![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the approach to aquired heart disease on a plain film
|
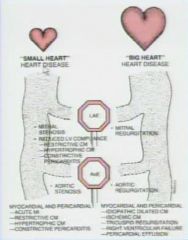
|
|
|
What is the first thing to do decide in aquired heart disease
|
if the heart is big or normal
|
|
|
What are the 2 sign post of aquired heart disease
|
left atrial enlargement
enlarged aortic arch |
|
|
If a pt has a small/normal heart and has left atrial enlargement what is the differential
|
mitral stenosis
reduced LV compliance |
|
|
What are 3 causes of left ventricular compliance
|
restrictive CM
hypertrophic CM constrictive pericarditis |
|
|
If a pt has restrictive CM, hypetrophic CM, or constrictive pericarditis they have a normal/small heart with LAE
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the patient has a small/normal heart and has a large aorta
|
aortic stenosis
|
|
|
What is the ddx for a normal sized heart with disease
|
Acute MI
restrictive CM hypertrophic CM contrstrictive CM |
|
|
Can restrictive CM, hypertrophic CM and Constrictive pericarditis have either a enlarged left atrium or normal
|
yes
|
|
|
What are 2 classic plain film findings of mitral stenosis
|
LAE
enlarged PA |
|
|
What do you expect to see in a pt with aortic stenosis
|
enlarged aorta and normal sized heart
|
|
|
What is the MC cause of acute pulmonary edema with normal heart size
|
acute MI
|
|
|
What are the two sign post for big heart disease
|
LAE
Aortic regurtitation |
|
|
What is the only cause of LAE in a big heart disease
|
mitral regurgitation
|
|
|
What is the only cause of AoE in a big heart disease
|
aortic regurgitation
|
|
|
What should you suspect if there is big heart disease without LAE or AoE
|
idiopathic dilated CM
Ischemic CM tricuspid regurgitation RV failure Pericardial effusion |
|
|
What do you suspect if there is left atrial enlargement in a big heart
|
mitral regurgitation
|
|
|
What do you suspect if there is AoE in a big heart
|
aortic regurgitation
|
|
|
What is the differential of a markedly enlarged heart
|
tricuspid regurgitation (wall to wall heart)
large pericardial effusion |
|
|
Why is differentiation of restrictive and constrictive pericarditis important
|
difference in managment (pericarditis you just take the pericardium off)
|
|
|
Where do you typically see pericardial calcifications in constrictive pericarditis
|
pericardial grooves
|
|
|
What are the 4 MC causes of constrictive pericarditis
|
cardiac surgery
radiation therapy viral TB |
|
|
What are 5 diagnostic features of constrictive pericarditis
|
pericardial thickness greater than 4mm
septal bounce RA enlargement No RV enlargement Dilated IVC |
|
|
What is septal bounce
|
this is bounce of the septum towards the left ventricle upon opening of the tricuspid valve
|
|
|
What are the 2 most common causes of constrictive pericarditis
|
surgery
radiation |
|
|
How do you determine constrictive Vs restrictive cardiac physiology
|
cardiac catheterization
|
|
|
Which way does the septum bounce in restrictive/constrictive heart diseasee
|
towards the left ventricle
|
|
|
What is the appearance of an acute hematoma on MRI
|
bright
|
|
|
What is the appearance of a subacute hematoma
|
heterogeneous
|
|
|
What is the appearance of a chronic hematoma on MRI T1
(fix last two its for T1) |
Homogenous intermediate
|
|
|
What is the characteristic area you may see a pericardial cyst
|
right cardiophrenic angle
|
|
|
What does a pericardial cyst look like
|
homogenous low density lesion on T1 and bright on T2 (no enhancement)
|
|
|
What are two patterns of delayed enhancement of ischemic heart disease
|
subendocardial
transmural |
|
|
What are the 2 patterns of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy
|
sub-epicardial
mid wall |
|
|
What pattern of delayed enhancement would be expected in a patient with myocarditis
|
midwall
|
|
|
What would you expect to see 2 months later in a patient who had myocarditis
|
resolution of delayed enhancement
|
|
|
How do you differentiate between ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy and non ischemic dilated CM
|
look for delayed patterns of enhancement
|
|
|
What are some causes of non-ischemic dilated CM
6 |
HTN
alcohol toxins obesity DM idopathic |
|
|
What is the MCC of dilated CM
|
ischemic
|
|
|
What are the findings of Non-ischemic dilated CM
|
LV enlargement
decreased systolic function normal wall thickness delayed enhancement (Not always but if they do it will most likely be a non-ischemic pattern but it can be ischemic) |
|
|
What are the patterns of delayed enhancemet for non-ischemic dilated CM
|
59% None
28% midwall 13% ischemic pattern |
|
|
When do you make diagnosis of HOCM
|
hypertrophy with no cause for it
|
|
|
What percent of HOCM have asymmetric septal hypertrophy
