![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Takayasu Arteritis
|
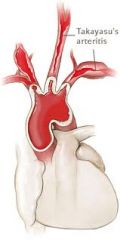
Pulseless disease
Asia; affects young and middle aged women Narrowing of the major arterial branches; loss of pulse in the upper extremities bc affects aortic arch and major branches |
|
|
Giant cell Arteritis
|
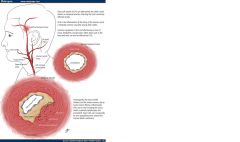
temporal arteritis; primarily affects elderly females; associated with HLA-DR4; cranial arteries
Throbbing headache, tender firm temporal arteries, facial pain Elevated ESR Segmental granulomatous vasculitis; fragmentation of the internal elastic lamina biopsy tx w steroids |
|
|
Polyarteritis Nodosa
|
Immune complex mediated transmural vasculitis with fibrinoid necrosis
Hep B association systemic vasculitis EXCEPT LUNGS |
|
|
Kawasaki Disease
|
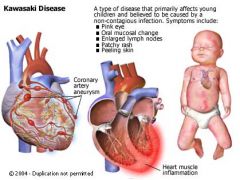
Asian children; Japan; segmental necrotizing vasculitis which affects coronary aneurysms (Strawberry tongue
"Mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome") |
|
|
Churg-Strauss Syndrome
|
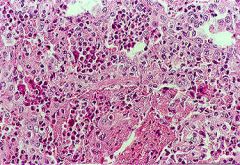
Allergic granulomatosis and angitis
Variant of PAN Associated w asthma; systemic necrotizing vascluitis with granulomas and EOSINOPHILIA; classically involves the nose, sinuses, lungs and kidneys p-ANCA Often peripheral neuropathy (wrist/foot drop) |
|
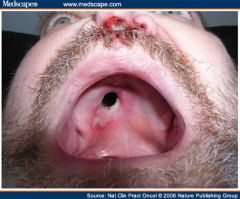
Wegener's Granulomatosis
|
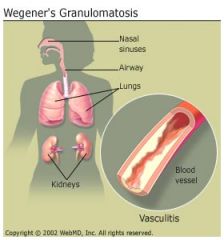
Triad:
1. Necrotizing vascultis 2. Necrotizing Glomerulonephritis 3. Necrotizing granulomas (lung + upper airways) c-ANCA is strong marker |
|
|
Microscopic Polyangiitis
|

Like Wegener's but lacks granulomas
p-ANCA affects small vessels |
|
|
Sturge Weber Disease
|
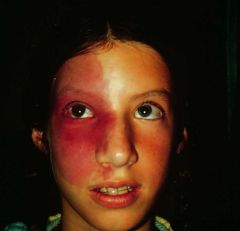
Vascular disorder that affects capillary sized blood vessels
Port wine stain on face |
|
|
Buerger's Disease
|

Thromboangiitis obliterans
Young males + heavy smoking; involves extremities Segmental thrombosis leads to vascular insufficiency Tx: smoking cessation |
|
|
Raynaud's Disease
|

Decreased blood flow to the skin due to arteriolar vasospasm in response to cold temperature or emotional stress; often in fingers and toes
Called Raynaud's phenomenon when secondary to a mixed connective tissue disease, SLE or CREST syndrome affects small vessels Cyanosis of fingers or toes precipitated by cold temperature and emotions w no underlying disease or pathology |
|
|
Raynaud's Phenomenon
|

Arterial insufficiency secondary to an underlying dz (SLE, buerger dz, atherosclerosis, scleroderma)
|

