![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Acute Bronchitis
|
Brief, self limited inflammatory process of large/midsized airways; dry or productive cough of less than 3 weeks duration; most prevalent in winter; primarily caused by viruses
|
|
|
Bacteria associated with acute bronchitis
|
Mycoplasma pneumoniae; chalmydophila pneumoniae; bordetella pertussis
|
|
|
Most common viral cause of acute bronchitis in the winter
|
Influenza viruses
|
|
|
Which other illness must you differentiate from acute bronchitis?
|
pneumoniae; commonly s. pneumoniae
|
|
|
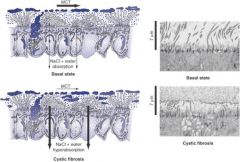
Cystic Fibrosis
|
|
|
Why are cystic fibrosis males often infertile
|
Bilateral absence of vas deferences
|
|
|
CFTR function in lungs and GI tract
|
Secretes Cl- in lungs and GI tract;
|
|
|
CTFR function in sweat glands
|
Reabsorbs cl- from sweat
|
|
|
Meconium Ileus in newborns
|
Cystic fibrosis
|
|
|
Biochemically what happens to the CTFR
|
Mutation causes abnormal protein folding, resulting in degradation of channel before reaching cell surface
|
|
|
Diagnostic test for cystic fibrosis?
|
Increase concentratio nof Cl- ions (>60mmol/liter) in sweat is diagnostic
|
|
|
What is the most common CFTR mutation
|
Phe 508; causes CFTR to be recognized as midfolded in the ER and degraded via UPS
|
|
|
Bronchiectasis
|
Dilation of the bronchi and bronchioles (due to destruction of elastic tissues); caused by chronic necrotizing infections, dilation is permanent
|
|
|
Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia (Kartagener Syndrome)
|
Impaired cilia functioning; recurrent infections and retention of secretions
|
|
|
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis
|
Hypersensitivity reaction to aspergillus fumigatus; can occur in pts with asthma and Cf; can lead to bronchiectasis and pulmonary fibrosis of untreated
|
|
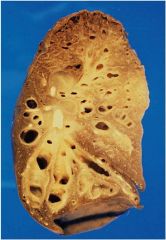
|
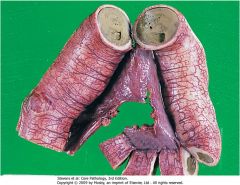
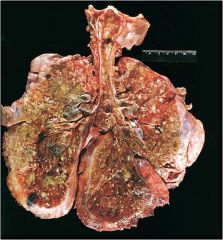
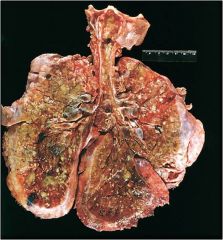
Bronchiectasis; note widely dilated bronchi and thickening of the bronchial walls and fibrosis of the parenchyma; can be secondary to cystic fibrosis
|
|
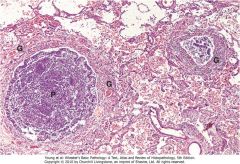
|
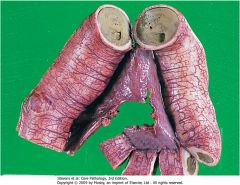
Note the 2 bronchi and their lumens are filled with pus; fibrovascular granulation tissue in walls with infiltration of inflammatory cells
|
|
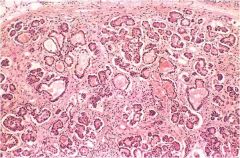
|
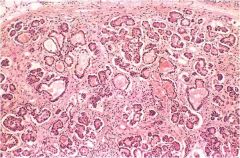
Pancreas w cystic fibrosis; the ducts are dilated and plugged with mucin; the parenchymal glands are atrophic and have been replaced by fibrous tissue
