![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
120 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
You are using a 5 MHz, 40 mm linear array transducer to image a structure. What is the width of the image? |
b
|
|
|
You have selected a wide-bandwidth transducer with multiple transmit frequencies to perform a sonographic exam. Which transmit frequency should you select for maximum penetration?
a. 3 MHz b. 3.5 MHz c. 4 MHz d. 5 MHz e. Penetration is not affected by frequency |
a
|
|
|
Which probe would provide the best axial resolution to measure the thickness of a small structure?
a. 5 MHz linear array b. 7 MHz linear array c. 10 MHz linear array d. 5 MHz curved array e. 5 MHz phased array |
c
|
|
|
You are performing a sonographic exam with a wide-bandwidth transducer. The advantage you obtain with this transducer compared to narrow-band transducer is:
a. decreased acoustic power b. improved axial resolution c. improved lateral resolution d. improved focusing e. wide-bandwidth transducers can be autoclaved |
b
|
|
|
Which transducer would provide the longest near zone length?
a. 10 MHz, 6 mm diameter aperture b. 10 MHz, 5 mm diameter aperture c. 10 MHz, 4 mm diameter aperture d. 10 MHz, 3 mm diameter aperture e. 10 MHz, 2 mm diameter aperture |
a
|
|
|
The location where the sound beam reaches its narrowest diameter is known as the:
a. fraunhofer zone b. beam area c. fresnel zone d. curie point e. focal zone |
e
|
|
|
Which of the following transducers creates a rectangle image shape?
a. linear array b. phased array c. annular array d. curved array e. b and c only |
a
|
|
|
The term for a transducer that has an array of rectangular elements arranged in a straight line is:
a. annular array b. linear array c. curved array d. oscillating mechanical transducer e. convex sequenced array |
b
|
|
|
For a linear array transducer consisting of a single row of elements, what method is most used to focus the beam in the elevational direction?
a. transmit focusing b. dynamic receive focusing c. aperture focusing d. mechanical focusing e. none of the above |
d
|
|
|
What type of transducer could you choose to produce a beam that is symmetrical about the beam axis?
a. annular array b. linear sequenced array c. phased array d. curved array e. tightly curved array |
a
|
|
|
The ultrasound system in your lab has a transducer with a small footprint. This kind of transducer has the following disadvantages:
a. it cannot be focused in the elevation direction b. the field of view in the far field is only 1/4 the diameter of the transducer c. the near field lateral resolution is poor d. the Q value is very high e. resolution is degraded at large distanced |
e
|
|
|
Which of the following will not improve axial resolution?
a. increased damping b. increased transducer frequency c. increased bandwidth d. decreased pulse length e. increased focusing |
e
|
|
|
You are reviewing an ultrasound image that has a sector display format that narrows to a point at the transducer surface. What kind of transducer was most likely used to acquire this image?
a. linear array b. phased array c. curved array d. annular array e. mechanical sector |
b
|
|
|
Where is the point of maximum intensity in a sound beam?
a. curie point b. fresnel zone c. focal point d. fraunhofer zone e. F number |
c
|
|
|
What is the main advantage of using a 1 1/2D or multirow array transducer?
a. narrow slice thickness over large part of the scanned volume b. increased penetration c. improved axial resolution d. faster frame rates e. smaller footprint |
a
|
|
|
What benefit would you obtain by choosing a transducer having a large diameter compared to one having a small diameter?
a. it can focus at greater depths b. increases the frequency c. increased the beam diameter in the far field d. a and c e. all of the above |
a
|
|
|
You are using a linear array transducer with 4 transmit focal zones. How many pulses are required on each scan line to create an image?
a. 1 b. 2 c. 4 d. 6 e. 8 |
c
|
|
|
What type of transducer has the same measurement for elevational and lateral resolution?
a. convex linear array b. phased linear array c. annular array d. sequential linear array e. mechanical sector |
c
|
|
|
With a 1D linear array, where is the dimension of the sound beam in the out-of-plane dimension the narrowest?
