![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Amino Acid |
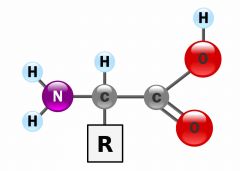
Carbon compounds joined by peptide bonds that create proteins. |
|
|
Carbohydrate |
Organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms for each carbon atoms. Example: glucose=C6H12O6 |
|
|
DNA |
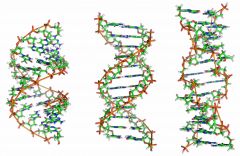
The nucleic acid that transmits traits from one generation to the next (Deoxyribonucleic acid). |
|
|
Inorganic |
Not having the structure or organization characteristic of living bodies and does not contain Carbon. |
|
|
Lipid |
An organic molecule composed mostly of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Example: fats, oils, and waxes |
|
|
Macromolecule |
A large complex organic molecule, such as nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, with relatively large molecular weight. |
|
|
Monomer |
A subunit of a polymer and covalently linked to one another through the removal of water. Example: Glucose |
|
|
Nucleic Acid |
A large, complex macromolecule containing carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Example: DNA and RNA |
|
|
Nucleotide |
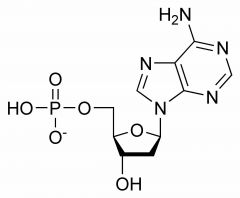
A unit of a nucleic acid, made up of a phosphate, the sugar ribose or deoxyribose, and a nitrogenous base. |
|
|
Organic |
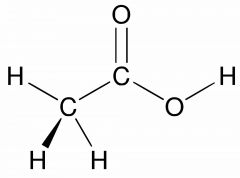
A molecule or compound that ALWAYS contains Carbon and sometimes Hydrogen. |
|
|
Protien |
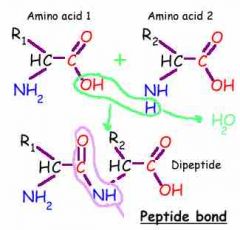
Organic compound made of amino acids joined by peptide bonds; primary building block of organisms. |
|
|
RNA |
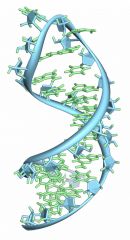
ribonucleic acid; guides protein synthesis |
|
|
Monosaccharide |
a carbohydrate that is made up of only one simple sugar molecule Example: glucose, galactose, and fructose |
|
|
Disaccharide |
Two monosaccharide molecules bonded together. Example: sucrose |
|
|
Polysaccharide |
Chains of monosaccharides. Example: starch, cellulose, and glycogen are made up of chains of glucose |
|
|
Polymer |
A large molecule consisting of many smaller subunits bonded together. Example: polysaccharide |
|
|
Fatty Acid |
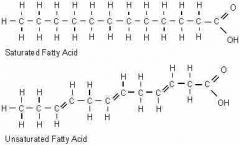
A glycerol molecule and a fatty acid chain make up a lipid. |
|
|
Steriod |
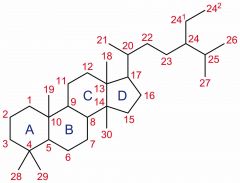
Any of a large group of fat-soluble organic compounds. |
|
|
Phopholipid |
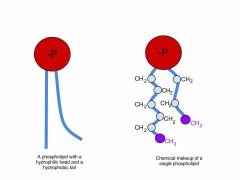
A structure that makes up the cell membrane that consists of a phosphate group and fat (lipids). Also known as a phospholipid bilayer. |
|
|
Triglyceride |
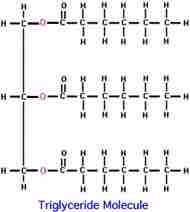
A glycerol bound to three fatty acids. It is the main constituent of vegetable oil and animal fats. |

