![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Sensors |
Gather information about conditions inside and outside of the body. |
|
|
|
Control center |
Compares information with the set points at which the body functions best |
|
|
|
Targets |
Organs,tissues, or cells that changes its activity in response to a message |
|
|
|
Communication system |
Nervouse system and endocrine system carry messages throughout the body |
|
|
|
Skin |
Absorbs ultraviolet light from the sun and produces an inactive form of vitamin D |
Organ |
|
|
Liver |
Changes the inactive form to an intermediate compound |
Organ |
|
|
Kidneys |
Converts the intermediate compound into vitamin D |
Organ |
|
|
Vitamin D works with hormones to regulate levels of _______ and ________ required for healthy bones. |
Calcium,phosphorus |
|
|
|
Negative feedback |
Counteracts(acts against) a change in a way that helps bring the body back to normal. Ex: Breathing faster while running to keep oxygen moving into muscle cells. |
|
|
|
Positive feedback |
Increases change in a way that enables the body to accomplish a specific task.Ex: blood clotting to begin healing a wound |
|
|
|
Superior or cranial |
Towards the head; upper,top,above. |
|
|
|
Inferior or caudal |
Away from the head;lower,bottom,below. |
|
|
|
Anterior or ventral |
Front |
|
|
|
Posterior or dorsal |
Back |
|
|
|
Medial |
Towards the midline of the body;middle. |
Median > middle |
|
|
Lateral |
Away from the midline of the body;towards the side. |
|
|
|
Proximal |
Toward or nearest the trunk (chest and abdomen), or the point of origin of a part |
|
|
|
Distal |
Away from or farthest from the trunk or the point of origin of a part |
|
|
|
Frontal plane |

Vertical line running fron side to side;dividing the body into anterior (front ) and posterior (back) parts. |
Also known as the Coronal plane |
|
|
Lateral plane (sagittal plane) |

Vertical plane running front front to back;dividing the body into left and right sides |
|
|
|
Transverse plane (axial plane) |

Horizontal plane;divides the body or any parts into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) parts |
|
|
|
Thoracic cavity |
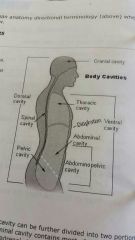
Contains the heart,lungs,trachea,esophagus,large blood vessels,and nerves. |
Chest cavity. Remember the 2 "c's" |
|
|
Abdominal and pelvic cavity |
Lower part of the ventral (abdominopelvic) cavity, that's divided into two portions: abdominal portion ans pelvic portion. |
|
|
|
Dorsal cavity |
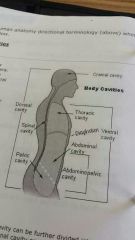
The smaller of the two main cavities. Contains organs lying more posterior in the body |
|
|
|
Homeostasis |
Involves keeping the internal environment within set range. |
Sweat cools the body.Goosebumps warm the body. |
|
|
Specialized cells in multicullular organisms arise from the zygotr |
. |
|
|
|
Two main body cavities |
Ventral (front;neck to waist),dorsal (back;skull to waist) |
|
|
|
Types if tissue |
Epithelial tissue,connective tissue,muscle tissue,nervous tissue |
|
|
|
Circulatory function |
Transports oxygen,nutrients,wastes;helps regulate body temperature;collects fluid lost from blood vessels and returns it to circulatory system |
|
|
|
Digestive function |
Breaks down and absorbs nutrients,salts,water,eliminates some water |
|
|
|
Endocrine function |
Influences growth,development,metabolism;helps maintain homeostasis |
|
|
|
Excretory |
Eliminates waste products;helps maintain homeostasis |
|
|
|
Immune function |
Protects against disease; stores and generates white blood cells |
|
|
|
Intergumentary function |
Acts as a barrier against infection,injury,UV radiation;helps regulate body temperature |
|
|
|
Muscular function |
Produces voluntary and involuntary movements;helps to circulate blood and move food through digestive system |
|
|
|
Nervous function |
Regulates body's response to changes in internal and external environment; processes information |
|
|
|
Reproductive function |
Produces reproductive cells; in females,provides environment for embryo |
|
|
|
Respiratory function |
Brings in O2 for cells;expels CO2 and water vapor |
|
|
|
Skeletal functions |
Supports and protects vital organs,allows movement, stores minerals;serves as the site for red blood cell production
|
|
|
|
Thermoregulation |
Process maintaining a steady body temperature under various conditions |
|