a. it is at the point of mechanical focusing b. is is at the point of electronic focusing c. the beam is the same width throughout the image d. it is in the far field e. is is always located at a depth equal to 1/2 of the transducer aperature |
a
|
|
|
Another name for axial resolution is:
a. transverse resolution b. azimuthal resolution c. angular resolution d. range resolution e. a and c |
d
|
|
|
Dynamic apodization is a method employed to:
a.focus the beam at multiple depths on transmit b. focus the beam at multiple depths on receive c. reduce side lobes d. reduce beam width in the z axis e. steer the beam |
c
|
|
|
Which statement is most accurate regarding resolution with a standard one dimensional linear array transducer?
a. axial resolution is the worst measure of resolution with this type of transducer b. lateral resolution is the worst measure of resolution with this type of transducer c. elevational resolution is the worst measure of resolution with this type of transducer d. isotropic spatial resolution is achieved e. temporal resolution is the worst measure of resolution with this type of transducer |
c
|
|
|
During the course of a sonogrphic exam, you notice lateral splayings of the echoes in the far field. What can you do to improve the image?
a. use the max acoustic power b. use the lowest line density setting c. increase the number of transmit focal zones and optimize their location d. decrease the scanning depth e. increase the sector width |
c
|
|
|
You suspect that a bright spot on the b mode image is a calcification, but a posterior acoustic shadow is not present. How can you best optimize your system to demonstrate a shadow distal to the calcification?
a. move the focal zone well below the hyperechoic focus b. increase the transducer frequency c. increase the acoustic power output d. increase the dynamic range e. decrease the scan line density |
b
|
|
|
When an electric signal is applied to a piezoelectric element, what happens to the element?
a. it undergoes temperature fluctuations b. it expands and contracts c. it produced an electrical signal of the opposite polarity d. it emits electromagnetic radiation e. it loses its piezoelectric properties |
b
|
|
|
You are scanning a phantom containing multiple rows of identical 5 mm spherical fluid structures embedded in a tissue-mimmicking material. What type of resolution is best evaluated with this phantom?
a. axial b. lateral c. contrast d. elevational e. temporal |
d
|
|
|
What statement is not true regarding lateral resolution?
a. it is equal to beam width b. it is improved by focusing c. it is defined as the minimum seperation required to resolve two structures perpendicular to the beam axis d. it is also known as azimuthal resolution e. it remains constant throughout scanning depth |
e
|
|
|
Which type of transducer should you select to produce the narrowest slice thickness throughout the image plane?
a. a 1.5D multi-row array b. a phased array with a small footprint c. a tightly curved curvilinear array d. a mechanical sector e. a mechanically rocked 3D transducer |
a
|
|
|
The matching layer between the piezoelectric element and the tissue is designed to:
a. insulate the patient from the hot element b. reduce the vibration of the transducer c. reduce the acoustic impedance mismatch between the element and tissue d. increase the reflection coefficient at the transducer - skin interface e. decrease spatial pulse length |
c
|
|
|
If you choose a lower frequency transducer to image a highly attenuating structure, what tradeoff are you making?
a. decreased penetration for increased resolution b. decreases beam intensity for longer wavelengths c. decreased spatial resolution for improved penetration d. increased beam refraction for higher sound speed e. increased round trip travel time for improved resolution |
c
|
|
|
You have been asked to perform an ultrasound study of a structure located about 3 cm below the skin surface. Which transducer frequency range would be most appropriate for this study?
a. 2-5 MHz b. 4-8 MHz c. 8-10 MHz d. 10-12 MHz e. 5 MHz |
d
|
|
|
Dynamic receive focusing uses:
a. mechanical means to focus the beam b. time delays to excite array elements c. variable number of elements to form the transmitted beam d. time delays before echo signals from array elements are combined e. all of the above |
d
|
|
|
Varying the excitation voltage to each element in the group used to form the ultrasound pulse is called:
a. apodization b. dynamic aperature c. interelement isolation d. subdicing e. rectification |
a
|
|
|
Which of the following statements describes a phased array transducer?
