![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The enzyme must stabilize the EX‡ transition state more than it stabilizes _______.
|
ES
(energy barrier between ES and EX‡ must be smaller than the barrier between S and X‡) |
|
|
Tighter S binding results in ________ ES energy, expanding the activation energy barrier & thus ____________ rxn rate
|
lowered ; lowering
|
|
|
Substrates typically lose waters of hydration (--generally, charged groups are more stable in hydrated form —ΔHsolv) in the formation of the ES complex.
___________ (of charged groups) raises the energy of the ES complex, making it more reactive. |
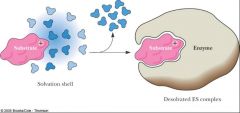
Desolvation
|
|
|
Charged groups may be forced to interact with similarly charged residues, resulting in _______________.
If such charge repulsion is relieved in the course of the reaction, (the first answer) can result in a rate ___________. |
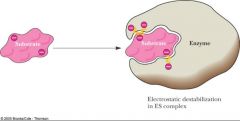
electrostatic destabilization; increase
|
|
|
You could use transition state analogs to _________________.
|
study transition states
|
|
|
TSA’s bind ________ strongly than S or other types of competitive inhibitors
|
more
|
|
|
Which is not an example of a transition state analog?
a. proline racemace b. Pyrrole-2-carboxylate c. Δ-1-pyrroline-2-carboxylate d. proline dehydroxinase e. Phosphoglycolohydroxamate f. hydrated from of purine ribonucleoside |
d.
|
|
|
Covalent (aka nucleophillic) catalysis:
Enzyme and substrate become linked in a __________ covalent bond at one or more points in the reaction pathway. Covalent bond formation provides the chemistry that speeds the reaction. |
transient
|
|
|
In _______________ catalysis, H+ or OH- concentration affects the reaction rate, kobs is pH-dependent, but buffers (which accept or donate H+/OH-) have no effect.
|
specific acid-base
|
|
|
In _____________ catalysis, an ionizable buffer may donate or accept a proton in the transition state, kobs is dependent on buffer concentration.
|
general acid - base
|
|
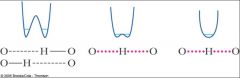
In low-barrier H bond catalysis, as the O-O distance _________, the hydrogen bond becomes stronger, and the bond order of the weakest interaction increases.
|
decreases
|
|
|
In Metal-ion catalysis, Ions such as ______and ______ may be either structural or catalytic (“loosely bound”)
|
Mg2+ , Zn2+
|
|
|
Metal ions participate in the catalytic process in three major ways. Which of the following is not true?:
1. By binding to substrates to orient them properly for reaction. 2. By mediating oxidation–reduction reactions through reversible changes in the metal ion's oxidation state. 3. By providing a covalent linkage site for stabilization 4. By electrostatically stabilizing or shielding negative charges. 5. All of these are true |
3.
|
|
|
Serine proteases are homologous, but locations of the three crucial residues differ somewhat. What are the 3 crucial residues?
|
Ser, His, Asp
|

