![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Primary Location of Megakaryotes in Bone Marrow
|
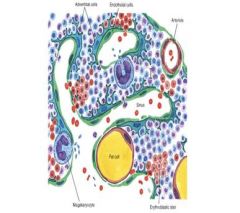
Close to sinus endothelial cells to expel platets directly into sinuses; platelets are fragments of the cytoplasm of megakaryocytes
|
|
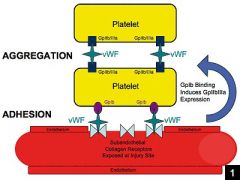
Function of Glycoproteoin Ib (GPIb)
|
Platelet receptor for vWF; noncovalently associated with GP IX; complex is called GPIb/IX
|
|
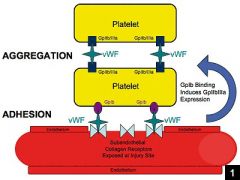
Function of Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa
|
Major plasma membrane receptor for fibrnogen; hidden in resting platelets and has a low affinity for fibrinogen; when platelet is activated GpIIb/IIIa is converted to a high affinity binding form
|
|
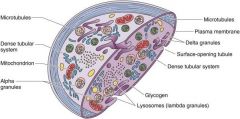
Structural Zone
|
Comprised of microtubules + filaments/microfiliaments
Function is to mediate shape change when the platelet is activated |
|
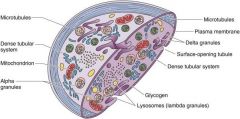
Organelle Zone
|
Contains granules filled with proteins for platelet function
|
|
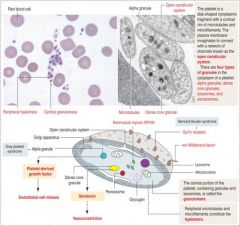
Alpha and Dense Granules
|
Alpha: contain platelet growth factors
Dense: Serotonin for vasoconstriction |
|
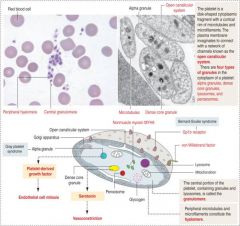
Platelet derived agonists
|
ADP, serotonin, platelet activating factor, thromboxane A2
|
|
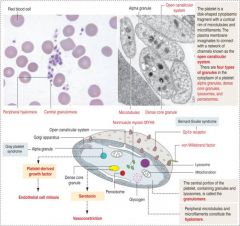
Nonplatelet derived agonists
|
Collagen, thrombin, epinephrine
|
|
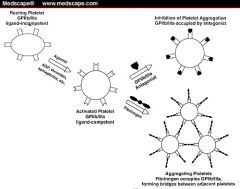
How do platelets change in shape once activated?
|
Discoid shape -> one with long projections emanating from the surface
|
|
|
Thrombosis
|
Pathologic counterpart of hemostasis; formation of blood clot within intact vessels
|
|
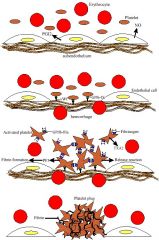
Primary Hemostasis
|
Platelets interact with injured blood vessel and one another to form a hemostatic plug; plug arrests bleeding but can be easily dislodged
|
|
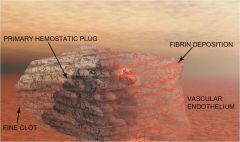
Secondary Hemostasis
|
Coagulations factors recruit fibrin -> strands deposited on the platelet plug stabilizing it
|
|
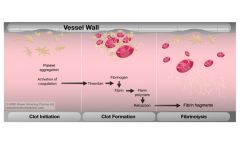
Fibrinolysis
|
Dissolution of the clot
|
|
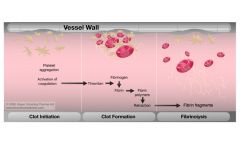
Fibrinolysis
|
Dissolution of the clot
|
|
Arteriolar Vasoconstriction
|
Transient event; cant main hemostasis
|
|
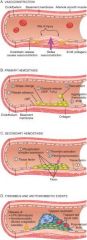
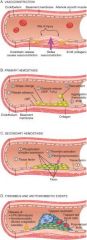
Platelet Adherence and Activation
|
Endothelial injury exposes extracellular matrix; platelet activation and adherence; platelets increase their surface area by changing shape; platelets release secondary granules which recruit additional platelets = formation o fplug