a. electronically focused in two dimensions and mechanically steered b. electronically focused along the length of the array, mechanically focused along the elevational dimension, and electronically steered c. electronically focused along the elevational dimension of the array, mechanically focused along the length of the array, unsteered d. mechanically focused in two dimensions and mechanically steered e. electronically focused along the width of the array, mechanically focused along the length of the array, and mechanically steered |
b
|
|
|
Resolution of two structures at different depths along the path of the sound beam is termed:
a. contrast resolution b. temporal resolution c. axial resolution d. lateral resolution e. azimuthal resolution |
c
|
|
|
Which transducer has the same distance between the scan lines in both the near and far fields?
a. convex array b. phased array c. curvilinear array d. linear array e. mechanical sector |
d
|
|
|
Which of the following minimizes the degree to which beam width varies with depth?
a. apodization b. dynamic aperture c. coprocessing d. rectification e. frame averaging |
b
|
|
|
The sound beam can be focused by all of the following except:
a. acoustic mirror b. acoustic lens c. curved crystal d. matching layer e. electronic phasing |
d
|
|
|
What type of focusing decreases the frame rate?
a. mechanical focusing b. dynamic receive focusing c. dynamic aperture focusing d. multiple transmit focusing e. curved crystal focusing |
d
|
|
|
For a single transducer to offer multiple frequency selections for scanning, it must have:
a. large dynamic range b. wide bandwidth c. multiple rows of elements in the elevational plane d. dynamic aperture e. electronic steering capability |
b
|
|
|
The ability to distinguish between adjacent structures that produce echoes of similar amplitude is termed:
a. spatial resolution b. axial resolution c. lateral resolution d. temporal resolution e. contrast resolution |
b
|
|
|
When you increase the scan line density in the b mode image, you improve:
a. temporal resolution b. contrast resolution' c. slice thickness d. axial resolution e. lateral resolution |
e
|
|
|
The conversion of an incident pressure wave to an electrical signal is the:
a. curie effect b. piezoelectric effect c. doppler effect d. snell effect e. huygen's effect |
b
|
|
|
Electronic focusing in the transmit mode is accomplished using:
a. curved crystal elements b. changeable lens c. time delays to excite transducer elements d. high pulse repetition frequency e. receive time delays |
c
|
|
|
What is the purpose of subdicing?
a. to focus the beam upon transmit b. to reduce grating lobes c. to increase transmitted intensity d. to alter the transmitted frequency e. to focus the beam upon receive |
b
|
|
|
What transducer component is designed to control ringing of the piezoelectric element?
a. backing material b. electric insulator c. matching layer d. radiofrequency shield e. lens |
a
|
|
|
The transducer you are using is an array assembly. What is an advantage of this type of transducer?
a. transducer arrays produce pure, single frequency beams b. transducer arrays enable mechanical steering c. transducer arrays produce very long pulses for improved axial resolution d. transducer arrays have greater dynamic range, resulting in more displayed shades of grey e. transducer arrays enable electronic focusing and steering |
e
|
|
|
What is an advantage of single crystal or pure wave crystal transducers?
a. wide bandwidth b. lower frequencies at higher resolution c. absence of aliasing with pulsed doppler d. higher frame rates e. greater steering angles |
a
|
|
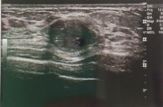
What type of transducer produced this image?
a. curved linear array b. linear array c. sector d. phased array e. tightly curved array |
b
|
|
|
When increasing the number of transmit focal zones to improve spatial resolution, the tradeoff is:
a. lateral resolution vs axial resolution b. lateral resolution vs temporal resolution c. spatial resolution vs contrast resolution d. contrast resolution vs frame rate e. elevational resolution vs frame rate |
b
|
|
|
Which of the following is not associated with a low Q transducer?
a. wide bandwidth b. multifrequency selection c. long pulse length d. diagnostic pulsed wave ultrasound e. loss of most energy in first few vibrations |
c
|
|
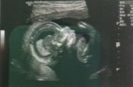
This image shows clear distinction between the gray scale of various structures in the fetal brain. The ability to distinguish similar structures with varying gray scale is termed:
a. axial resolution b. contrast resolution c. lateral resolution d. temporal resolution e. none of the above |
b
|
|
|
If the number of cycles in the transmitted pulse wave is increased:
a. axial resolution is degraded b. lateral resolution is degraded c. spatial pulse length becomes shorter d. rate of attenuation is increased e. penetration is decreased |
a
|
|
|
If the frame rate is too slow for adequate temporal resolution, what action could you take to improve frame rate?
