![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
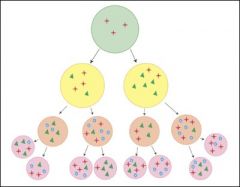
Tumor Heterogeneity
|
A tumor is a mix of benign and malignant cells; this can effect the therapy administered
Mutations later down the line (4th or later in the slides) become malignant |
|
|
Proto-oncogenes
|
Stimulate normal cell proliferation
|
|
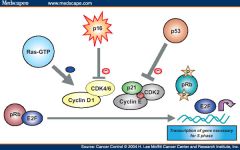
Tumor suppresor genes
|
Normally inhibit cell proliferation
|
|
|
Regulators of apoptosis
|
Pro and anti cell deathDNA
|
|
|
DNA Repair Genes
|
Maintain genomic stability, indirectly regulate cell proliferation;
|
|
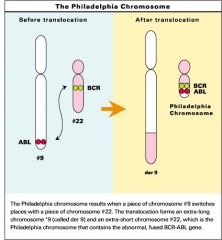
Philadelphia Chromosome
|
bcr-abl hybrid (chimeric gene) resulting in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
"Philadelphia CreaML cheese" |
|
|
How would a mutation in DNA repair genes cause?
|
Increases genomic instability and mutation in proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressors
|
|
|
Frequency of sporadic vs inherited forms of cancer?
|
Sporadic (90%)
Inherited (5-10%); mutation in germline so ALL the cells carry the mutation instead of just one as in a sporadic mutation |
|
|
c-myc
|
Oncogene; Burkitt's lymphoma
|
|
|
ras
|
Oncogene; Colon carcinoma
|
|
|
Rb
|
Tumor suppressor gene; retinoblastoma
|
|
|
p53
|
Most human cancers
|
|
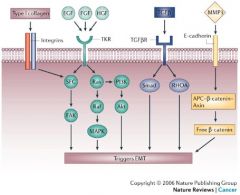
What type of receptor do growth factors bind to?
|
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
|
|
|
These proto-oncogenes are the most commonly mutated
|
Ras
|
|
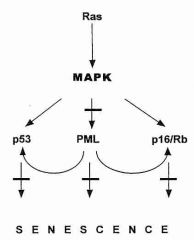
Which pathway does Ras use for signaling?
|
MAPK, which is critical for proper cell cycle regulation
|
|
|
Gene amplification of N-Myc is linked to what tumor?
|
Neuroblastoma
|
|
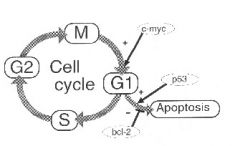
What is the principle role of Myc related to the cell cycle?
|
Increase the transcription of the G1 cyclins (also called the D cyclins)
|
|
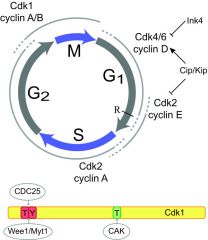
Which two cyclin-Cdk pair is required to pass the restriction point in the cell cycle?
|
Cdk-4 and cyclin D
|
|
|
What two things are required to active Cdks?
|
1. binding of their appropriate cyclin
2. phosphorylation by an upstream kinase called a Cdk-activating kinase (CAK) |
|
|
How are Rb and E2F protein related?
|
E2F -> dna synthesis
E2F + Rb -> inactivated |
|
|
Activation of p53 induces what
|
Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
|
|
|
Apoptosis vs Necrosis
|
Apoptosis: Cell destruction w/o inflammatory response
Necrosis: Cell destruction w/ inflammatory response |
|
|
Caspases
|
cysteine-aspartic-proteases; play essential roles in apoptosis
|
|
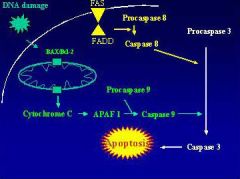
Extrinsic Apoptotic Pathway
|
Fas death receptor binds Fas ligand; recruit of FADD adaptor protein which recruits procaspase 8 or 10 -> apoptosis
|
|
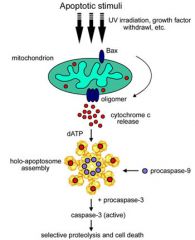
Intrinsic Apoptotic Pathway
|
Cytochrome c + procaspase 9 -> adaptor protein (apoptosome) -> executioner caspases activated -> apoptosis
|
|
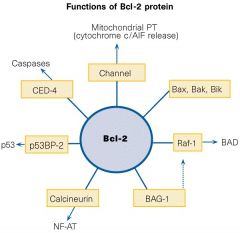
Bcl2
|
Inhibits BH123 (Bax or Bak) channel from releasing cytochrome c
Bcl2 is an oncogene associated with B-cell lymp |
|
|
What apoptotic stiulus protein inactivates anti-apoptotic Bcl2 protein?
|
BH-3 only proteins (Bad and Bid)
|
|
|
Loss of heterozygosity
|
1. inactivating mutation in one allele of a tumor suppressor gene occurs in germline cell
2. LOH occurs when remaining functional allele becomes inactivated by mutation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
How can loss of APC function lead to deregulated cell proliferation?
|
PREDISPOSITION for developing cancer is inherited (100% penetrance); los of heterozygosity required for colon cancer development
|
|
|
Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer
|
Inherited defects in DNA repair mechanisms = genetic instability (compared to FAP which only predisposes to cancer)
|
|
|
Describe how an accumulation of mutations in a single somatic cell lineage gives rise to cancer
|
1. One mutant APC gene
2. LOH at another APC gene 3. K-RAS mut 4. p53 LOH |
|
|
Increased transcription of B-catenin/Tcf increases what cyclin protein
|
cyclin D
|
|
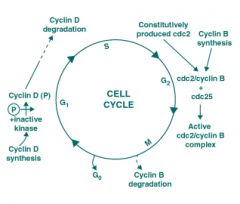
Function of cyclin D
|
G1 -> S in cell cycle
|
|
Adenoma
|
Benign tumor of glandular origin
Hyperplastic growth; no disruption of the basement membrane |
|
|
Invasive Carcinoma
|
Invasive malignant tumor consisting of transformed epithelial cells
Penetration through the basement membrane; infiltration into submucosa and beyond |
|
|
What is the ratio of cancer stem cells to transit amplifying cells in a tumor mass?
|
Cancer stem cells are the minority; transit amplifying cells are the majority
|
|
|
Despite the tremendous genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity, why are tumors considered to be monoclonal?
|
Because tumorigenesis still ocurs at the level of a single cell
|
|
|
Describe the concept of darwinian evolution and clonal succession o ftumor cells
|
One cell amid a large population acquires a mutation that confers a proliferative advantage over its siblings
|