|
|
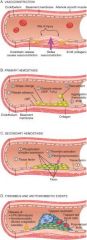
Exposure of Tissue Factor
|
Tissue factor + VII = invivo coagulation; formation of thrombin which creates fibrin meshwork
|
|
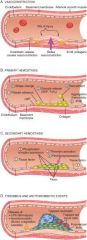
Secondary Hemostasis
|
Reinforces initial platelet plug
|
|
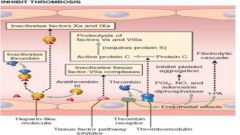
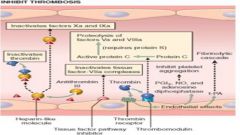
Antiplatelet and Antithrombotic Endothelial Properties
|
Protein S also produced by endothelium; cofactor for Protein C
|
|
t-PA
|
Protease that converts plasminogen into plasmin; plasmin cleaves fibrin
|
|
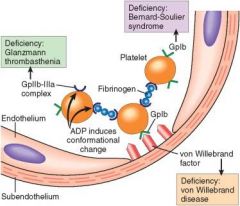
Formatoin of Vascular Plug
|
Glanzman Thrombasthenia; Bleeding disorder due to GP IIb/IIIa deficiency
|
|
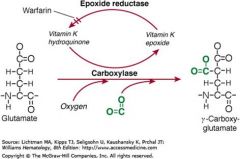
There are many blood coagulation proteins that need vitaminK
|
Vit K needed for gamma carboxylation of glutamic acid residues; otherwise factors cant bind to the negatively charged phospholipid surfaces by way of calcium bridges
|
|
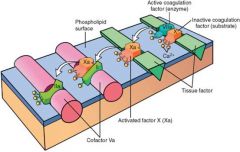
X->Xa via extrinsic pathway
|
The above illustration shows the conversion of factor X to factor Xa by way of the extrinsic pathway. Note that calcium ions hold the components together and are essential for the reaction. The activated factor Xa becomes the proteases for the following complex.
|
|
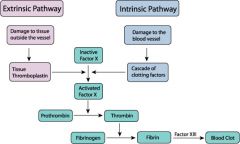
Extrinsic vs Intrinsic cascade
|
Extrinsic vs Intrinsic cascade
|
|
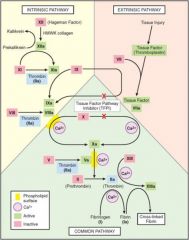
Note common pathway
|
Extrinsic and intrinsic pathways converge at common pathway
Factor X (K dependent); Xa activates prothrombin to thrombin |
|
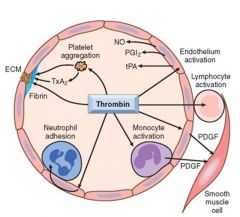
Function of Thrombin
|
Procoagulant, antithrombotic, roles in inflammation, roles in cellular proliferation
|
|
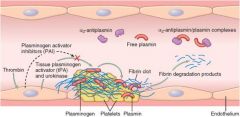
|
PA converts Plasminogen to plasmin; plasminogen binds fibrin and degrades it
|
|
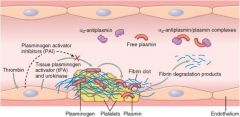
tPA
|
Plasminogen + tPA -> Plasmin -> cleavage of fibrin mesh
|
|
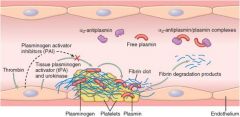
Thrombin Activatable Fibronolysis Inhibitor
|
TFAI activated by thrombin/thrombomodulin complex; protects fibrin clot from lysis by inhibiting plasminogen
|
|
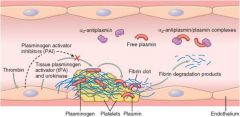
Alpha 2 Antiplasmin
|
Binds free plasmin to prevent fibrinolysis; however if plasmin is already bound to fibrin it's protected since its activation site is occupied
|
|
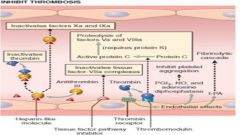
Anti-coagulatoin
|
Antithrombin inactivates factors II, VII, IX, X, and XI; ultimately inactivates thrombin
