![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
2 synapomorphies of Arthropods
|
1. One pair of jointed appendages per segment
2. Compound eyes |
|
|
Characteristics:
|
-Segmentation via teloblastic growth
-Strong heteronomy (TAGMOSIS) -Multilayered exoskeleton of alpha chitin -No functional cilia -Coelom reduced -Open circulatory system -Isolated bands of muscles -Growth via ecdysis -Ladder-like NS -Direct, indirect and mixed development |
|
|
Exoskeleton of chitin is a modified cuticle of _________.
|
alpha chitin
|
|
|
How does an animal encased in armor still breathe?
|
1. Evolve internal respiratory structures that bring O2 to internal tissues and organs
2. Evolve external respiratory structures that are still encased in cuticle, but cuticle is thin to limit diffusion distance 3. Miniaturization (tardigrades) very small, limits diffusion distance |
|
|
Onychophora retained _____-like body form, but gained _______________.
|
worm;
flexible exoskeleton |
|
|
Parapodia in Onychophora and Tardigrada are/are not homologous to those in Polychates?
|
are NOT
|
|
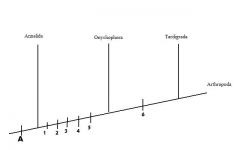
Define the missing characteristics
|
A - segmentation via teloblastic growth
1. exoskeleton of alpha chitin 2. Ecdysis 3. Reduced coelom 4. Loss of trochophore larva 5. Dorsal tubular heart 6. Three part cerebral ganglion |
|
|
Regarding the loss of the vermiform body, what are some of the changes that were required?
|
- exoskeleton limits worm movement (like a suit of armor)
- muscles have limited abiltiy to deform body - coelom is reduced; unable to change shape of body - cuticle covers body so cilia for locomotion can't work |
|
|
5 Subphylums of Arthropoda
|
1. Trilobitomorpha
2. Crustacea 3. Hexapoda 4. Myriapoda 5. Chelicerata |
|
|
Define tagmosis
|
Regional specialization of body parts
|
|
|
What does tagmosis in arthropods produce?
|
Extreme heteronomy and fusion of segments into specialized regions called tagmata
|
|
|
Hexapoda has _____ body segments. Name them.
|
3;
Head, thorax, abdomen |
|
|
Name the 5 fused segments that make up the head of a Hexapod.
|
antennae
labrum mandibles maxillae labium |
|
|
Chelicerata have ____ tagmata. Name them.
|
2;
Prosoma, Opisthosoma; joined by the pedicel |
|
|
What is the body part that joins the Prosoma and Opisthosoma of a Chelicerate?
|
Pedicel
|
|
|
Myriaopda have ____ tagmata. Name them.
|
2;
Head, Thorax |
|
|
The Myriapoda thorax has a variable number of segments, but all may be described as ____________.
|
homonomous
|
|
|
Because millipedes segments have fused to form ___________, it has ___ pairs of legs per segment as opposed to ___ in the centipede.
|
diplosegments; 2; 1
|
|
|
What are forcipules?
|
"Fangs" on a centipede (and only centipede)
|
|
|
Define maxillipeds
|
Thoracic appendages modified for food handling
|
|
|
Crustacea have ___ tagmata. Name them.
|
3;
Cephalon, Thorax, Abdomen |
|
|
What is the cephalothorax? In what subphylum is it found?
|
Fusion of the cephalon and thorax;
Crustacea |
|
|
What is different about Crustacean head appendages?
|
They have 2 pairs of antennae and maxillae as opposed to one.
|
|
|
Chelicerates have what head appendages?
|
pedipalps and chelicera
|
|
|
Swimmerets are also known as __________ and are found in the subphylum ____________.
|
pleopods;
Crustacea |
|
|
What is the primitive condition of arthropod appendages? What is the derived condition?
|
Biramous; Uniramous (one branch: lost exopod, retained endopod)
|
|
|
What part of an appendage exists in all arthropods?
|
Protopod
|
|
|
Where is an epipod found? Give an example of an epipod.
|
Epipods arise off of coxa (1st article of protopod); Gills
|
|
|
What are the 2 articles of a protopod?
|
Coxa, Basis
|
|
|
A Crustacean's pincer is also known as a ________ and consists of the static _________ and hinged _________.
|
chela;
propodus; dactyl |
|
|
Uniramous appendages are found mostly in what subphylum(s)?
|
Hexapoda, Myriapoda, Chelicerata (except horseshoe crabs)
|
|
|
What are the hard plates surrounding the body called?
|
tergites (dorsal), pleurites, and sternites (ventral)
|
|
|
In appendages, muscles exist in ____________________.
|
antagonistic pairs
|
|
|
What do extrinsic muscles do?
|
They are important for the initial movement and swinging of an appendage
|
|
|
What do intrinsic muscles do?
