![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the ddx of mediastinal widening
|
hemorrhage
tumor pus fluid fat |
|
|
What are the CXR numbers for mediastinal widening
|
>8cm or 25% of thorax
|
|
|
What is the CXR measurment for widening of right paratracheal stripe
|
>4mm
|
|
|
What are the CXR signs of traumatic aortic injury
|
mediastinal widening
generalized widening abnormal aorta mass effect froma a hematoma apical cap left hemothorax |
|
|
What are the top 3 cause of hemorrhage in the mediastinum following trauma
|
venous bleeds
fx aortic injury |
|
|
Where are the typical locations of TAI
|
isthmus (90%)
Ascending aorta (5-10%) descending aorta at the diaphrgam |
|
|
Where does ascending aorta TAI commonly occur
|
at the ductus (site of attachement)
|
|
|
Is a focal saccular outpouching with a narrow neck a typical sign of a pseudoaneurysm
|
yes
|
|
|
What are the direct signs of TAI
|
pseudoaneurysm
intimal flap wall irregularity |
|
|
What are the indirect signs of TAI
|
hematoma
|
|
|
What is the MC direct sign of TAI
|
pseuoaneurysm
|
|
|
What if the hemorrhage does not touch the aorta and there is a fat plane between hemorrhage and the aorta what is the MC etiology
|
venous bleeding
|
|
|
What is the next step if you see hemorrhage that touches the aorta and there is no fat plane and no direct sign
|
angiography
|
|
|
If the ascending aorta dilates what part of the mediastium does it overlie on CXR
|
the right hilum
|
|
|
What should you suspect if you see isolated dilation of the ascending aorta
|
aortic stenosis
|
|
|
What is the size of a normal thoracic aorta
|
less than 4cm
|
|
|
What is the size of a dilated or ectatic aorta
|
4-5cm
|
|
|
What is the size of a aneurysmal aorta
|
>5cm
|
|
|
What size aorta will require surgery
|
>6cm (marfans less)
|
|
|
Besides aortic stenosis what is a common cause of ascending aortic aneurysm
|
HTN
|
|
|
What is the ddx of aortic aneurysms (true)
7 |
degenerative
post stenotic htn atherosclerosis connective tissue mycotic syphillis dissections (not true) |
|
|
What is a pseudoaneurysm
|
saccular outpouching of the aorta
|
|
|
What are common causes of aortic pseuodaneurysms
(top 4) |
traumatic
iatrogenic mycotic penetrating ulcer |
|
|
Name 4 acute aortic syndromes
|
dissection
intramural hematoma ulcerative plaque penetrating ulcer |
|
|
Where does blood dissect during a dissection
|
the media
|
|
|
Is a dissection ever focal
|
no, it will spread proximal or distal or both
|
|
|
What are some causes of dissection
|
htn
Connective tissue penetrating ulcer |
|
|
What is the most worrisome feature of aortic dissection
|
end organ ischemia
|
|
|
What is the difference between an intramural hematoma and dissection
|
blood in the wall WITHOUT A FLAP (there is no connection seen between the true lumen and the blood in the wall)
|
|
|
Do some people say that a dissection and hematoma r a spectrum of the same disease
|
yes
|
|
|
What may cause the blood to accumulate in an intramural hematoma
|
vasovasorum (not blood from the lumen)
|
|
|
What are the causes of an intramural hematoma
|
HTN, CTD, penetrating ulcer
|
|
|
What is an intramural hematoma according to stat dx
|
No intimal flap, spontaneous medial hematoma secondary to rupture of the vasa vasorum into the media
Hemorrhage due to rupture of vasa vasorum within aortic media, resulting in noncommunicating dissection, with typical absence of intimal tear |
|
|
What is a dissection according to stat dx
|
Spontaneous intimal tear with propagation of subintimal hematoma
|
|
|
Can an intramural hematoma leads to an aortic dissection
|
yes
|
|
|
Is an ulcerative plaque associated with future stroke
|
yes
|
|
|
Does an ulcerative plaque always cause problems
|
no
|
|
|
What are the potential problems caused by an ulcerative plaque
|
embolization (ie brain)
transform to penetrating ulcer |
|
|
What is the definition of a pseudoaneurysm
|
njury to all 3 layers of arterial wall, resulting in contained rupture with perfused sac that communicates with artery
|
|
|
What is a penetrating ucler
|
this is an ulcerative plaque that is so deep it is in the wall of the aorta itself (media or deeper)
|
|
|
Where are the classic locations of a penetrating ulcer
|
the arch or the descending aorta
|
|
|
What are 4 complications of a penetrating ulcer
|
dissection
pseudoaneurysm intramural hematoma rupture |
|
|
Can an intramural hematoma convert to a dissection
|
yes
|
|
|
What does a pseudoaneursm look like
|
a narrow neck, does not contain all walls, connections with true lumen
|
|
|
What is the ddx of a posterior impression of the esophagus
|
abberant right sublavian