Herparin accelerates inhibition of target proteases; vascualr endothelium has 'heparin like' molecules |
|
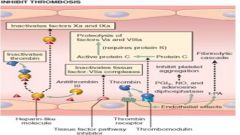
Thrombomodulin
|
Alters the activity of thrombin from procoagulant to anticoagulant
|
|
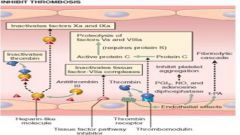
Protein C (requires protein S)
|
Activated protein C inhibits factor Va and VIIIa
|
|
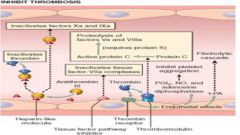
Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor
|
TFPT binds and inhibits active site on Xa; this complex then reacts with VIIa in complex with tissue factor; inactivation of both proteases
|
|
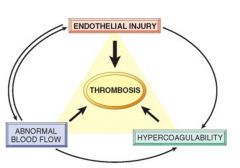
Thrombosis
|
Due to endothelial injury, stasis or turbulent blood flow or hypercoagulability of blood = Vichow's Triad
|
|
|
Venous Thrombi
|
Initiated at sites of stasis
|
|
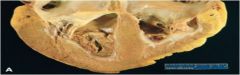
Note thrombi in the left and right ventircular apices; they are overlying white fibrous scar tissue
|
Mural Thrombi in Heart Chambers
|
|
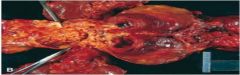
This is a laminated thrombus in a dilated abdominal aortic aneurysm
|
Mural Thrombi in Aortic Lumen
|
|

|
Lines of Zhan
alternating pale pink bands of platelets with fibrin and red bands of red blood cells. |
|
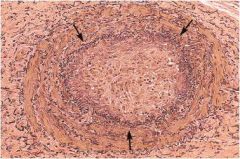
|
Thrombosed artery. The lumen is delineated by the internal elastic lamina (arrows). The lumen is filled with organized thrombus. The white spaces represent recanalized endothelium lined channels.
|
|
|
Superficial Venous Thrombi
|
Superficial venous thrombi
Generally occur in saphenous veins in the setting of varicosities May cause local swelling, congestion, pain, and tenderness Edema and impaired venous drainage predispose the skin to infections and varicose ulcers Rarely embolize |
|
|
Postmortem Clots
|
Gelatinous consistency with bottom portion being dark red from settling of red cells and the top portion being yellow
|
|
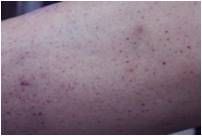
Primary or secondary?
|
Primary Hemostatic Defect
|
|
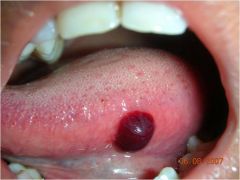
Primary or secondary defect?
|
Primary Defect
|
|
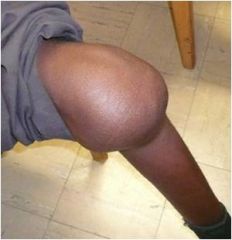
Primary or secondary defect?
|
Secondary; bleeding in joints
|
|
|
Secondary Hemostatic Defect
|
Bleeding in joints (hemarthroses) or deep tissues.
Delayed bleeding after injury. Usually indicates clotting factor deficiency or clotting factor inhibitor. |
|
|
Primary Hemostatic Defect
|
Skin or mucosal bleeding.
Bleeding immediately after injury. Usually suggests numerical or functional abnormalities of platelets or von Willebrand disease. |
|
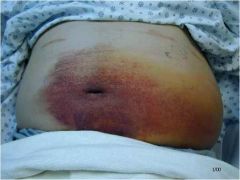
Primary or Secondary?
