![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why does decreased cardiac output cause cyanosis?
|
Redistribution of flow; shifts blood to venous side = increased levels of unsaturated hemoglobin = increased unsaturated hemoglobin content gives tissues the bluish color
|
|
|
What anatomic reason would exist for oxygen saturation issues causing cyanosis?
|
anatomic shunts; right to left where blood does not get 02 or expel C02; low Pa02 and decreases oxygen carrying capacity of the blood; increases presence of unsat hb in arterial blood due to venous mixing
|
|
|
What are peripheral causes of cyanosis?
|
Flow related causes (normal arterial oxygen sat happening in lungs)
|
|
|
What are central causes of cyanosis?
|
Oxygen saturation related issues; low arterial oxygen sat
|
|
|
How does decreased cardiac output relate to peripheral blood flow causes of cyanosis
|

It's like adding blood to the system but only to the venous side and thus we volume load the heart;
|
|
|
How does cold exposure relate to cyanosis?
|
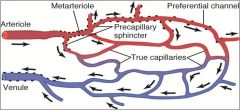
Contraction of precapillary sphincters; shunts blood to venous vessels causing reduced 02 delivery/hypoxia of skin; bluish discoloration is due to an increase in the content of unsat hemoglobin
|
|
|
How would low alveolar minute volume affect arterial oxygen saturation?
|
alveolar carbon dioxide content would increase and oxygen content would decrease bc V/Q ratio would increase causing C02 levels to rise in the alveoli which would decrease the partial pressure of all gases leading to less saturation of hb with oxygen
|
|
|
What abnormalities might cause low alveolar minute volume?
|
Any condition that decreases respiratory rate or gas exchange
Central nervous system abnormalities; interference in reflex operation of the respiratory system; pulmonary edema or pneumonia |
|
|
What abnormalities cause Fe2+ iron oxidation to Fe3+?
|
Methmoglobinemias; sulfhemoglobinemias; any low affinity hemoglobinopathies
Cause an increase in unsaturated hemoglobin and result in cyanosis |
|
|
Why will right to left shunts influence oxygen saturation?
|
Any mixing of unsaturated blood with saturated blood will decrease the overall saturation of the blood
|
|
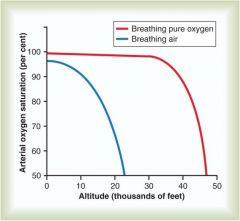
Oxygen Saturations at Altitude
|
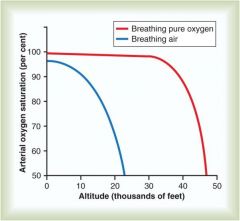
Breathing normal oxygen at higher altitudes drops off fast
Breathing pure oxygen at thousands of feet can maintain 02 sats; this is why you msut put the mask on w a loss of cabin pressure |
|
|
Travel to high altitude from sea level 12-36 hours later
|
HC03 in CSF decreases; pH returns toward normal; central chemo receptor discharge increases and minute ventilation is increased
HC03 excreted from plasma by kidney returns pH toward normal; peripheral chemoreceptor stim increases and thus after 36 hrs of arriving at high altitude, minute ventilation increases significantly |
|
|
C02 + H20 - where does this reaction occur to drive respiration?
|
The reaction occurs INSIDE the CSF; if it occurs outside the H+ ions are slow to cross BBB and will not drive respiration
|
|
|
Quantity of 02 in blood for sea level vs mountain dwellers
|
Difference in quantity of oxygen in blood for mountain dwellers (shifted up to the left) while sea level dwellers in down to the right
Arterial values: When P02 in blood is at 100 for sea level dwellers, the mountain dwellers have a greater quantity of 02 in blood EVEN THOUGH their P02 is lower (40) Venous values: Even though mountain dwellers have much less partial pressure in the arterial blood, the conc in the veins was similar to that of sea level dwellers, which means there was an increased efficiency in delivery of 02 to peripheral tisses |
|
|
Quantity of 02 in blood for sea level vs mountain dwellers
|
Difference in quantity of oxygen in blood for mountain dwellers (shifted up to the left) while sea level dwellers in down to the right
Arterial values: When P02 in blood is at 100 for sea level dwellers, the mountain dwellers have a greater quantity of 02 in blood EVEN THOUGH their P02 is lower (40) Venous values: Even though mountain dwellers have much less partial pressure in the arterial blood, the conc in the veins was similar to that of sea level dwellers, which means there was an increased efficiency in delivery of 02 to peripheral tisses |
|
|
Acute Cerebral Edema
|
Dilation of the arterioles increases blood flow into the capillaries, thus increasing capillary pressure, which in turn causes fluid to leak into cerebral tissue
|
|
|
High Altitude Pulmonary Edema
|
Caused by increased resistance that appearances in circulatory beds at high altitudes
HAPE is noncardiogenic, hydrostatic pulmonary edema due to pulmonary hypertension Left ventricular function is normal Pathcy hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction and hypoxic permeability of pulmonary capillary walls results in ahigh pressure, high permeability leak Dexamethasone stabilizes membranes and can be used to tx |
|
|
Chronic Mountain Sickness
|
Red blood cell mass increase