|
90%
|
|
|
Why is MR better than echo for looking at the potential HOCM pts
|
because you can measure complete LV mass
|
|
|
What ratio is diagnostic of asymmetric HOCM
|
septal/lateral: >1.5
|
|
|
Do you see delay enhancement in HOCM
|
yes (80% of cases) in the diseased portions
|
|
|
What do you see in HOCM
|
the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve will not close during systole and therefore you will never see those valves close together
|
|
|
What type of dysfunction occurs in restrictive CM; diastolic or systolic
|
diastolic
|
|
|
can pt with restrictive CM have systolic dysfunction too
|
yes
|
|
|
What chambers tend to be enlarged restrictive CM
|
RA and LA
|
|
|
Are the ventricles small in restrictive CM
|
yes with wall thickening
|
|
|
What are the findings of restrictive CM
|
RA and LAE
small ventricles wall thickening |
|
|
What type of CM is caused by amyloid
|
restrictive CM
|
|
|
What should you suspect if there is global subendocardial delayed enhancement
|
amyloid (will not respect coronary artery territories)
|
|
|
What percent of cases of amyloid will have global delayed hyperenhancement
|
70%
|
|
|
Are both amyloid and sarcoid types of restrictive CM
|
yes
|
|
|
What percent of pts with pulmonary sarcoid will have cardiac sarcoid
|
11%
|
|
|
Where is hyperenchancement typical seen in sarcoid
|
anterolateral and anteroseptal regions
|
|
|
What pattern of delayed enhancement is seen in sarcoid
|
midwall
|
|
|
What does ARVD stand for
|
arrhythomgenic right ventricular dysplasia
|
|
|
What ventricle is effected by ARVD
|
the right ventricle
|
|
|
What is the clinical SS of ARVD
|
syncope/sudden death during exercise
|
|
|
What do you see on EKG as a result of ARVD
|
recurrent VT or PVCs with a RV origin
|
|
|
What is the pathophysiology of ARVD
|
fatty or fibrous degeneration of RV
|
|
|
What are the MR finding of ARVD
5 |
increased signal on T1
wall thinning aneurysm RV enlargement Regional or global contraction abnormalities |
|
|
What is the T1 MR characteristic of ARVD
|
bright (fatty)
|
|
|
What is the role of MRI for cardiac mass evaluations
|
extent and location
tumor Vs thrombus primary Vs secondary benign Vs malignant |
|
|
What are 4 descriptive terms for location of the tumor with regards to the heart
|
intracavitary
itnramural pericardial paracardial |
|
|
What is the MC cardiac mass
|
thrombus
|
|
|
What is the appearance of a thrombus on Cine MR
|
dark
|
|
|
Does a thrombus enhance
|
no
|
|
|
What are 2 characteristics of a thrombus in the heart
|
dark on cine
no enhancment |
|
|
What is the appearance of tumor on cine
|
intermediate
|
|
|
Does a tumor enhance
|
yes
|
|
|
what are two characterictis of a tumor on MR
|
intermediate on MR
contrast enhancement |
|
|
What is the only exception of a intermediate tumor on MR
|
myxoma
|
|
|
Does a myxoma have a stalk
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the appearance of a mxyoma on cine
|
brighter than muscle
|
|
|
T or F; secondary tumors are 40 x more frequent than primary tumors of the heart
|
true
|
|
|
What are the 3 MC secondary tumors of the heart
|
breast
lymphoma melanoma |
|
|
What are the 2 most common primary benign tumors of the heart
|
myxoma
lipoma |
|
|
What is a common primary malignant tumor of the heart
|
angiosarcoma
|
|
|
What are malignant tumor characteristics of the heart
6 |
wide point of attachment
necrosis or cavitation involvment of > 1 chamber pericardial effusion pulmon mets extension beyond the heart |
|
|
Is angiosarcoma a primary malignancy of the heart
|
yes
|
|
|
Is a wide point of attachement to the heart a sign of a malignant tumor
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the primary technique for evaluation of valvular disease
|
echo
|
|
|
What are the qualitative ways to evaluate the heart
|
Cardiac CT and Cine MRI
|
|
|
What is the best way to quantitatively evaluate the heart
|
cine MRI (velocity encoded)
Note Cine MRI is good for qualtitative also |
|
|
What is quantitative cine MR used to evaluate
|
the amount of regurgitation
|
|
|
What is the mercedes benz sign associated with
|
inabiltiy of the aortic leaflets to open....aortic stenosis
|
|
|
If there is alot of calcifications does it significantly limit echocardiography
|
yes
|
|
|
What is a fish mouth aortic valve characteristic of
|
a bicuspid aortic valve
|
|
|
Can you estimate the pressure gradient across a stenosis with velocity encoded cine
|
yes (by the bernoulli equation and the peak velocity)
|
|
|
What annular aortic ectasia (widening of the sinus of valsalva) associtated with
|
aortic regurgitation
|
|
|
What do you expect to see in the flow curve in aortic regurgitation on a flow diagram
|
postive flow during systole
negative flow during diastole |

