![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Diphenhydramine
|
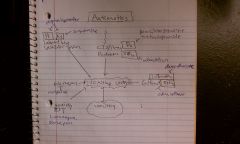
Antihistamine/Antimuscarinic (H1 and M1); motion sickness;
|
|

Lorazepam and diazepam
|
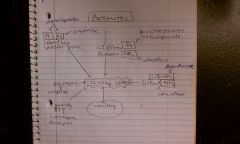
GABAR; Reduce N&V from central cortical regions; used for anticipatory nausea
|
|
Scopolamine
|
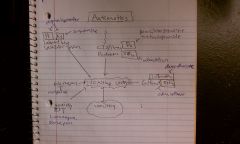
Muscarinic antagonist; used to PREVENT but not tx motion sickness
|
|

Prochlorperazine, metoclopramide
|
DA antagonist; DA blockers stop emesis; used to tx chemotherapy induced, estrogen induced and other blood borne causes of N&V
|
|
Odansetron
|
5HT3 antagonist; 5HT3R found in area prostrena, peripheral sensory and enteric nerves;
Decrease emesis in chemo and radiation and posteroperatively |
|
Dexamethasone
|
Corticosteroids; inhibits inflammatory mediated gut 5HT release
|
|
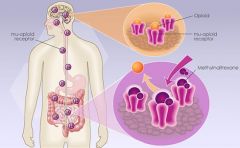
Loperamide and Diphenoxylate
|
Opiate antidiarrheal; decrease GI motility;
|
|
|
Precaution with loperamide and diphenoxylate (opiates) for antidiarrheal
|
Increases oral bioavailability of other drugs
|
|

Nabilone and dronabinol
|
CB1 agonists; used to tx NV after chemo
|
|

Psyllium (metamucil)
|
Absorbant; used for mild diarrhea and constipation; absorbs water
|
|
Cholestyramine
|
Bile binding resin; absorbant; antidiarrheal; inactivates osmotic activity of bile acids; used to tx bile acid induced diarrhea due to bile malabsorption or during tx for cholelithiasis with bile acids; binds bile acids
|
|

Bismuth Subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol)
|
Tx acute diarrhea (traveler's diarrhea); mechanism not understood; temp black tongue and black stools may confound melena
|
|
|
Why might you not want to get an antimcirobial agent during acute diarrhea?
|
Diarrhea plays a protective role in expelling pathogenic organisms/toxins; don't want to interfere with that
|
|

Cascara and Senna
|
Anthraquinones; laxative; needs bacteria to convert into emodium which stimulates gut motility
|
|

Phenolphthaline and Bisacodyl
|
Stool softener/surfactant; Laxative; must be absorbed into blood and eliminated in the bile as the active glucuronide;
Detergent -> stool softener |
|
|
What must be a consideration when giving Phenolphthaline and Bisacodyl
|
Needs to follow enterohepatic metabolism; won't work in patients taking cholestyramine (bile binding resins) or in pts with bile duct obstruction
|
|

Castor Oil
|
Laxative; converted to ricinoleic acid by pancreatic lipase which acts as an irritant promoting GI motility
|
|
Lubiprostone (PGE1 analog)
|
Laxative; enhances chloride secretion into intestinal lumen
|
|

Dioctyl Sodium Sulfosuccinate
|
Stool softener or surfactant
|
|

MgS04
|
water retaining -> increased intraluminal pressure
|
|
|
Bisacodyl
|
Direct intestinal walls stimulant
|
|
|
Methylcellulose
|
Collects water and swells -> increased bulk
|
|
|
Docusate
|
Detergent -> stool softener
|
|
|
Mineral oil
|
Lubricant
|
|
|
Lactulose
|
Hyperosmotic (also indicated for systemic encephalopathy); non-absorable sugar
|
|
|
Psyllium [Metamucil]
|
Collects water and swells -> increased bulk (could stimulate motility when touches gut wall or inhibit diarrhea by absorbing water)
|
|

Oral Nalaxone
|
Opiod antagonist; increases gut motility; doesn't interfere w/ hydroxodone
|
|

Almivopan
|
Opiod antagonist; increases gut motility
|
|

Methylnaltrexone (Relistor)
|
Opiod antagonist; increases gut motility
|
|

Erythromicin
|
Tx constipation; cholinergic agonist -> motility
|
|
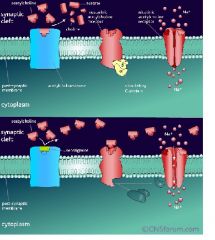
Neostigmine
|
Tx constipation; increases ACh stimulation by preventing ACh breakdown; used after surgery to stimulate bowel movement
|
|