|
Secondary; deep bleed
|
|
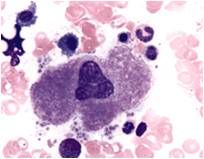
|
Forms platelets in BM
|
|
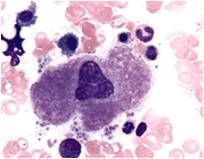
|
Forms platelets in BM
|
|
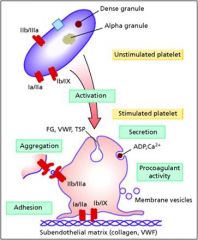
Characteristics of platelets
|
Cricualte for 7-10 days; removed by reticuloendothelial system third of the platelet pool is in the spleen
|
|
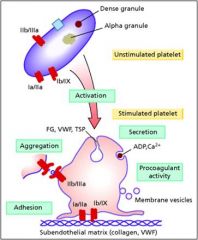
Ib-IX
|
Platelet receptor to adhere to endothelial surface
|
|
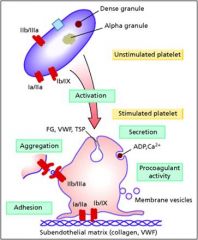
IIb-IIIa
|
Platelet-Platelet interaction
|
|
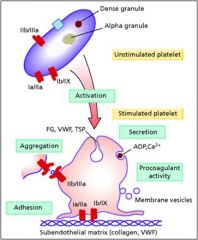
Granules
|
Procoagulin factors inside them; contents released when paltelets get activated
|
|
|
Pseudothrombocytopenia; platelets clot and result in low platelet count
|
|
|
Any splenomegaly condition will produce what
|
Thrombocytopenia due to destruction of platelets
|
|
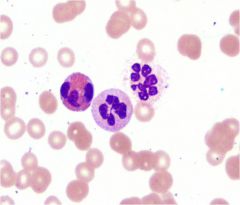
|
B12 deficiency; folate deficiency; myelodysplasia
|
|
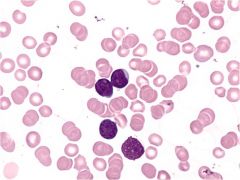
|
Acute leukemia; myelodysplasia; chronic leukemia
|
|
|
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
|
Excessive activation of coagulation system; thrombi formation in microcirculation; PT and PTT prolonged
|
|
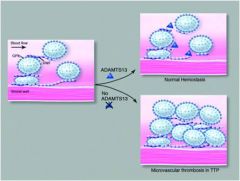
|
Thrombotic thromboytopenic Purpura; deficiency of von willebrand cleaving enzyme; coaglation factors not consumed but platelet plug keeps growing so = thrombocytopeina
|
|
|
Chronic Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
|
Adults; detected by routine CBC; diagnosis of exclusoin, no splenomegaly
IgG Ab against paltelet glycoproteins; thrombocytopenia due to platelet removal by reticuloendothelial system |
|
|
Acute Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
|
IgG Ab against paltelet glycoproteins; thrombocytopenia due to platelet removal by reticuloendothelial system
Seen in children following petechae + viral illness (chills, sore throat, etc) |
|
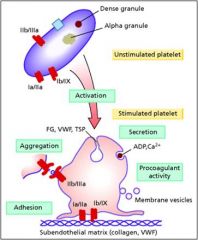
Bernard-Soulier Syndrome
|
Deficiency of 1b-IX
|
|
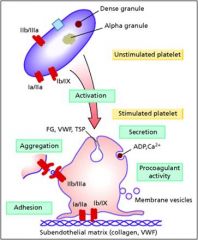
Glanzman's Thrombasthenia
|
Deficiency of Ib-IIIa; can't form plug
|
|
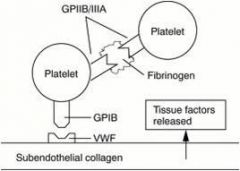
von Willebrand Factor
|
Bridge between platelets and vessel wall; carrier molecule for factor VIII (so deficiency of vWF may lead to deficiency of VIII)
|
|
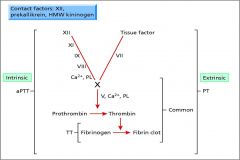
|
Clotting Cascade
note intrinsic vs extrinsic factor both contribute to common pathway |
|
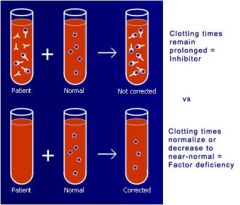
|
Mixing Study can tell you whether you're dealing with a factor deficiency or inhibitor
|
|
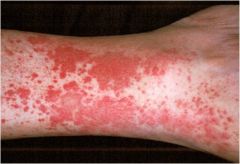
|
Palpale Purpura; immune complex deposition disease
|