a. reduce the number of transmit focal zones b. increase the scan line density c. increase the scanning depth d. decrease the dynamic range e. reduce the transmit frequency |
a
|
|
|
You have been requested to image a superficial mass and to adjust your equipment to optimize spatial resolution. Spatial resolution consists of:
a. contrast and temporal resolution b. temporal and axial resolution c. axial and contrast resolution d. contrast and lateral resolution e. lateral and axial resolution |
e
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the radiofrequency shield that is placed around the crystal and backing material of the ultrasound probe?
a. it helps to transmit radio waves into the body b. it aids transmission of the electric signal to the crystal c. it reduced the incoming electric signal strength from the body d. it reduced electromagnetic interference e. it improves axial resolution |
d
|
|

The image on the left demonstrates poor lateral resolution compared to the image on the right. How were the system controls adjusted to optimize the image on the right?
a. increases dynamic range b. decreased transducer frequency c. changed gray map d. increased line density e. reduced frame averaging |
d
|
|
|
What type of resolution is affected most by pulse duration?
a. lateral resolution b. contrast resolution c. temporal resolution d. axial resolution e. elevational resolution |
d
|
|
|
With a standard one dimensional linear array transducer, what type of resolution is affected most by electronic focusing and dynamic aperture?
a. lateral resolution b. contrast resolution c. temporal resolution d. axial resolution e. elevational resolution |
a
|
|
|
What type of resolution is most affected by the mechanical focus on a linear array transducer?
a. lateral resolution b. contrast resolution c. temporal resolution d. axial resolution e. elevational resolution |
e
|
|
|
The spectrum of frequencies emitted by a pulsed wave transducer is known as:
a. reynolds number b. center frequency c. f number d. resonance frequency e. bandwidth |
e
|
|
|
What is the optimal thickness for the matching layer?
a. equal to the thickness of the crystal b. 1/4 of a wavelength c. 1/2 of the pulse length d. twice the transducer diameter e. 1/2 the width of the backing material |
b
|
|
|
A method used to improve frame rates with multizone electronic focusing is termed:
a. apodization b. parallel processing c. f number focusing d. low q transducer e. none of the above |
b
|
|
|
Which of the following best describes the f number?
a. focal length divided by the aperture b. aperture multiplied by the number of elements in the transducer c. number of transducer elements divided by the fraunhofer zone d. beam width 1 cm from the transducer surface e. focal length multiplied by the number of elements in the transducer |
a
|
|
|
If you wish to use an array transducer that allows you to control transmit focal depth, what type would you select?
a. linear array b. convex array c. phased array d. annular array e. any of the above |
e
|
|
|
If you wish to perform a sonogram with the largest possible field of view in both the near field and at depth, what type of array transducer would be most preferable?
a. linear array b. curved array c. phased array d. sector e. any of the above |
b
|
|
|
A commonly used material in modern transducer elements is:
a. tungsten powder and epoxy resin b. quartz c. lead zirconate titanate d. rubber e. none of the above |
c
|
|
|
You are using a linear array transducer to evaluate the thyroid gland. For standard b mode imaging, this transducer most likely produced pulses of how many cycles?
a. 1-3 b. 3-6 c. 6-9 d. 9-12 e. 12-15 |
a
|
|
|
What is the purpose of applying multiple matching layers to the transducer face?