Antacids (NaHC03), Al(OH)2, Ca(CO)3, Mg(OH)2
|
Ca, Mg and Al hydroxides neutralize protons in the gut lumen
AluMINIMUm amount of feces (Al = constipation) Mg = Must Go to the bathroom (Mg = diarrhea) Together they balance eachother out and have a high acid neutraizing capability |
|
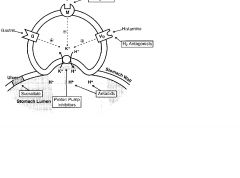
Ranitidine, Cimetidine
|
H2R antagonist; indirectly decrease proton pump activity
|
|
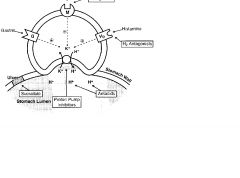
Omeprazole (-prazoles)
|
PPI; tx GERD, NSAID PUD, Zollinger Ellison
May cause hypergastrinemia as well as anemia |
|
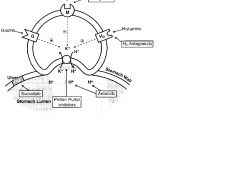
Pirenzepine
|
M1 Muscarinic Antagonist; reduces gastric acid secretion;
|
|
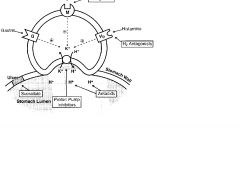
Misoprostol
|
PGE1 analog; increases production and secretion of gastric mucous barrier; decreased acid production; tx NSAID ulcers
|
|
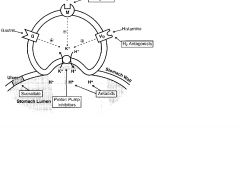
Sucralfate
|
Bind ulcer base, proving physical protection; allows HC03 secretion to reestablish pH gradient in mucous layer; increase ulcer healing, traveler's diarrhea
|
|
|
PPI + Clarithryomycin + Amoxacillin or Metronidazole
|
Combo used to kill H. Pylori (Metronidazole used when pt is allergic to penicillin)
|
|
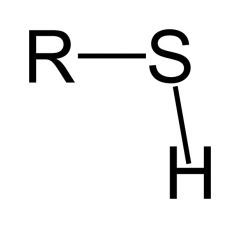
N-acetylcysteine (NAC)
|
Tx acetaminophen hepatoxicity; NAPQ1 metabolite of acetominophen is very toxic; NAC supplies -SH groups for it to react with
|
|
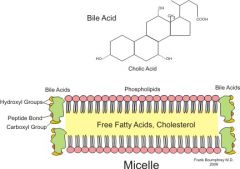
Chenodeoxycholic acid, Ursodeoxycholic acid
|
Tx gallstones; increase conc. of bile acids in gall bladder -> reduces bile lipis and cholesterol concentration which causes gallstones; dissolves slowly
|
|
|
How can Lactulose tx liver failure
|
Degraded by colonic bacteria into lactic acid; protonated ammonia which then stays in lumen and is excreted
|
|
Rifaximin
|
Tx liver failure; eliminate urease producing bacteria and reduce the amount of ammonium produced
|
|
Interferon Alpha
|
Tx Chronic hepatitis C; IFN activates JAK-STAT which transcribes viral resistance proteins
|
|
Ribavirin
|
Tx chronic hepatitis C; inhibit viral RNA polymerases
|
|
Lamivudine and Entecavir
|
Tx chronic hepatitis B; inhbiit viral reverse transcriptase
|
|
|
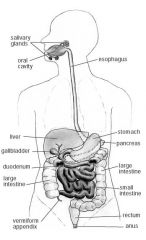
Uncoated lipase + PPI
|
Steatorrhea due to pancreatitis; Failure to secrete lipase = steatorrhea; uncoated so it will activate in duodenum to replace lost; need PPI bc gastric acid will degrade lipase
|
|
|
Protease
|
Chronic pancreatitis; failure to secrete proteases results in pain; without protease (trypsin) can't inactivate CCK releasing peptide, which causes colonic pressure; give protease to prevent pain and replace lost protease
|
|
|
Ferrous Sulfate
|
Tx microcytic, hypochromic anemia; must continue to be given even after anemia is fixed to replenish ferritin; doses >100-200mg/day saturate active transport mechanism thus no additional benefit
|
|

Ferrous Gluconate (oral)
|
Tx microcytic, hypochromic anemia; must continue to be given even after anemia is fixed to replenish ferritin; doses >100-200mg/day saturate active transport mechanism thus no additional benefit
|
|

