![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Organ system |
A group of organs that work together to perform a general task
|
|
|
Organ
|
A part of the body that is composed of different tissues
|
|
|
Tissue
|
Usually a mass, tube, or sheets of cells
|
|
|
Parenchyma cells
|
*living when mature
*metabolism and storage *can differentiate |
|
|
Collenchyma
|
*Provide flexible supports to parts that are still growing
*alive when mature |
|
|
Sclerenchyma
|
*support
* have thick secondary walls made of cellulose and strengthened by lignin * dead when mature so cannot grow |
|
|
Lignin
|
Tough organic polymer that provides rigidity
|
|
|
Meristematic cells
|
Can replicate
|
|
|
Apical meristem
|
Are on the tips of young shoots and roots and increase in length as the shoot grows
|
|
|
Primary meristems
|
Responsible for increase in length of stems and roots
|
|
|
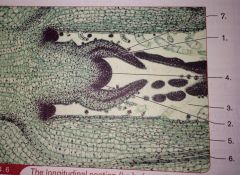
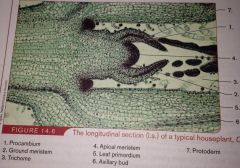
Protoderm
|
(primary meristem) Produces the outer epidermis to stems and roots
|
|
|
Procambium
|
(Primary meristem) produces the vascular tissues in stems and roots
|
|
|
Ground Meristem
|
(Primary meristem) produces the ground tissues of stems and roots
|
|
|
Lateral meristem
|
Responsible for secondary growth they increase the girth of stems and roots
|
|
|
Lateral meristem
|
Responsible for secondary growth they increase the girth of stems and roots
|
|
|
Vascular Cambium
|
(Lateral Meristem) produces tissues that increase the girth of the plant
*found between the xylem and phloem |
|
|
Cork cambium
|
(Lateral meristem) produces a thick covering for large stems and roots
|
|
|
Dermal tissue
|
(Non-meristematic) consist of the epidermis which acts as the outer skin of the plant
|
|
|
Dermal tissue
|
(Non-meristematic) consist of the epidermis which acts as the outer skin of the plant
|
|
|
Cutin
|
Helps the shoot system retain water
|
|
|
Dermal tissue
|
(Non-meristematic) consist of the epidermis which acts as the outer skin of the plant
|
|
|
Cutin
|
Helps the shoot system retain water
|
|
|
Vascular tissue
|
(Nonmeritstematic) are involved in the transport of materials through the plant
|
|
|
Xylem
|
Carries water from roots to stems and leaves
|
|
|
Phloem
|
Carries carbohydrates from one part of the plant to the other
|
|
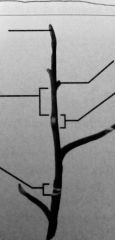
Label
|
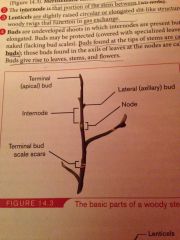
|
|

|
Lenticels
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pith
|
Located in the center of the stem after they form the cells breakdown creating a hollow area in the middle of the stem
|
|
|
Sieve-tube members
|
The cells that make up the phloem tube
|
|
|
Sieve-tube members
|
The cells that pick up the phloem tube
|
|
|
Companion cells
|
Assists sieve tube members in maintaining cell metabolism and function
|
|
|
Sieve-tube members
|
The cells that pick up the phloem tube
|
|
|
Companion cells
|
Assists sieve tube members in maintaining cell metabolism and function
|
|
|
Translocation
|
sugars are actively transported into sieve tube members and then osmosis occurs
|
|
|
Transpiration
|
When water evaporates it moves xylem sap up the plant
|
|
|
tracheids |
involved in support and in transport of xylem sap |
|
|
suberin |
water proof substance that protects tree |
|
|
heartwood |
the darkend central region used as mechanical support |
|
|
sapwood |
the outer lighter region, functions as mechanical support and transport |
|

|

|
|
|
netted venation |
is where the leaf has one or more large veins from which smaller veins diverge *eudicots possess this type of venation |
|
|
parallel venation |
where the leaf has several veins that are equal size, which run parallel down the leaf *monocots have parallel venation |
|
|
palisade mesophyll |
layer of elongated cells near the upper epidermis |
|
|
deciduous plants |
plants whose leaves drop with change in season |
|
|
abscission |
the process of leave shedding |
|
|
leaf scar |
place where leaf once was |
|
|
primary root |
the first root to emerge from seed |
|
|
tap root system |
if the primary root is the largest of all the other roots (eudicots have these) |
|
|
fibrous root system |
many lateral roots that are all slender (monocots have these) |
|
|
primary growth |
the enlargement and differentiation of cells produced by the apical meristem |
|
|
primary tissues |
all tissues made by the apical meristem |
|
|
secondary growth |
the enlargement and differentiaiton of cells produced by lateral meristem (causes an increase in girth) |
|
|
differentiation |
return to an immature state |
|
|
secondary tissues |
tissues made by the lateral meristem |
|
|
root cap |
covers the root apex |
|
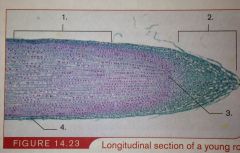
|

|
|
|
region of cell elongation |
ajacent to the apical meristem, and consist of cells that are increasing in size longitudinally |
|
|
protoderm |
layer of cells on the outside that turn into the epidermis |
|
|
ground meristem |
produces the cortex and the endodermis |
|

|

|
|
|
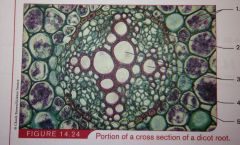
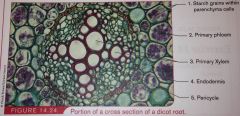
cortex |
stores starches and orhter materials *located on the interior of the epidermis and includes the endodermis |
|
|
endodermis |
surround the stele and regulates which minerals pass from cortex to vascular tissue. |
|
|
|
|
|
pericyle |
layer of cells just inside the endodermis *unspecialized perchyma cells (potential to undergo cell division) *make lateral roots |