|
|
|
Meconium Ileus; obstruction of the terminal ileum due to accumulation of tenacious meconium
|
|
|
Obstructive Azospermia
|
Lack of semen in sperm; secondary to congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferns in cystic fibrosis
|
|
|
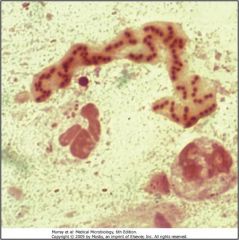
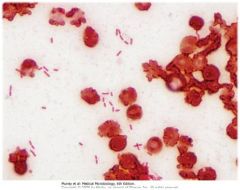
P. aeruginosa isolated from Cf pt; note thick mucoid capsule
|
|
|
lungs of CF pt w P. aeruginosa; not characteristic greenish color
|
|
|
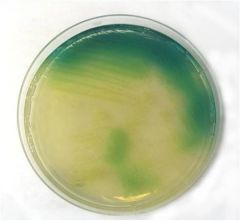
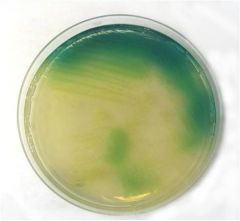
Five distinguishing features of P. aeruginosa are:
The synthesis of pyocyanin (blue) and pyoverdin (yellow-green) pigments under aerobic conditions. Pyocyanin generates superoxide radicals and hydrogen peroxide. Pyoverdin is a siderophore. Fruity grape-like smell Oxidase positive Presence of a mucoid alginate capsule |
|
|
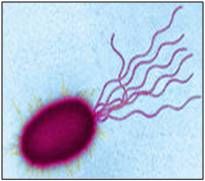
Pseudomonas aeruginosa; gram negative rods in pairs or chains; opportunistic so very common source of nosocomial infections; presence of pili and flagella important for establishment of infection in lower respiratory tract
|
|
|
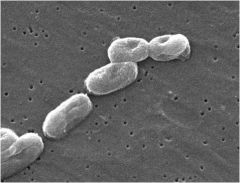
Small gram negative rods (coccobacilli); polyribol capsule
|
|
|
Burkholderia cepacia; not common but is a huge concern for Cf pts as it results in a highly accelerated course of the dz and poor prognosis
|
|
Most common tx?
|
Antibiotic resistance is a major problem
Acute: Ceftazidime, tobramycin Chronic: Azithromycin |
|
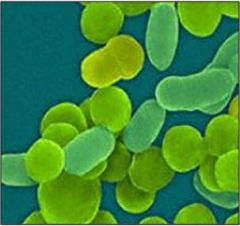
Best treatment?
|
H. influenzae
Ampicillin or broad spectrum cephalosporins are commonly used Immunization is of course important for prevention for type b |
|
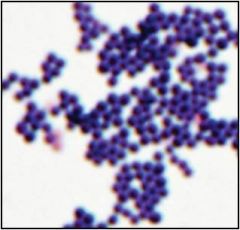
|
Staph aureus
Resistance to penicillins a problem; MRSA in particular Vancomycin the drug of choice with MRSA Oxacillin, clindamycin and doxycyline are also commonly used |
|
|
Atopic Asthma
|
type I IgE mediated hypersensitivity reaction; starts in childhood; triggered by environmental allergins; family history
SKIN TEST FOR ALLERGEN POSITIVE |
|
|
Non atopic asthma
|
No evidence of allergin sensitization and skin tests are generally negative
|
|
|
Drug Induced Asthma
|
Asprin sensitive asthma in pts w recurrent sinusitis and nasal polyps
|
|
|
Occupational Asthma
|
Triggered by various chemicals
|
|
|
Late Phase Reaction
|
In asthma; leukocyte recruitment secondary to chemokine production by mast cells, epithelial cells, T cells and other cytokines
|
|
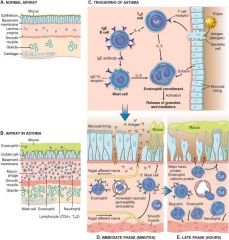
