusion to stabalize scoliosis?
|
--Log roll when changing position to avoid damage to the fusion.
(EXCEPTION - Luque procedure pts are kept flat for 12 hrs) --Skin care and integrity --Neuro status of extremities requires SPECIAL attention to monitor for delayed paralysis that might require another surgery. --Monitor for paralytic ileus. --Pain management --Encourage exercise by having pt contract& relax thigh & calf muscles periodically. |
|
|
Name the four stages of bone healing.
|
Stage 1 - Hematoma Formation
Stage 2 - Cellular Proliferation Stage 3 - Callus Formation Stage 4 - Ossification Stage 5 - Consolidation & Remodeling |