a. the gel gradually erodes the matching layer, and using multiple layers lengthens the life of the transducer assembly b. because the impedance of tissue is quite variable from one patient to the next, multiple matching layers improve the likelihood of providing a close impendance match to each patient c. each individual coating of the matching layer contributed to the damping of the sound pulse, which results in improved axial resolution d. multiple matching layers result in increased transducer bandwidth e. each coating of the matching layer provided focusing at a specific depth. With matching layers, multiple points of focus are possible |
d
|
|
|
For a nonfocused transducer, the region between the transducer element and the point at which the sound beam is narrowest is called the:
a. far field b. fraunhofer zone c. near focal length d. focal distance e. both a and b |
c
|
|
|
Axial resolution is chiefly determined by:
a. beam width b. transducer diameter c. pulse duration d. line density e. frame rate |
c
|
|
|
What is the main advantage of using an intracavitary probe compared to a standard transducer?
a. the intracavitary probe has superior focusing capabilities because of the increased radius of the curved probe face b. the intracavitary probe used a lower frequency that provides superior penetration and closer inspection of the pelvic structures c. the intracavitary probe does not demonstrate side lobes or grating lobes because of the close spacing and curvature of the elements d. since the intracavitary probe is closer to the area of interest, a higher frequency transducer can be used, resulting in superior spatial resolution e. bioeffects are greatly reduced with the intracavitary probe because of its frequency range and power output |
d
|
|
|
What defines the best axial resolution that can be obtained with a given transducer?
a. spatial pulse length x 2 b. spatial pulse length x 4 c. spatial pulse length / 2 d. spatial pulse length / 4 e. equal to the spatial pulse length |
c
|
|
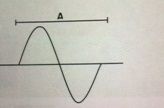
The following illustration depicts acoustic pressure vs distance in a medium in which a sound wave is present. What sound parameter is measured by the length of the bar labeled A in the following illustration?
a. amplitude b. wavelength c. pressure d. pulse repetition frequency e. duty factor |
b
|
|
|
What term describes the ability of an imaging device to separate closely spaced objects?
a. resolution b. penetration c. duty factor d. interference e. refelction |
a
|
|
|
What happens when pressure is applied to a piezoelectric crystal?
a. it emits an electric signal b. it increases temperature c. it emits radio waves d. it emits photons e. it becomes phosphorescent |
a
|
|
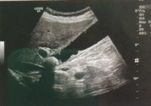
What type of transducer was used to obtain this image?
a. linear array b. sector c. phased array d. micro convex e. curved array |
e
|
|
|
The interpreting physician has asked you to use a stand off pad to elevate a superficial mass. What is the main advantage the stand off pad provides to improve the image?
a. the stand off pad has an acoustic impedance closer to that of the crystal which results in improved transmission of sound into the body b. the stand off pad has a propagation speed equal to twice that of soft tissue which decreases the wavelength of the sound beam c. the stand off pad increases the distance between the transducer and the mass, making it more likely that the mass will be located close to the elevational focus of the sound beam d. the stand off pad creates a soft interface between the crystal and the tissue, increasing constructive interface and reducing scattering e. the stand off pad eliminates artifacts associated with reverberation, side lobes, and grating lobes |
c
|
|
|
What array transducer fires all of the elements for each acoustic scan line, using small time delays to steer the beam?
a. linear segmental array b. convex array c. annular array d. linear sequential array e. phased array |
e
|
|
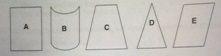
The shape corresponding to the image created by a phased array transducer most closely corresponds to which of the following:
a. b. c. d. e. |
d
|
|
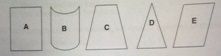
A linear array will produce which of the following image shapes?
a. a or b b. b or c c. c or d d. d or e e. a, c or e |
e
|
|
|
If you are using a transducer with poor elevation resolution, which of the following problems are you most likely to encounter?
a. inability to resolve two structures that lie close together and parallel to the path of the beam b. inability to resolve two structures that lie close together, perpendicular to the path of the beam, and parallel to the long axis of the transducer c. inability to penetrate through dense tissue d. inability to clearly demonstrate small cystic structures e. inability to demonstrate rapidly moving structures accurately |
d
|
|
|
What can you do to achieve a higher frame rate?
a. decrease the number of focal zones b. decrease the line density c. decrease the sector width d. all of the above e. none of the above |
d
|
|
|
What can you do to improve contrast resolution in the ultrasound image?
