![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which type of acute gastric ulcer is most common in individuals with shock, sepsis or severe trauma?
|
Stress ulcers
|
|
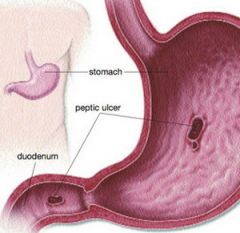
Which type of acute gastric ulcer is most commonly associated with severe burns or trauma?
|
Curling ulcer; occur in the proximal duodenum
|
|
|
Which type of acute gastric, esophageal, or duodenal ulcer is most commonly associated with intracranial disease?
|
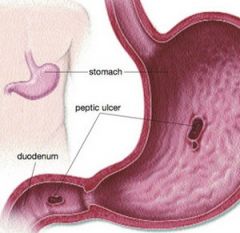
Cushing ulcer; carry a high incidence of perforation
|
|
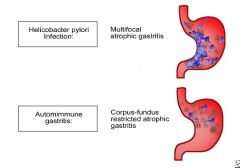
Upon gastric biopsy, you note spiral shaped organisms concentrated within the superficial mucus overlying epithelial cells in the surface and neck regions. What is this organism?
|
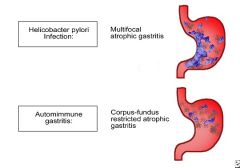
H. pylori; most common cause of chronic gastritis
|
|
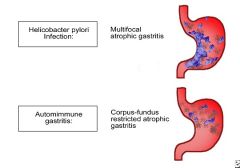
What are some characteristics of autoimmune gastritis?
|
Located in the body of the stomach; inflammatory infiltrate lymphcytes and macrophages; acid production is decreased so gastrin production is increased; antibodies to parietal cells/their products are found; patients often also have other autoimmune diseases going on
|
|
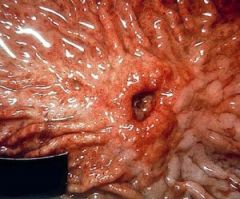
While treating a patient with a Meckel diverticulum, you note a round to oval, sharply punched out defect in the adjacent mucosa. Diagnosis?
|
Peptic Ulcer; pretty much always associated with chronic gastritis
|
|
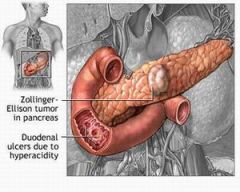
Which disease is characterized by uncontrolled release of gastrin by a tumor which results in massive acid production?
|
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome; multiple peptic ulcerations in the stomach and duodenum
|
|
|
Is a peptic ulcer more likely to occur in the stomach or the proximal duodenum?
|
Proximal duodenum
|
|

