![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the infrahyoid neck spaces
|
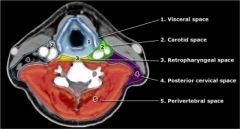
|
|
|
What are the 8 suprahyoid neck spaces
|
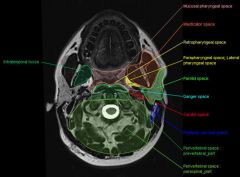
pharngeal space
masticator space carotid space parapharyngeal space parotid space retropharyngeal space perivetebral space deep (posterior) cervical space |
|
|
What muscles form the pharynx
|
the constrictor muscles
|
|
|
What percent of tumors of the head and neck are Squamous cell carcinoma
|
95%
|
|
|
What are the two main categories of neck spaces
|
suprahyoid and infrahyoid
|
|
|
What are the two components of the perivetebral space
|
prevetebral part
paraspinal part |
|
|
Where does the pharynx hang down from
|
the skull base
|
|
|
Where is the hypopharynx
|
the level of the hyoid bone down to the esophagus
|
|
|
Where is the larnyx
|
the level of the hyoid bone (more anteriorly) to the level of the trachea
|
|
|
What determines the deeps spaces of the neck
|
the deep cervical fascia
|
|
|
How many layers of deep cervical fascia are there
|
3
superficial middle deep |
|
|
What layer of deep cervical facia surrounds the pharynx
|
the middle
|
|
|
What are the 4 anterior spaces of the suprahyoid neck
|
masticator space
parotid space carotid space parapharyngeal space |
|
|
What determines the masticator space
|
the superficial layer of DCF
|
|
|
In the coronal image where is the most cephalad part of the superificial masticator space
|
all the way up along the temporalis muscle
|
|
|
What muscle does masticator space contain
4 |
medial pterygoid
lateral pterygoid masstator temporalis |
|
|
What is the attachments of the lateral pterygoid
|
condyle of the mandible and the disc of the TMJ
|
|
|
What are the contents of the masticator space
|
muscle, mandible (bone and teeth)
Cranial nerve 5v3 (mandibular division of trigeminal nerve) |
|
|
What is the mc source of any mass in the masticator space
|
teeth (dental infection)
|
|
|
What is the foramen that CN5v3 goes throught
|
foramen ovale
|
|
|
What layer is the parotid space defined by
|
the superficial layer of deep cervical fascia
|
|
|
What is the most superior aspect of the parotid space on coronal images
|
the skull base
|
|
|
What is contained with in the parotid space
|
salivary gland
lymph nodes (lymphoma, Squamous cell carcinoma) CN 7 |
|
|
What is a potential complication of a tumor of the parotid space
|
tumor invading the temporal bone by crawling along the temporal bone
|
|
|
What layers of deep cervical fascia make up the carotid space
3 |
superficial
middle deep |
|
|
What are the contents of the carotid space
4 |
carotid artery (carotid body)
jugular vein CN 9 - 12 nodes (around it not really with in the sheath) |
|
|
What are the 4 anterior neck spaces
|
masticator space
carotid space parotid space parapharyngeal space |
|
|
What layers comprise the parapharyngeal space
|
superficial
middle deep |
|
|
What does the parapharyngeal space look like
|
a triangle of fat that is medial to the masticator space
|
|
|
What is contained within the masticator space
|
fat
|
|
|
Why is the parapharyngeal space so useful
|
the direction of displacement will indicate what space is being affected
|
|
|
What direction does a mass of the masticator space push the PPS
|
posterior medial
|
|
|
What direction does a mass of the parotid space push the PPS
|
Anterior medial
|
|
|
What direction does a mass of the Carotid space push the PPS
|
anterior lateral
|
|
|
What direction does a mass of the pharngeal space push the PPS
|
posterior lateral
|
|
|
What space does the facial nerve run through
|
the parotid space
|
|
|
What space does V3 of the trigeminal run through
|
Masticator space
|
|
|
What are the 3 posterior neck spaces
|
perivetebral space
retropharyngeal space posterior cervical space |
|
|
What layer of DSF surrounds the perivetebral space
|
deep layer
|
|
|
What are the muscles that are most anterior portion of the perivetebral space
|
longus coli and longus capitis
|
|
|
What muscles are located posteriorly in the perivetebral space
|
the paraspinous muscles
|
|
|
What are the contents of the perivetebral space
|
vetebrae
disk paraspinous muscles prevetebral muscles (longus colli and capitus) nerves |
|
|
What is the ddx of disease of the perivetebral space
|
vetebral body pathology-- mets, osteomyelitis
disc- discitis muscle-sarcomas nerves- nerve sheath tumors |
|
|
Where is the retropharyngeal space in relation to the periveterbral space
|
anterior
|
|
|
What layers of the deep cervical fascia make up the retropharyngeal space
|
middle and deep DCF
|
|
|
What is the name of the sleeves that are lateral to the retropharyngeal fascia and are part of the deep DCF
|
alar fascia (covers the lateral aspect of the retropharyngeal space
|
|
|
What occupies the retropharnygeal space
2 |
nodes and fat
|
|
|
Where is the posterior cervical space
|
fatty space down the posterior aspect of the neck between the SCM and the paraspinous muscles
|
|
|
What is contained in the posterior cervical space
|
nodes
fat CN 11 |
|
|
What do the nodes of the posterior cervical space typically drain
|
scalp lesions
|
|
|
What are the 5 regions of the pharynx
|
nasopharynx
oropharnyx oral cavity hypopharynx larynx |

