![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
What are the markers of hepatobiliary clearance?
|
Bilirubin
Alkaline Phosphtase GGT Elevation of these indicates an cholestatic pattern LFT |
|
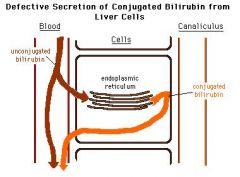
Isolated direct bilirubin elevation indicates which two syndromes?
|
Dubin Johnson Syndrome
Rotor Syndrome |
|
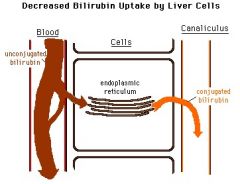
Indirect Bilirubin Elevation with decreased uptake or conjugation indicates what two syndromes
|
Gilbert's Syndrome
Crigler-Najjar Syndrome |
|
|
Difference between conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin
|
Unconjugated br is insoluble in water - exists in tight complexes with serum albumin and can't be excreted by urine
Excess conjugated be can be excreted |
|
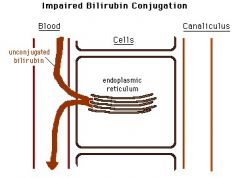
Crigler-Najjar Syndrome I & II
|
Hepatic UGT1A1 completely absent (or decreased) -> unconjugated bilirubin reaches very high levels -> jaundice/icterus -> death secondary to kernicterus within 18 months
|
|
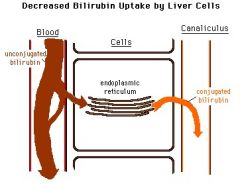
Gilbert's Syndrome
|
Milder form of Crigler-Najjarr Syndrome; Decreased UGTA1 activity -> unconjugated bilirubin mildly elevated -> generallly innocuous
HOWEVER, pts with GS may be more susceptible to adverse ffects of drugs metabolized by UGT1A1 |
|
|
Rotor Syndrome
|
Rare form of asymptomatic conjugated hyperbilirubinemia associated with multiple defects in hepatocellular uptake and excretion of bilirubin pigments.
|
|
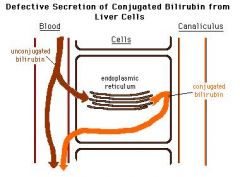
Dubin Johnson Syndrome
|
AR disorder; chronic conjugated hyperbilirubinemia due to defect in hepatocellular excretion of bilruubin glucuronides across the canicular membrane
|
|
|
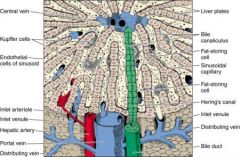
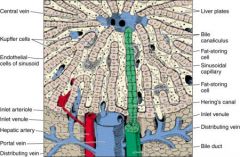
What is the ratio of blood flow into the liver?
|
75% = venous blood from the portal vein
25% = arterial blood from hepatic artery |
|
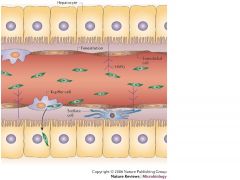
Where do the hepatic portal vein and hepatic artery mix in the liver?
|
Sinusoids
|
|
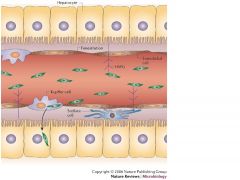
What kind of endothelium is characteristic of sinusoids?
|
Fenestrated and discontinuous endothelium; they are highly permeable with fewer tight junctions than capillaries; the purpose is to allow small and medium sized proteins (ALBUMIN) to enter and leave the blood stream
|
|
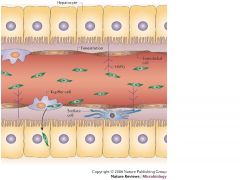
What separates liver sinusoids from hepatocytes?
|
Space of disse
|
|
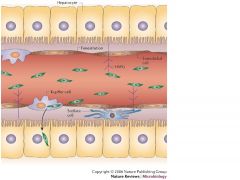
Where are Kupffer cells found?
|
Sinusoids
|
|
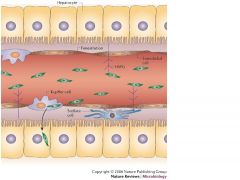
Where is a major fraction of the body's lymph filtered?
|
As blood flows through the sinusoids, a considerable amount of plasma is filtered into the space between endothelium and hepatocytes (space of disse)
|
|
Where are the bile canaliculi located?
|
they are the dilated intracellular space between adjacent hepatocytes
|
|
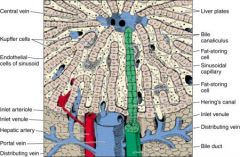
In which direction does bile flow?
|
In the parallel opposite direction from the sinusoidal flow of mixed venous and arterial blood; back towards the portal triad in the bile canaliculi (dilated intracelullar space between adjacent hepatocytes)
|
|
What is the most common cause of amebic liver abscesses?
|
E. histolytica; "anchovy paste abscesses"
Diagnose w/ positive serology for antiamebic antibodies along w/ CT or ultrasound |
|
Most common gram negative causes of pyogenic liver abscess?