If a patient presents with free air under the diaphragm and epigastric pain, what has probably happened?
|
Acute gastric perforation
|
|
|
How is the risk of adenocarcinoma in gastric adenomas related to the size of the lesion?
|
Increased lesion size = increased risk of malignancy
|
|
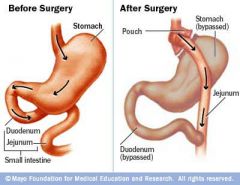
Which disease is characterized by large fixed mucosal polyps arising in the stomach proximal to an old gastroenterostomy.
|
Gastritis cystica
|
|
|
A gastric biopsy reveals a doubling of oxyntic (parietal) mucosal thickness along with multiple peptic ulcers. Likely diagnosis?
|
Zollinger Ellison Syndrome; increased secretion of gastric by tumors = lots of acid
|
|
|
A biopsy reveals enlargement of rugal folds. There is no inflammation.
|
Menetrier's Disease; caused by excessive secretion of transforming growth factor a (TGF-alpha)
|
|
|
A patient presents with a well differentiated neuroendocrine tumor in the tracheobronchial tree and lungs.
|
Carninoids; clinical features are determined by what hormones are produced
|
|
|
A patient presents with epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, GI bleeding. Labs are notable for c-KIT. Diagnosis?
|
Gastro-intestinal stromal tumors
|
|
|
A 70 year old male is a survivor of a massive fire in his residential complex. He has 40% burns. He complains of epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, and two episodes of hematemesis. Dx?
|
Curling Ulcer
|
|
|
A 70 yo F has a massive stroke. She complains of epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, and two episodes of hematemesis. Dx?
|
Cushings Ulcer
|
|
|
A 42 yo man presents with a recent history of abdominal pain, distension and nausea. Urea breath testing for H. pylori is positive. Dx?
|
Chronic gastritis
|
|
|
A 70-year old male presents with history of epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting and two episodes of hematemesis. He is on NSAIDS for chronic degenerative arthritis. Physical examination is remarkable for tachycardia and conjunctival pallor .
|
Acute gastritis
|
|
|
70-year-old woman presents with a 2-month history of increasing fatigue, difficulty with ambulation, and memory deficits. Family history is notable for autoimmune disease. Laboratory evaluation is remarkable for a macrocytic anemia, a markedly reduced serum vitamin B12, and presence of antiparietal cell antibodies.
|
Chronic Auto-Immune Gastritis
|
|
|
A 40-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with a 2-month history of intermittent upper abdominal pain. He describes the pain as a dull, gnawing ache. The pain sometimes wakes him at night, is relieved by food and drinking milk, and is helped partially by ranitidine. He had a similar but milder episode about 5 years ago, which was treated with omeprazole. Physical examination reveals a fit, apparently healthy man in no distress. The only abnormal finding is mild epigastric tenderness on palpation of the abdomen.
|
Gastric Ulcer
|
|
|
A 54-yo male presents with severe epigastric pain, nausea, bloating, abdominal fullness since last several months. OTC drugs are not beneficial. His primary care physician prescribes proton pump inhibitors. After 6 weeks on PPI, the symptoms have not resolved. Subsequent endoscopy reveals multiple punched out lesions in fundus of the stomach, and in duodenum.
|
Zollinger Ellison Syndrome; caused by gastrin secreting tumors
|
|
|
A 70yo male presents with recurrent, intractable watery diarrhea, cloikyabdominal pain, , flushing and wheezing. A colonoscopy revealed a mass in stomach (biopsy shown). Additionally, a chest CT revealed pulmonary infiltrates.
|
Carcinoid
|
|
|
Which GI disease microscopically shows whorled texture?
|
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
|
|
|
What are two histological markers of stomach tissue?
|
Columnar epithelium and gastric glands
|
|
|
What type of cell are gastric polyps derived from?
|
foveolar cells
|
|
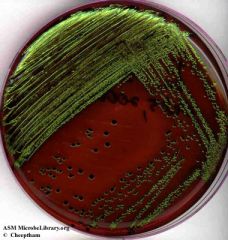
Which organism will typically show a green-metallic growth on EMB plates?
|
E. coli; strong lactose fermenter/lactose positive
|
|

Kligler's Iron Agar shows red at the top with yellow at the bottom
|
Shigella
|
|

Kligler's Iron Agar shows red at the top with BLACK on the bottom.
|
Salmonella
|
|

Klignler's Iron Agar shows an all yellow tube which has a layer of gas at the bottom.
|
E. coli
|
|
|
Which organism is being looked for with a urease test?
|
Urease-positive genus Proteus
Acid changes tube from orange -> yellow Urease + Nh3 changes tube from orange -> pink/red |
|

Which two enteric bacteria produce citrate and can thus be used in simmons citrate media?
|
Enterobacter aerogenes and Salmonella enterica
Control tube = green in color Citrase Positive tube = blue |
|
|
Which two organisms produce a black precipitate in SIM medium?
|
Salmonella and Citrobacter; both produces hydrogen sulfide which reacts with sodium thiosulfate to produce the black precipitate
|
|
|
Which orgainsm produces indole in SIM medium?
|
E. coli; indol reacts with Kovac's reagent to produce a red color in the medium
|
|
|
What is the COFFEe pneumonic for?
|
enterobacteriacae
Capsular (K antigen related to virulence of bug) O anigen (polysaccharide of endotoxin) Flagellar antigen (H antigen) found in all motile species Ferment glucose Enterobacteriaceae |

