![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
extremophiles
|
live in stressful environments of high temperatures (thermophiles), saltiness (halophiles), or low oxygen
|
|
|
bacillus
|
elongated rods
|
|
|
coccus
|
circular
|
|
|
vibrio
|
comma shaped rods
|
|
|
spirillum
|
thick nonflexible spiral
|
|
|
spirochaetes
|
corkscrew shape
|
|
|
strepto-
|
long chains of bacteria
|
|
|
staphylo-
|
clusters
|
|
|
diplo-
|
connected pairs
|
|
|
Domain Archaea
|
prokaryotic organisms, extremophiles
|
|
|
Domain Bacteria
|
prokaryotic organisms, proteobacteria (gram negative), gram positive bacteria, spirochetes, cyanobacteria (autotrophic bacteria)
|
|
|
Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Protista (9 phyla)
|
Dinoflagellata
Bacillariophyta Chlorophyta phaeophyta euglenophyta Rhizopoda Kinetoplastida Apicomplexa Ciliata |
|
|
autotrophs
|
organisms capable of photosynthesis
|
|
|
endosymbionts
|
live inside other unicellular organisms or inside other cells
|
|
|
gram stain
|
common technique to differentiate between gram positive and negative bacteria
|
|
|
gram positive bacteria
|
petidoglycan in cell walls, purple
|
|
|
Gram negative bacteria
|
doesn't retain purple, reddish
|
|
|
Protists
|
unicellular, eukaryotic organisms
|
|
|
dinoflagellates
|
pair of flagella, autotrophic, cause red tide
|
|
|
Diatoms (phylum Bacillariophyta)
|
hard cell wall, glass, marine and freshwater
|
|
|
chlorophyta
|
form colonies, freshwater and land
|
|
|
kelp anatomy 4
|
body= thallus
stem= stipe leaves= blades holdfast |
|
|
phylum euglenophyta
|
small, two flagella,unique starch paramylon, stigma (eyespot),
|
|
|
phylum rhizopoda
|
amoebas, food vacuoles for phagocytosis
|
|
|
phagocytosis
|
cell surrounds its prey with pseudopodia
|
|
|
endoplasm
|
inside of the cell
|
|
|
ectoplasm
|
rim of stiff cytoplasm
|
|
|
phylum kinetoplastida
|
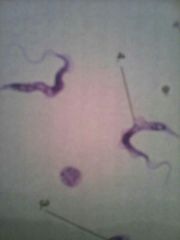
flagellates
|
|
|
phylum apicomplexa
|
have an apical complex
|
|
|
apical complex
|
group of organelles that penetrate host cells
|
|
|
intermediate host
|
human
|
|
|
definitive host
|
insect
|
|
|
phylum ciliata
|
ciliary action/ cilia
|
|
|
fission
|
cell divides
|
|
|
conjugation
|
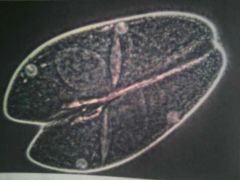
exchange genetic material
|

