![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Molecular formula |
The chemical formula of a molecular substance showing the identity of the atom in each molecule and the ratios of those atoms to one another |
|
|
Structural formula |
A two-dimensional drawing or diagram that shows how the atoms in a molecule are connected each line represents a covalent bond |
|
|
Isomer |
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formula isomers differ in molecular structure and in chemical and physical properties |
|
|
triple bond |
A covalent bond with three electron pairs are shared between two atoms |
|
|
Lewis Dot structure |
A diagram of molecule structure that uses dots to represent the valence electrons |
|
|
Octet rule |
Non-metal atoms combine by sharing electrons so that each atom has a total of eight valence electrons after bonding each atom resembles a Noble gas and its electron arrangements |
|
|
Double bond |
A covalent bond where four electrons are shared between two atoms |
|
|
Electron domain |
The space occupied by bonding pairs or lone pairs of valence electrons in a molecule electron domains affect all over shape of molecule |
|
|
Linear |
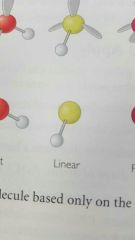
|
|
|
Bent |
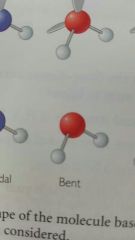
|
|
|
Trigonal planar |
A flat triangular shape that is found in small molecules with three electron domains surrounding a central atom |
|
|
Tetrahedral |
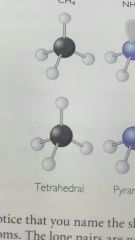
|
|
|
Polar molecule |
A molecule that has a negatively charged end and a positively charged and new to electronegativity differences between the atoms and or the asymmetry of its structure |
|
|
Intermolecular force |
A force of attraction that occurs between molecules |
|
|
Dipole |
A molecule or covalent bond with a non symmetrical distribution of electrical charge that makes a molecule or Bond polar |
|
|
Non-polar molecule |
A molecule that is not attracted to an electrical charge a molecule is nonpolar if each atom shares electrons equally or there is no net dipole in the molecule |
|
|
Electronegativity |
A measure of the ability of an atom in a molecule or substance to attract electrons to itself |

