![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Atom
|
The smallest particle of a substance that can exist by itself or be combined with other atoms to form a molecule
|
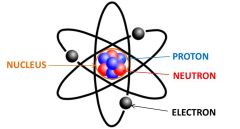
An atom consists of electrons, protons, and neutrons. Protons and neutrons make up the nucleus.
|
|
|
Atomic mass
|
Atomic mass or atomic weight is the average mass of atoms of an element , calculated using the relative abundance of isotopes in a naturally-occurring element.
|
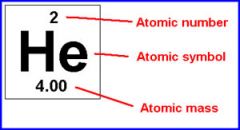
The atomic mass of helium is 4.003.
|
|
|
Atomic mass unit
|
A unit of mass for expressing masses of atoms, molecules, or nuclear particles equal to 1⁄12 the mass of a single atom of the most abundant carbon isotope 12C —called also dalton
|
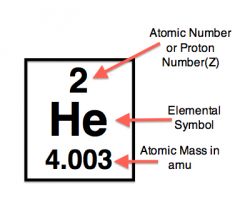
The atomic mass of helium is 4.003 amu.
|
|
|
Atomic number
|
An experimentally determined number characteristic of a chemical element that represents the number of protons in the nucleus which in a neutral atom equals the number of electrons outside the nucleus and that determines the place of the element in the periodic table.
|
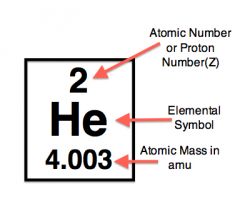
The atomic mass of helium is 2
|
|
|
Atomic symbol
|
A notation to distinguish one isotope from another.
|
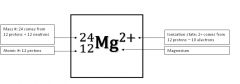
The atomic symbol shows the mass #, atomic #, ionization,and chemical symbol.
|
|
|
Chemical symbol
|
An abbreviation or short representation of a chemical element; the symbols in the periodic table
|
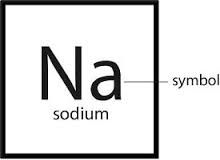
The chemical symbol for sodium is Na.
|
|
|
Electron
|
An elementary particle consisting of a charge of negative.
|
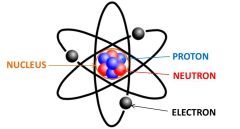
Electrons are the outermost part of an atom.
|
|
|
Group
|
An assemblage of elements forming one of the vertical columns of the periodic table.
|
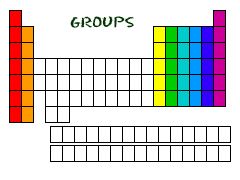
All the elements in the red column are in a group.
|
|
|
Isotope
|
Any one of various forms in which the atoms of a chemical element can occur
|
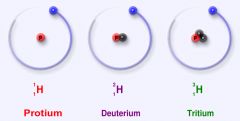
Hydrogen has 3 isotopes.
|
|
|
Mass number
|
An integer that approximates the mass of an isotope and designates the number of nucleons in the nucleus.
|
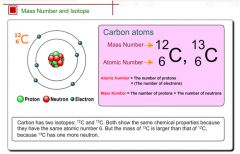
The mass number of carbon is 12.
|
|
|
Metal
|
Matter set in metal type
|
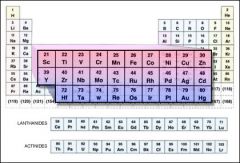
Nickel and silver are metals on the periodic table.
|
|
|
Metalloid
|
An element intermediate in properties between the typical metals and nonmetals.
|
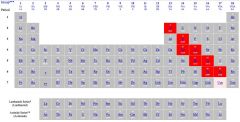
The elements in red are all metalloids.
Ex. Boron is a metalloid. |
|
|
Neutron
|
A very small particle of matter that has no electrical charge and is part of the nucleus of all atoms except hydrogen atoms.
|
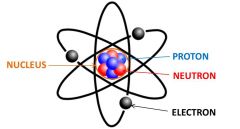
Neutrons are located in the nucleus.
|
|
|
Nonmetal
|
A chemical element (as boron, carbon, or nitrogen) that lacks the characteristics of a metal.
|

Nitrogen is a nonmetal.
|
|
|
Nucleus
|
The central part of an atom that is made up of protons and neutrons.
|
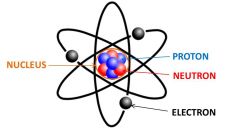
The nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons.
|
|
|
Period
|
A period is the name given to a horizontal row of the periodic table.
|
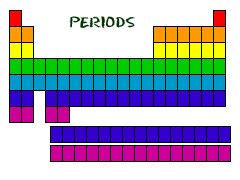
Hydrogen and helium are in the same period.
|
|
|
Proton
|
A very small particle of matter that is part of the nucleus of an atom and that has a positive electrical charge.
|
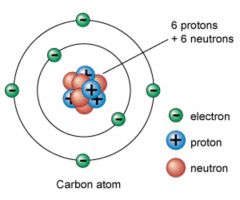
A carbon atom has 6 protons.
|
|
|
Subatomic particle
|
A particle smaller than an atom (e.g., a neutron) or a cluster of such particles (e.g., an alpha particle).
|
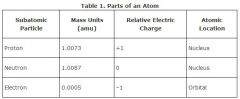
An example of a subatomic particle is a proton.
|

