![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
85 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Percent of Earth covered by oceans
|
71% |
|
|
Name 3 main causes of currents
|
wind, Earth's rotation, and solar heating |
|
|
Identify closest current by name and flow direction
|
California current goes down to California |
|
|
Define El Niño and describe its impact on the ecosystems |
Impact-weather extremes (flooding, droughts) Cold water plants and animals die off, high end consumers starve |
|
|
Main causes of ocean waves
|
sometimes earthquakes (tsunamis) |
|
|
define sneaker waves
|
large unexpected waves that rush on shore faster and farther than previous waves
|
|
|
warning signs sneaker waves
|
long time between breakers, very strong ebb |
|
|
impacts of sneaker waves
|
knock people down/off rocks, spins people under logs, pulls people out to sea |
|
|
guidelines of sneaker waves
|
watch ocean when near surf and avoid logs |
|
|
name main cause of tides |
Mostly gravitational pull of Moon |
|
|
frequency of tides
|
every 12 hours (12.4)
|
|
|
Tidal range of mid ocean
|
About 1 feet Hawaii |
|
|
Tidal range of continental shores
|
6-8 feet Newport Oregon |
|
|
Tidal range long, narrow bays
|
|
|
|
Define long shore current
|
near-shore current that flows parallel to shore
|
|
|
Cause of long shore
|
waves striking beach at an angle |
|
|
define rip currents
|
high-velocity currents flowing seaward from shore |
|
|
causes of rip currents
|
long shore current meeting a pier, headland, or jetty |
|

|
European beach grass
|
|

|
blood worm |
|

|
beach hoppers eat seaweed |
|

|
mole crab crustaceans without pincers |
|

|
smooth bay shrimp isopod parasite on gill chamber |
|

|
mysid shrimp carry young under thorax (like an opossum) |
|

|
western snowy plover solitary dry sand |
|

|
sanderlings social |
|
|
how are hollows and rock sculptures in the rocky shoreline were created
|
unequal wave erosion |
|

|
sea cliff |
|

|
sea cave |
|

|
headland
|
|

|
sea stack |
|

|
sea urchin |
|

|
test (skeleton of sea urchin) |
|

|
ochre sea star |
|

|
sunflower star |
|

|
giant green anemone |
|

|
aggregating sea anemone
|
|

|
piddock clam
|
|

|
California mussel |
|

|
black turban snail |
|

|
keyhole limpet |
|

|
lined chiton |
|

|
black katy chiton |
|

|
gumboot chiton |
|

|
giant pacific octopus |
|

|
purple shore crab |
|

|
porcelain crab |
|

|
kelp crab |
|

|
rock crab |
|

|
hermit crab |
|

|
acorn barnacle |
|

|
goose neck barnacle |
|

|
sculpin |
|

|
black prickleback |
|

|
black oyster catcher |
|

|
common murres |
|

|
harbor seal |
|

|
black pine |
|

|
rockweed |
|

|
sugar wrack |
|

|
encrusting coralline algae |
|

|
articulated coralline algae |
|

|
sea lettuce |
|
|
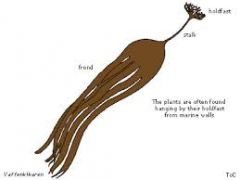
oar weed |
|

|
feather boa kelp |
|

|
winged kelp |
|

|
surf grass |
|
|
define estuary and describe its significance to the marine ecosystem
|
-protective nursery for the young of many crustaceans and fish |
|

|
eelgrass spreads with rhizomes |
|

|
Dungeness crab |
|

|
gunnel |
|

|
flatfish eye migrates during development |
|

|
sea gull |
|

|
great blue heron |
|

|
cormorant |
|

|
pigeon guillemot |
|

|
California sea lion male and female |
|
|
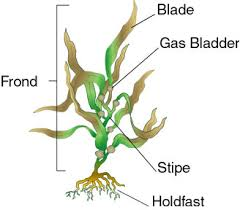
bull kelp (gas bladder=float) |
|

|
sea nettle toxic venom causes burns and blisters |
|

|
by-the-wind sailors venom harmless to humans |
|

|
moon jellies mild venom causes rash or itch |
|

|
sea otter |
|

|
killer whale |
|

|
gray whale |
|
|
|
|

