![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Arenes |
Aromatic hydrocarbons with one or more benzene ring |
|
|
4 examples of products benzene can produce. |
Explosives, dyestuffs, pharmaceuticals and detergents |
|
|
Two natural sources of arenes |
Crude oil and coal |
|
|
Two natural sources of benzene |
Volcanoes and forest fires |
|
|
Carcinogenic |
Any chemical which can cause cancer in humans |
|
|
Problems with kekule's model |
If there were c=c then addition reactions would occur but they do not. Only reacts with br2 with a halogen carrier Bond length is an intermediate between short C=C and long C-C The enthalpy change of hydrogenation is less exothermic than expected |
|
|
Benzene structure and bonding |
-P orbital above and below the carbon plane overlap and form a high electron density PIE ring. -Hexagonal planar ring, trigonal planar round each carbon, bond angles 120. -4 electrons in carbons outer shell, 3 are bonded -6 electrons 6 carbons C6H6 |
|
|
Delocalised |
Electrons which do not belong to a specific carbon but are shared between carbons |
|
|
Why does benzene undergo electrophilic substitution |
To maintain its stability |
|
|
Nitration of benzene |
Concentrated nitric acid Concentrated sulphuric acid 50 degrees Produces water Round bottom flask |
|
|
Three uses of nitrobenzene |
Dye preperation, pharmaceuticals, pesticides. |
|
|
Why must nitration be below 50 degrees? |
So no more than one NO2 group substitutes. |
|
|
Electrophilic substitution steps in benzene |
-electrophilie attracted and a electron pair accepted, forming a covalent bond -benzene becomes unstable so rapidly lose its h and the electron ring reforms |
|
|
Why is cyclohexene more reactive with br2 than benzene? |
Alkenes have localised pi electrons which can polarise br2 and have a higher electron density than benzene. Electrophiles less attracted to benzene and more energy is required to break the pi cloud. |
|
|
Phenol and sodium hydroxide |
Water and sodium phenoxide salt |
|
|
Phenol and sodium |
Sodium phenoxide and hydrogen gas |
|
|
Why does phenol react with bromine at room temperature?? |
The lone pair of electrons in oxygen 's p orbital it drawn into the delocalised electron ring which created a higher electron density and activates the ring. This means bromine can be polarised. |
|
|
Two uses of alkyl phenols |
Surfactants, detergents |
|
|
Two uses of chlorophyll phenols |
Antiseptics, disenfectants |
|
|
4 uses of phenols |
Epoxy resin for paints, aspirin, pharmaceuticals and dyes |
|
|
What would you see when bromine water is added to phenol? |
Turns from Orange to colourless and a white precipitate is formed |
|
|
When oxidising acidified potassium dichromate changes from... |
Orange to green |
|
|
Reducing agent |
NaBH4 |
|
|
How can you detect the precence of an aldehyde or a ketone? |
Add bradys reagent (2,4-DNP) and an orange precipitate will form. |
|
|
Ethanoic acid and Na react together to form... |
Sodium ethonoate and hydrogen gas. |
|
|
Propanpic acid and potassium hydroxide reacts together to form... |
Potassium propanoate and water |
|
|
Methanoic acid and sodium carbonate reacts to form... |
Sodium methonoate, carbon dioxide and water |
|
|
Acid anhydride and alcohol with gentle heat reacts to form... |
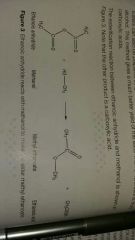
An ester and a carboxylic acid |
|
|
How do you form an acid anhydride |
The removal of a water molecule from two carboxylic acid molecules |
|
|
Acid hydrolysis conditions and reagents |

Water, aq HCL, reflux |
|
|
Alkali hyrolysis conditions |
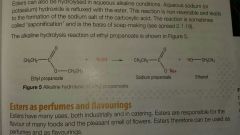
Reflux, aq sodium hydroxide |
|
|
Three uses of esters |
Perfumes, solvents and flavourings |
|
|
When an unsaturated fat has one double bond it is refered to as a... |
Mono unsaturated fat |
|
|
Octadeca-9,12,-enoic acid written in short hand |
18:2 (9,12) |
|
|
Glycerol and 3 fatty acids under reflux with conc. H2SO4 |
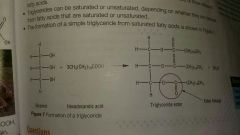
Triglyceride ester |
|
|
Why are trans fats bad for us? |
Increase the amount of LDL'S in the blood and decrease the amount of HDL's |
|
|
What is biodeisel |

Ethyl or methyl ester of a fatty acid |
|
|
name this compound (CH3CH2)NH(CH3) |
N-methyly ethyl amine |
|
|
Propyl amine and hydrochloric acid forms |
Propyl ammonium chloride |
|
|
What do you need to prepare amines from halogenoalkanes? |
Ethanol and NH3 |
|
|
What conditions are required to reduce nitrobenzene to phenylamine? |
Sn (tin) concentrated HCL heated under reflux |
|
|
What is needed to form benzadizonium chloride from phenyl amine? |
HCL aq NaNO2 below 10 degress |
|
|
How do you form an aozo dye from benzendiazonium chloride? |
NaOH, alkaline conditions, phenol |
|
|
What are fatty acids? |
Long chain carboxylic acids |
|
|
Curly arrow |
Movement of a pair of electrons to either make or break a bond |
|
|
How to male tolled reagent/ ammoniacal silver nitrate |
Aq NaOH added to aq silver nitrate until a brown precipitate of silver oxide forms. Dilute aq amonia is added until precipitate just disolves. |
|
|
What is the oxidising species in tollens reagent? |
Silver ion which gets reduced to silver metal |
|
|
Trans isomer |
E isomer Different sides |
|
|
Why is reflux used? |
To prevent loss of reactants and products via evaporation |
|
|
Primary amine |
A compound containing nitrogen where the nitrogen is attached to one carbon only |