a. increase the sector width b. decrease the number of focal zones c. use a 1.5D or multi-row array transducer d. use a phased array transducer e. use a curved array transducer |
c
|
|
|
Increasing which of the following will result in improved axial resolution?
a. pulse duration b. pulse length c. frequency d. period e. focusing |
c
|
|
|
Which represents the best measure of resolution for modern day ultrasound scanners?
a. contrast b. axial c. elevational d. temporal e. lateral |
b
|
|
|
Which of the following transducers produces side lobes?
a. mechanical sector b. linear sequential array c. phased array d. convex array e. all of the above |
e
|
|
|
Which transducer type is best suited to vascular imaging?
a. mechanical sector b. linear array c. phased array d. convex array e. annular array |
b
|
|
|
Which of the following transducer types is best suited to cardiac imaging?
a. mechanical sector b. linear array c. phased array d. convex array e. annular array |
c
|
|
|
Which of the following can not be elevated with a tissue equivalent phantom?
a. axial resolution b. lateral resolution c. contrast resolution d. slice thickness e. temporal resolution |
e
|
|
|
Increasing the frequency on a multifrequency from 3.5 MHz to 5 MHz will:
a. increase the sound propagation speed b. increase the pulse length c. increase penetration d. decrease the prf e. decrease the wavelength |
e
|
|
|
You notice a loss of detail in the lateral dimension of the ultrasound image. What can you do to improve this?
a. decrease the number of focal zones b. increase the scan line density c. decrease the transducer frequency d. increase the frame averaging e. increase the dynamic range |
b
|
|
|
You are performing a sonogram on a patient with highly attenuating tissue. Which of the following solutions would be most likely to improve penetration through the tissue?
a. decrease dynamic range b. decrease near field tgc c. choose a lower frequency transducer d. increase the scan line density e. change the gray scale map |
c
|
|
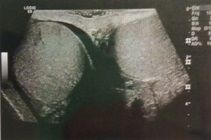
This image was obtained with a linear array transducer. The trapezoidal field of view increases the field of view. How is the trapezoidal shape created?
a. electronic beam steering b. side lobes c. grating lobes d. mechanically steering elements e. mirror |
a
|
|
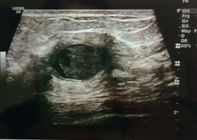
In the image below, how many transmit focal zones are being used?
a. the number of transmit focal zones is not indicated b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 e. 4 |
d
|
|
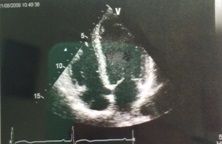
What type of probe was used to take this image?
a. curved array b. phased array c. linear array d. mechanical sector e. tightly curved array |
b
|
|
|
What best describes the method used to create the triangular shaped image format in the image above?
a. mechanical steering b. electronic steering with elements fired in small groups c. electronic steering with most elements fired for each pulse echo sequence. Small time differences steer the beam d. curved lens e. mirror |
c
|
|
|
You can reduce beam width to improve spatial resolution in the image by which of the following:
a. focusing b. decreasing aperture c. decreasing transducer diameter d. decreasing transducer width e. increasing backing material |
a
|
|
|
Which transducer frequency would have the thinnest crystal?
a. 15 MHz center frequency b. 10 MHz center frequency c. 7 MHz center frequency d. 5 MHz center frequency e. all would have the same crystal thickness |
a
|
|
|
What component of a pulsed wave transducer helps to reduce the spatial pulse length and improve axial resolution?
a. matching layer b. lens c. element d. backing material e. radiofrequency shield |
d
|
|
|
Which transducer would have a lower line density in the far field compared to the near field?
a. linear array b. curved array c. tightly curved array d. phased array e. b,c, and d |
e
|
|
|
What transducer component reduced reflection at the transducer/skin interface?
a. matching layer b. lens c. element d. backing material e. radiofrequency shield |
a
|
|
|
Axial resolution is improved with:
a. increased bandwidth b. shorter pulse length c. shorter wavelength d. b and c e. all of the above |
e
|
|
|
What is a side lobe?