|
E. coli; klebisella (enteric bacteria)
|
|
|
Most common gram positive causes of pyogenic liver abscess?
|
streptococcus intermedius
|
|

How can you differentiate between the two common gram negative causes of pyogenic liver abscess?
|
E. coli: NEGATIVE VP test
k. pneumoniae: POSITIVE VP test |
|
|
What is the most common cause of liver abscess in hemachromatosis patients?
|
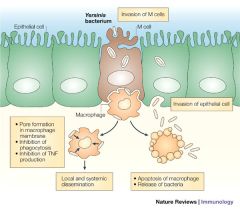
Yersinia enterocolitica; this organism is UNABLE TO PRODUCE THEIR OWN SIDEROPHORES (which can usually be used to sequester iron); with excess liver iron deposition this organism can now thrive
|
|
Leukocytosis is present in 80% of what kind of liver disease patients?
|
Liver abscess patients
|
|
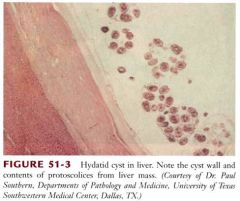
What organism can cause mutliple large liver cysts, leukocytosis and is transmittered fecal oral related to sheep and dogs?
|
Echinococcosis
|
|
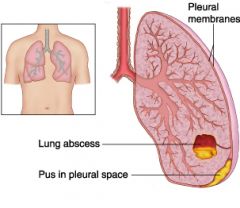
Empyema
|
Collection of pus in the space between the lung and the inside of the chest wall (pleural space)
|
|
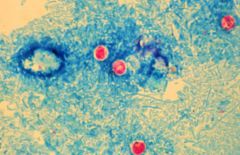
What is the most common pathogen of AIDS related sclerosis cholangitis?
|
Cryptosporidium
Small round structure aligned along the brush border of the intestinal lumen in biopsy; detected by acid fast stain which reveals pinkish red round to oval structures in stool/biopsy; animal reservoir Normally just causes diarrhea but in AIDS patients can be life threatening fluid loss |
|
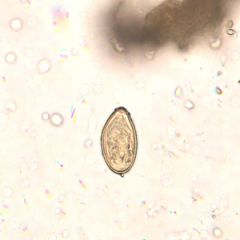
A biopsy reveals distinctive eggs with shoulders around the operculum and a tiny knob at one end. What organism does this describe?
|
Opisthorchis sinensis
Fish animal resevoir |
|
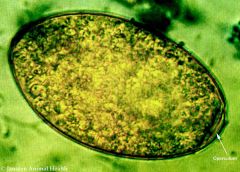
What organism is acquired by eating contaminated water cress?
|
Fasciola hepatica
|
|
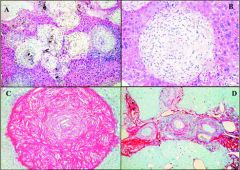
What organism causes clay pipestem fibrosis?
|
Schistosoma mansoni (fibrous tissue reacting to the eggs in the liver surrounds the portal vein in a thick, grossly visible layer)
|
|
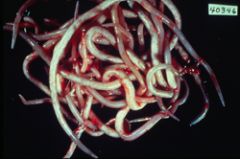
What is the most common human worm infection?
|
Ascaris lumbricoides; fecal oral transmission of infective eggs in soil contaminated food or water
|
|
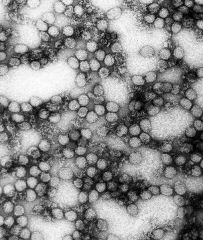
What disease carried by a mosquito vector produces hepatic coagulopathy producing hemorrhagic symptoms? (black vomit, nose bleed, bruising)
|
Yellow fever
|
|
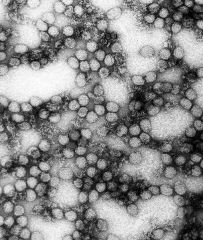
A patient presents with hepatocoagulopathy and jaundice. What organism likely caused this?
|
Flavis Virus/Yellow fever
mosquito vector in Africa and South America |
|
|
What is the epidemiology of the gram negative organism that causes liver absesses in people with hemochromatosis?
|
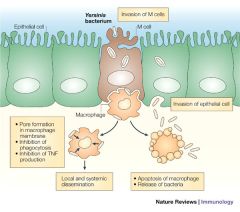
Y. enterocolitica; more common in European countries and colder regions of the US
|
|
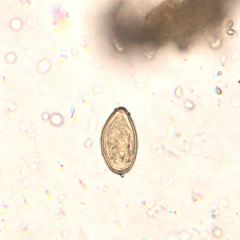
Which organism can cause biliary obstruction and chronic infection leading to adenocarcinoma of the bile ducts?
|
Trematode-Chinese liver fluke =Opisthorchis sinesis; undercooked fish; China, Japan, Korea, Vietnam (east asia)
|
|
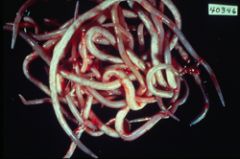
What nematode can cause biliary obstruction world wide?
|
Ascaris lumbricoides; most common worm infection
|