abberant left sublavian (right aortic arch) double aortic arch |
|
|
Describe the findings of an abberant right sublavian
|
last vessel off the arch
posterior to the esophagus diverticulum of kommerell |
|
|
Can both abberant left and right have an diverticulum of kommerell
|
yes (dilation at origin of abberant vessel)
|
|
|
What is the complication associated with a diverticulum of kommerell
|
dysphagia
|
|
|
What arch is classicaly larger in an double aortic arch
|
the right
|
|
|
Can one of the arches of a double aortic arch be hypoplastic
|
yes
|
|
|
What side does a double aortic arch descend
|
the left side
|
|
|
What is the MC type of aortic coarctation
|
Juxtaductal (postductal)
|
|
|
Is the juxtaductal type of coarctation focal
|
yes
|
|
|
What demographic typically gets the juxtaductal type of coarctation
|
adults
|
|
|
What clinical sign maybe found in an adult with juxtaductal coarctation
|
different blood pressure in both arms
|
|
|
What type of coarctation do infants get
|
tubular (preductal)
|
|
|
What is more severe the preductal (tubular) or juxtaductal (postductal)
|
preductal (tubular)
|
|
|
Why is preductal coarctation more severe
|
it involves a more diffuse portion of the aorta
|
|
|
What is a common presentation of a child with tubular coarctation
|
CHF
|
|
|
What are the CXR findings of coarctation
3 |
aortic dilation
inverted 3 sign (juxtaductal) rib notching |
|
|
What are the collaterals that may occur as a result of coarctatioin
|
internal mammary
intercostal arteries |
|
|
Where is the focal constriction seen on MRI in juxtaductal coarctation
|
distal to the ductus
|
|
|
What causes rib knotching
|
dilated intercostal arteries
|
|
|
How do you quantitate the flow in a patient with coarctation
|
velocity encoded cine just distal to the coarctation and at the diaphragm (should decrease in a normal person)
|
|
|
What may cause stenosis of the great vessels of the chest
|
takayasu arteritis
giant cell arteritis radiation williams syndrome (rare) neurofibromatosis (rare) |
|
|
Where is the classic location that giant cell arteritis will affect
|
coronaries
|
|
|
What is called when you see an entire coronary vessels within 1 image
|
curved multiplanar reformat
|
|
|
What are 4 indications for CTA
|
coronary artery disease
grafts stents anomalous coronary arteries |
|
|
What are the indications of CTA of the coronary arteries
|
intermediate suspicion in a young person
discrepant pre-test probability and symptoms in older patient |
|
|
Why do we do CTA of a graft
|
to look for stenosis
|
|
|
What is considered a significant lesion on coronary CTA
|
50%
|
|
|
What do you recommend if the lesion is greater than 50%
|
cardiac cath
|
|
|
How do you judge stenosis on a CTA coronary
|
minimal luminal diameter compared to pre or post
|
|
|
What is a major pitfall of coronary CTA
|
blooming artifact from calcification (looks bigger than it is)
|
|
|
What are 3 potential courses of the RCA if it arises from the aorta
|
infront of the RVOT
behind the aorta INBETWEEN THE RVOT AND AORTA (MOST DANGEROUS) |
|
|
What are the potential complication of the RCA going inbetween the aorta and RVOT
(malignant course) |
arrythmia and
sudden death |
|
|
What if the origin of the LCA arises from the right side and goes posterior to the aorta
|
it is not clinically significant
|
|
|
Why is the myocardium black in a delayed enhancement image
|
because it is an inversion recovery sequence and the myocardium is nulled by selecting the appropiate time to inversion (I think)
|
|
|
short axis
|
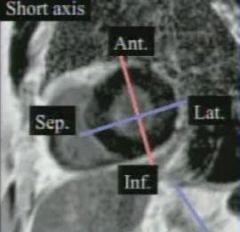
|
|
|
vertical long axis
|
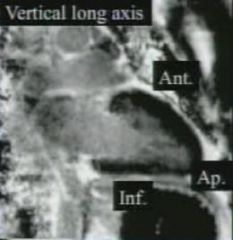
|
|
|
horizontal long axis
|
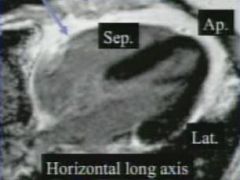
|
|
|
What is the ischemic pattern of enhancment
|
subendocardial and may extend to transmural (vascular distribution)
|
|
|
What is the non-ischemic pattern of enhancment
|
intramyocardial and subepicardial
|
|
|
What is the role of MR viability
|
to determine if a vessel leading do an infarcted area will the myocardium regain function
|
|
|
What is the measurement used to determine if it is worth opening up a vessel
|
if there is residual myocardium (non-enhancing) greater than 5.5mm then open the vessel up OR ratio of viable myocardium to total wall thickness >50% (in a vascular distribution)
|
|
|
What direction is the measurement made for determining if you will open up a vessel
|
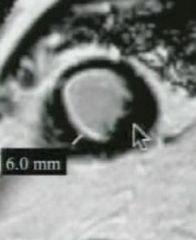
|
|
|
What do you look for in hibernating myocardium
|
wall thinning
motility dysfunction NO residual enhancment |
|
|
Will a patient regain function from opening a vessel with hibernating myocardium
|
yes
|