|
They move the leg internally (bending, etc.)
|
|
|
What is an articular membrane? What is made of?
|
the junction between articles of an appendage ;
it is made of resilin, which is rubbery and elastic |
|
|
The "biological hammer" is found in ______________.
|
Stomatopods
|
|
|
When a stomatopod such as a mantis shrip releases its hammer, it produces a __________.
|
cavitation bubble
|
|
|
What does the bubble produced by the biological hammer do?
|
Its shock wave cracks the shell of its prey
|
|
|
What part of the biological hammer stores energy? What kind of energy does it store?
|
saddle;
elastic |
|
|
What are 2 purposes of setae (hairs) on the epicuticle?
|
1. mechanoreception
2. chemoreception |
|
|
What are the layers of the arthropod cuticle?
|
epicuticle, exocuticle, endocuticle
|
|
|
What is the function of the epicuticle?
|
prevent loss of water from body; it was important for the invasion of land
|
|
|
What layer(s) adds structural rigidity to the body wall?
|
exocuticle; endocuticle
|
|
|
What part of the arthropods secretes the cuticle?
|
epidermis
|
|
|
What is different about the endocuticle in marine animals?
|
It contains CaCO3
|
|
|
What are functions of the exocuticle?
|
protective, sclerotization (tanning), and cross-linking of proteins
|
|
|
What is the hormone that signals release of enzymes to digest away old cuticle?
|
Ecdysone
|
|
|
What causes the 50-60% apparent growth during proecdysis?
|
sucking in (air in insects; water in crustaceans)
|
|
|
What are the 3 steps in postecdysis?
|
1. Cuticle becomes hardened (sclerotization)
2. Ca2+ salts are redeposited (in marine spp.) 3. Air/H2O pumped from body |
|
|
Regarding feeding strategies of Myriapoda, centipedes are ___________ while millipedes are _____________.
|
predatory;
scavengers |
|
|
Chelicerata are ______________ feeders.
|
predatory
|
|
|
What is the scorpion sensory organ?
|
Pectines - mechanoreceptors
|
|
|
What is the stinger of a scorpion called?
|
aculeus
|
|
|
How does the venom of a scorpion act?
|
Neurotoxin: Na2+, Ca2+, K+ shut down
|
|
|
What are chelicerae used for?
|
to pulverize prey
|
|
|
What is the only form of digestion known to spiders and scorpions?
|
extracorpeal (they cannot take in whole pieces of food; digest outside then suck in as soup)
|
|
|
Scorpions and tarantualas are examples of __________ predators.
|
hunter
|
|
|
Web spiders are examples of _____________ predators.
|
trapper
|
|
|
How to web spiders (trappers) detect their prey?
|
With their walking legs and pedipalps; sense movement on their web
|
|
|
Web spiders first use their ____________ to immobilize their prey, and then their ____________.
|
spinnerets;
neurotoxin delivered via fangs |
|
|
What is the main difference between a hunting spider and a trapping spider?
|
Method of detection
|
|
|
Arthropod circulatory systems have what characteristics?
|
-contains vessels
-dorsal ostiate heart |
|
|
Epipods in Crustaceans and pleopods in Horseshoe crabs are similar how?
|
they are external gills (but NOT homologous structures)
|
|
|
What are the primary organs of gas exchange in Myriapods, Hexapods and Chelicerates?
|
Trachea (although chelicerates also have book lungs)
|
|
|
What is unique about the arthropods circulatory system?
|
It plays no role in O2 exchange.
|
|
|
O2 enters chelicerates via ___________.
|
spiracles
|
|
|
What muscles cause the chelicerate heart's ostia to open, drawing oxygenated blood into the heart?
|
Alar muscles
|
|
|
When a chelicerate's pericardial muscles contract, what occurs?
|
Pericardial space expands drawing blood toward the heart from the book lung.
|
|
|
What characteristic is shared between tardigrades and onychophorans?
|
lobopods - unjointed walking legs that terminate in sharp claws
|
|
|
What is the defining characteristic of Tardigrada?
|
mouthparts that are protrusible stylets for piercing plants/animal tissues
|
|
|
Many tardigrades (water bears) live between sand grains, or ____________.
|
interstitially
|
|
|
What is cryptobiosis? What group of anmials exhibits this phenomenon?
|
ability to dehydrate and reduce metabolic rate to withstand extreme environmental conditions of low temp and desiccation stress;
tardigrades |
|
|
Onychophorans have specialized glands that secrete glue through the _______________.
|
oral papillae
|
|
|
Extant species of onychophorans are ______________.
|
terrestrial
|
|
|
What are pedipalps?
|
arms/pincer-like organs used to hold on to prey items; found in chelicerates
|
|
|
What are solpugids?
|
camel spiders (Iraq insect)
|