Iron Dextran
|
Tx microcytic, hypochromic anemia; perenteral; only used when oral iron replacement therapy is not enough
|
|
|
What is the only type of anemia that will respond to iron supplementation?
|
Iron deficiency; hypochromic, microcytic
|
|
|
Deferoxamine
|
Treat acute iron overdoses (A parenteral iron chelator, complex is excreted in urine)
"Defer Iron" |
|
|
Hydroxycobalamin (Vitamin B12)
|
Used to tx macrocytic hyperchromic (megaloblastic) anemia; co enzyme for tetrahydrofolate (needed for nucleotide synthesis)
|
|
|
Folic Acid
|
Tx macrocytic hyperchromic (megaloblastic) anemia; precursor for tetrahydrofolate (needed for nucleotide synthesis)
|
|
|
Erythropoietin EPO)
|
Tx microcytic anemia of CHRONIC inflammatory dx; also pts w end stage renal failure and normocytic anemia (increases RBC production)
|
|
|
Methotrexate
|
Tx rheumatoid arthritis; impedes tumor growth; can cause macrocytic hyperchromic anemia; no amount of dietary folates or folic acid supplements will overcome reductase inhbiition by MTX
|
|
Leucovorin (tetrahydrofolate)
|
Given to rescue BM & GI cells AFTER doses of MTX; do not take WHILE on MTX
|
|
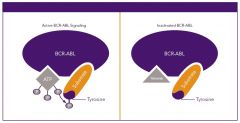
Imatinib = Gleevec (Novartis)
|
Tx CML; binds bcl-abl TK to block uncontrolled proliferation and induce apoptosis of cells with the philadelphia chromosome
|
|
|
Trastuzumab = Herceptin
|
Tx breast cancer; anti HER2 Ab
|
|
Filgrastim (G-CSF)
|
Stimulates production of neutrophils; used for marrow recovery
|
|
Azathioprine
|
Immunosuppresive oral med for organ transplantation pts and autoimmune disorders; impairs T&B lymphocyte proliferation. Converts to 6 mercaptopurine
Toxic if combined with allopurinol |
|
Cyclophosphamide
|
Tx lymphomas, leukemia, and somes olid tumors; alkylating agent that slows/stops cell growth
|
|
Cyclosporine (and tacrolimus)
|
Lipid soluble peptide antibiotic that improves organ and bone marrow graft survival; impairs differentiation and activation of CD4+ T cells; does not cause bone marrow suppression
|
|
Mycophenolate
|
Prevent organ transplant rejection; blocks purines ynthesis
|
|
|
Methotrexate
|
1. Immunosupressive, 2. anticancer cytotoxic drug (impede tumor growth) 3. tx RA
can cause macrocytic hyperchromic anemia |
|
|
Prednisone
|
Immunosuppressive glucocorticoids (inhibits inflammatory response); tx arthritis, modulate allergic response, also used in organ transplant, autoimmune dx (autoimmune hemolytic anemias)
|
|
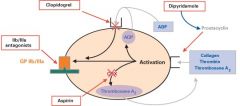
Asprin
|
Antiplatelet drug; Irreversibly inhibits COX in platelets = decreased activation
Low doses prevent MI and recurrence; Inhibits platelet enzyme that makes TXA2; also an NSAID with analgesic, antiptyretic and anti-inflammatory properties (irreversible inhbiits COX1&2) |
|
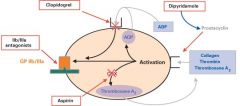
Clopidogrel
|
Antiplatelet drug; irreversible inhbiits platelet ADP-R; used after pt has balloon angiopalsty in coronary artery
|
|
Warfarin
|
Indirect anticoagulant; Vit K antagonist in the liver; prevent or tx venous thrombosis and prevent emboli from atrial fibrillation or synthetic heart valves
Teratogenic |
|
|
Heparin
|
Immediately inhibits coagulation; used to manage acute thromboembolic disorders (pulmonary embolism); can result in severe thrombocytopenia
|
|
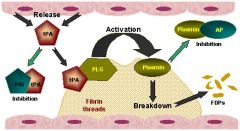
Tissue Plasminogen Activator (rtPA) (tenecteplase)
|
Thrombolytic (dissolver of blood clots); converts plasminogen to plasmin to dissolve clots; thrombolytic tx of acute phase of MI
|
|
|
INR
|
A high INR level indicates that there is a high chance of bleeding; The prothrombin time (PT) and its derived measures of prothrombin ratio (PR) and
international normalized ratio (INR) are measures of the extrinsic pathway of coagulation. They are used to determine the clotting tendency of blood, in the measure of warfarin dosage, liver damage, and vit. K status. |
|
|
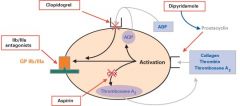
EXPLAIN THE MECHANISMS BY WHICH ASPIRIN AND CLOPRIDOGREL INHIBIT
PLATELET-DRIVEN THROMBOSIS. |
Platelets do not interact with the lining of normal, healthy
blood vessels; however, when the subendothelium is exposed/damaged platelets stick to the injured tissue and release (TxA2 and ADP). They also express gpIIb/IIIa that causes other platelets, fibrinogen and vWF to form a clot. Until it is reinforced by fibrin, this clot can break away and form an embolus. This matters because… Aspirin inhibits the platelet enzyme that makes Thromboxane A2 (TxA2) and Clopidogrel inhibits platelet ADP receptors. So, NO clot! |
|
|
LET’S TALK ABOUT ARACHIDONIC ACID (AGAIN):
|
Arachidonic Acid is converted to PGH2 which can then become either of
the following depending on which tissue it is in … (1) In PLATELETS (with COX-1) it is converted to THROMBOXANE, which stimulates platelet activation and constricts blood vessels (2) In VESSEL WALLS (with COX1&2) it is converted to PROSTACYCLIN, which inhibits platelet activation and dilates blood vessels. This matters because… Low dose aspirin stays in the liver and only inhibits COX-1 making it very effective to stop platelet activation and dilate blood vessels. A high dose gets past the liver and interacts with the blood vessel walls to be counter-therapeutic since it would stimulate platelet activation and constrict vessels. |

