![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Undefined Terms |
Words, usually readily understood, that are not formally explained by means of more basic words and concepts. The basic undefined terms of geometry are point, line, and plane. |
|
|
point |
A location; has no shape or size. |
|
|
Line |
Made of points; no thickness/width |
|
|
plane |
flat surface |
|
|
collinear |
points on the same line |
|
|
coplanar |
points on the same plane |
|
|
intersection |
Objects cross at a common point, line, or plane. |
|
|
Space |
a boundless, three-dimensional set of all points |
|
|
Line Segment |
Part of a line with two endpoints. |
|
|
betweenness of points |
For any two points A and B on a line, there is another point C between A and B if and only if A, B, and C are collinear and AC + BC = AB. |
|
|
between |
For any two points A and B on a line, there is another point C between A and B if and only if A, B, and C are collinear and AC + BC = AB. |
|
|
congruent segments |
Line Segments are equal. |
|
|
ray |
part of a line; one endpoint. |
|
|
opposite rays |
Two rays with a common endpoint; forms a straight line. |
|
|
Angle |
created by two noncollinear rays with one common endpoint |
|
|
sides |
The rays of an angle |
|
|
vertex |
common endpoint of an angle |
|
|
interior |
a point is in the interior of an angle if it does not lie on the angle itself and it lies on a segment with endpoints that are on the sides of the angle. |
|
|
exterior |
a point is in the exterior of an angle if it is neither on the angle nor in the interior of the angle. |
|
|
degree |
A unit of measure used in measuring angles and arcs. |
|
|
right angle |
angle in which the measurement is 90 degrees. |
|
|
acute angle |
angle in which the measurement is less than 90 degrees. |
|
|
obtuse angle |
angle in which the measurement is greater than 90 degrees. |
|
|
angle bisector |
Ray that divides an angle into two equal halves. |
|
|
adjacent angles |
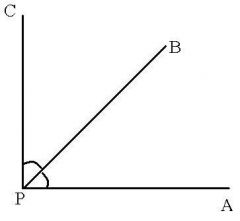
Two angles that lie in the same plane, have a common vertex and a common side, but no common interior points. |
|
|
linear pair |
2 angles that create a straight line |
|
|
vertical angles |
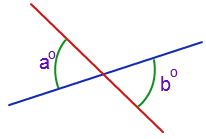
nonadjacent angles created by two intersecting lines; congruent. |
|
|
complementary angles |
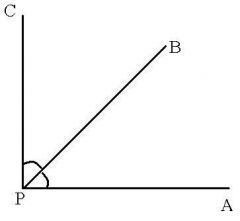
two angles with measures that have a sum of 90 degrees. |
|
|
supplementary angles |
two angles with measures that have a sum of 180 degrees. |
|
|
perpendicular lines |
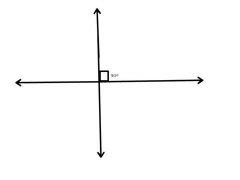
2 intersecting lines that make a 90 degree angle. |
|
|
inductive reasoning |
reasoning that requires a number of specific examples to arrive at a conclusion. |
|
|
conjecture |
educated guess |
|
|
counterexample |
example that makes the conjecture false |
|
|
deductive reasoning |
process of using logic to draw conclusions from given facts, definitions, rules, laws & properties. |
|
|
valid |
correct |
|
|
Law of Detachment |
(1)If H then C (2)If H is true (3)C must be true |
|
|
Law of Syllogism |
(1)If p->q and (2)q->r are true statements, then (3)p->r is a true statement. |