(1) The red cell mass and hematocrit become exceptionally high, (2) The pulmonary arterial pressure becomes elevated even more than the normal elevation that occurs during acclimatization, (3) The right side of the heart becomes greatly enlarged, (4) The peripheral arterial pressure begins to fall, (5) Congestive heart failure ensues, and (6) Death often follows unless the person is removed to a lower altitude. Similar problems can occur in an individual with idiopathic pulmonary hypertension |
|
|
Positive G force
|
Produced Greyout bc loss of color vision; occurs when airplane pulls blood to the lower portion of the body (blood centrigued downwards)
|
|
|
Negative G Pressure
|
redout; red shift in color vision
Seen when a pilot does an upside down loop; (blood pulls into head?) |
|
|
How can an individual reduce greyout
|
Flexing their leg muscles and constricting their abdominal muscles while exhaling slowly; this forces blood out of the legs and abdominal veins
|
|
|
How can an individual reduce redouts
|
there is no way to reduce the effects of negative G forces
|
|
|
Effects of prolonged microgravity/weightlessness in space
|
Effects of prolonged microgravity
(1) decrease in blood volume, (2) decrease in red blood cell mass, (3) decrease in muscle strength and work capacity, (4) decrease in maximum cardiac output, and (5) loss of calcium and phosphate from the bones, as well as loss of bone mass. Similar to keeping someone on bedrest for a long period of time |
|
|
Cephalic Fluid Shift
|

Fluid moves from legs to upper portion of body in space; face would swell after being space labs; body sees this as an increased plasma volume which increases urination and decreases circulating volume
thus on return on earth there is less volume and fluid redistributes to the lower extremities; amount of blood flow reaching brain decreases on earth so you get syncope Used to use salt tablets to increase blood volume |
|
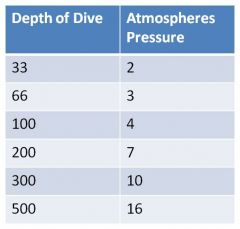
|
Pressures at depths; increases; scuba gear increases pressure delivered from tanks to lungs to equal that of surrounding water
when we're at 100 feet the amount of pressure we're breathing is 4x atmospheric pressure (4x760mmHg); when you use the increased figure to calculate the partial pressure of 02 you see it goes up tremendously |
|
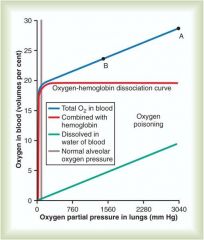
|
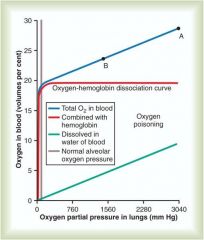
Red curve = 02 transported in hemoglobin, goes up quickly and flattens off at 20volumes percent = increasing partial pressure of 02 in lungs does not increase the amount of oxygen that can be carried by hemoglobin (once saturated, increasing P02 does not alter this)
However altering P02 in lungs has a significant (green line) effect on dissolved oxygen Blue line shows combined effect of saturated hb + dissolved in water portion of blood; you can see as you move right where oxygen poisoning is labeled; at pressures of this level you see 02 toxicity |
|
|
Nitrogen Narcosis
|
Similar to alcohol intoxication; believed to be nitrogens affect on altering membrane conductance or reducing neuronal excitability
|
|
|
Decompression Sickness (bends)
|
Divers surface too rapidly; similar to what happens when you open a soft drink and bubbles form when pressure is released from above soda; can cause extreme pain and result in death
As bubbles come out of muscle tissue time is required for it to equilibrate; when quick rising the gas pressure in the body tissue is greater than the atmosphere and gases can escape the dissolved state as nitrogen bubbles |
|
|
Why are helium-oxygen mixtures used in deep dives?
|
Helium has only 1/5 narcotic effect of nitrogen
Only about half as much volume of helium dissolves in body tissues, so it takes less time for helium to move out of tissue so you can ascend faster Helium has a lower density than nitrogen and moves through the airway easier and reduces resistance to breathing |
|
|
Time it takes to displace CO
|
CO levels (COHb%) have a time course of elimination from the body. The elimination half-life of CO while breathing:
Breathing room air - 320 minutes. Breathing 100% oxygen -90 minutes Breathing 100% oxygen at 3 atmospheres pressure (hyperbaric chamber) – 23 minutes |
|
|
When is HCN produced in fires?
|
HCN is produced when products such as wool, silk, cotton; nylon, plastics, polymers, foam, melamine, polyacrylonitriles and synthetic rubber burn;
|
|
|
Antidotes for CN Poisoning
|
Hydroxocobalamin; biologically active form of B12; based upon its ability to tightly bind cyanide ions; produces cyanocobalamin, is physiologially stable, nontoxic compound that is excreted in the urine
|
|
|
sodium nitroprusside
|
can release cyanide ions; this can be initiated by exposure to UV light; effective drug in controlling malignant or acute hypertension but must keep synringe and needle covered
|
|
|
Pulmonary Irritation in smoke inhilation
|
Activated leukocytes produce oxygen radicals and proteolytic enzymes; humoral mediators like prostanoids and leukotrienes also do this
could administer NSAIDs (COX inhibitors) to alleviate this |
|
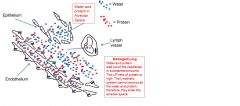
|
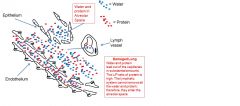
Water and protein moves into alveolar space and you see the problems associated with lung damage
|