a. uneven transducer element b. accessory pulse used for electronic steering c. sound beam emitted from the transducer that travels in a different direction from the main beam d. nonlinear propagation of the sound beam e. additional backing material on the transducer edge used to reduce lateral vibrations |
c
|
|
|
What is the purpose of curving the transducer elements or applying a lens over the elements?
a. to provide focusing in the out of plane (elevational) direction b. to reduce the acoustic impedance mismatch between the crystal and skin c. to reduce crystal ringing and improve axial resolution d. to help reduce electronic interference e. all of the above |
a
|
|
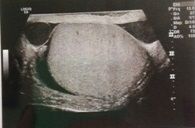
What advantage is obtained by steering a linear array transducer to create a trapezoidal shape to the display as demonstrated in this image?
a. improved lateral resolution b. improved axial resolution c. improved contrast resolution d. improved elevational resolution e. improved field of view |
e
|
|
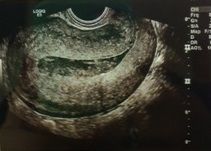
What type of transducer was used to create this image of the uterus?
a. linear array b. phased array c. single elemtn mechanical d. tightly curved array e. sector |
d
|
|
|
What disadvantage is related to the transducer type in the previous question?
a. axial resolution degrades with depth b. lateral resolution degrades with depth c. field of view is compromised compared to other transducer types d. temporal resolution is compromised compared to other transducer types e. elevation resolution is compromised compared to other transducer types |
b
|
|
|
What advantage is related to tightly curved array?
a. axial resolution is improved b. lateral resolution is improved c. field of view is improved d. temporal resolution is improved e. elevational resolution is improved |
c
|
|
|
What best describes the difference between the ultrasound frequencies used for doppler and for b mode imaging with a given transducer?
a. the frequency for doppler is usually lower than for imaging b. the frequency for doppler is usually higher than for imaging c. the transmit pulse for doppler has a greater bandwidth compared to the bandwidth for imaging d. the frequency for doppler and for b mode imaing must be identical for a given transducer e. the frequency for doppler is usually double that for b mode imaging |
a
|
|
|
In order to focus a sound beam relatively far away from the transducer, it is advantageous to:
a. increase the thickness of the element b. increase the diameter of the element c. decrease the width of the element d. decrease the frequency of the element e. increase the curvature of the element |
b
|
|
|
Which factor least influences axial resolution?
a. damping b. beam width c. frequency d. pulse duration e. pulse frequency |
b
|
|
|
Spatial pulse length is equal to:
a. the wavelength times the number of cycles in the pulse b. the wavelength minus the number of cycles in the pulse c. the wavelength times the axial resolution d. the wavelength times the beam width e. the wavelength divided by two |
a
|
|
|
What is the disadvantage of using multiple transmit focal zones?
a. decreased lateral resolution b. decreased temporal resolution c. decreased elevational resolution d. decreased axial resolution e. all of the above |
b
|
|
|
What is the advantage of using multiple transmit focal zones?
a. increased lateral resolution b. increased temporal resolution c. increased elevational resolution d. increased axial resolution e. all of the above |
a
|
|
|
What factor least influences lateral resolution?
a. frequency b. focus depth c. beam width d. transducer diameter e. damping |
e
|
|
|
Which transducer will exhibit the least amount of volume averaging?
a. mechanical single element b. 1.5D or multi-row array c. linear array d. phased array e. convex array |
b
|
|
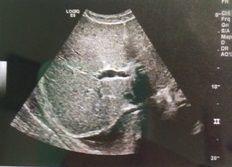
The ability to differentiate between two regions having similar echogenicity, such as in this liver image with focal fat, is termed:
a. temporal resolution b. contrast resolution c. axial resolution d. lateral resolution e. elevational resolution |
b
|
|
|
Imaging frame rate decreases when you:
a. decrease frequency b. increase dynamic range c. increase frame averaging d. increase sector width e. decrease the number of transmit focal zones |
d
|
|
|
The optimal transducer technology for cardiac scanning is:
a. curved array b. tightly curved array c. linear array d. phased array e. mechanical sector |
d
|