|
Asthma
|
|
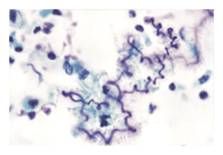
|
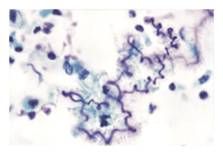
Curshmann spirals in asthma (shed epithelium from mucuous plugs)
|
|
|
Chest radiograph of diffuse interstitial disease
|
Bilateral infiltrative lesions that can take the form of nodules, irregular lines and ground glass shows
Lungs decrease in compliance; generally DILD is resistrictive |
|

|
Honeycomb lung representative of chronic diffuse interstitial lung disease
|
|
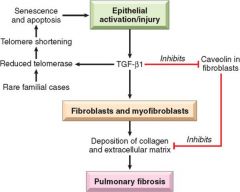
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
|
Repeated cycles of lung injury and wound healing with increases collagen
|
|
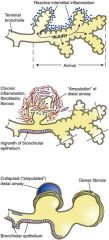
|
Formation of honeycomb lung; dense fibrosis = destruction of alveolar architecture
|
|
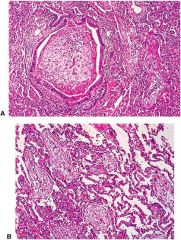
|
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneomonia Morphology; note polypoid loose plugs of organizing connective tissue located within alveolar ducts, alveoli and bronchiles
|
|
|
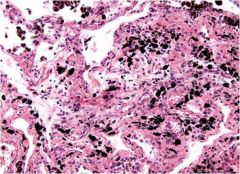
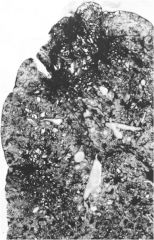
Coal Workers Pneumoconiosis; associated with coal miners (inhaled carbon taken up by macrophages); can resul tin cor pulmonale, Caplan's syndrome; affects upper lobes
|
|
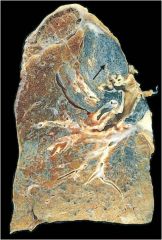
Silicosis
|
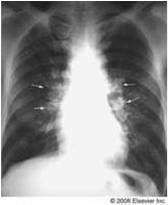
Inhalatoin of crystalline silicon dioxide (silica); Associated with foundries, sandblasting and mines
Macrophages respond to silica and release fibrogenic factors, leading to fibrosis; if is thought that silica may disrupt phagolysomes and impair macrophages, increasing susceptibility to TB Affects upper lobes, "eggshell" calcification of hiliar lymph nodes |
|
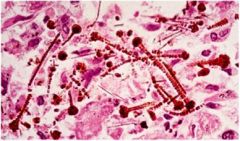
|
Asbestos bodies; golden brown beaded rods with a translucent center (ferruginous bodies = iron coating)
|
|
|
Sarcoidosis
|
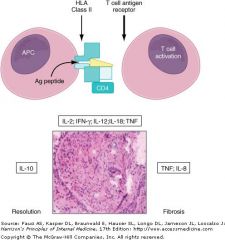
Proposed model for sarcoidosis
Antigen presenting cell/helper T cell interaction results in cytokine release leading to granuloma formation. Over time the disorder may resolve or result in chronic disease. |
|
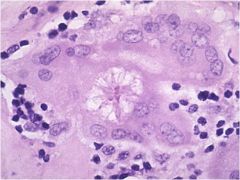
|
Asteroid body: stellate inclusions in the cytoplasm of epitheliod or giant cells; sarcoidosis
|
|
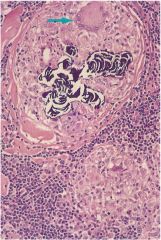
|
Schumann body; laminations composed of calcium and protein
Sarcoidosis |
|
|
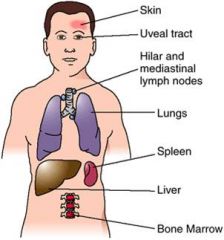
Organs commonly involved in sarcoidosis
|
|
|
Eosinophilic Granuloma
|
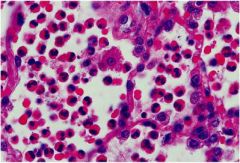
Infiltration of eosinophils
|

