![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
121 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are 3 caues of thoracic outlet syndrome
|
Venous
Arterial Neurogenic |
|
|
What is another name for the venous type of thoracic outlet syndrome
|
Paget-Schrotter syndrome
|
|
|
What is the arterial type associated with
|
cervical ribs
|
|
|
What may occur as a result of the arterial type of TOS
|
subclavian artery aneurysm
emboli to the arm/hand |
|
|
What is the MCC of TOS
|
neurogenic (95%)
|
|
|
Is neurogenic TOS associated with cervical ribs
|
yes, both arterial and neurogenic are associated with cervical ribs
|
|
|
What causes venous TOS
|
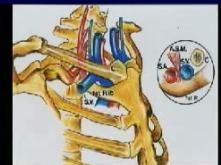
look at circular image (the anterior scalene is posterior and the clavicle is anterior)
|
|
|
What are the risk factors of venous TOS
6 |
manual labor
sports muscular build truncal obesity trauma iatrogenic (CVC and dialysis fistula grafts) |
|
|
What is the treatment
|
thrombolysis
surgical decompression of the TO Intraoperative angioplasty after decompression and stent placement as a last resort |
|
|
What is the problem in venous TOS
|
thrombosis
|
|
|
How is venous TOS diagnosed
|
by the adsons maneuver which involves abducting the arm and turning head away from affected arm while looking at an angiogram to see if there is compression
|
|
|
In severe TOS what should you expect to see on angiogram
|
collateral vessels
|
|
|
Does a thrombolytic catheter typically have many sideholes
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the medical therapy for venous TOS
|
catheter directed TPA with recombinant TPA and heparin
|
|
|
How long is TPA typicaly administered
|
36h
|
|
|
Once patency is restored via use of TPA what is typically the next step in tx of venous TOS
|
surgical decompression and angioplasty
|
|
|
What are the complications of treating venous TOS
|
bleeding
aterial injury pneumo phrenic nerve injury infection |
|
|
What is May Thurner syndrome
|
this is a cause of lower extremity DVT by compression of the left common iliac vein by the RIGHT common iliac artery
|
|
|
What demographics most commonly have May Thurner Syndrome
|
thin females
|
|
|
What are the indications for iliofemoral venous thrombolysis
|
LE DVT in young patient
Phlegmasia Cerulea Dolens severe pain or morbidity preservation of femoral venous access site prevention of post phlebitic syndrome |
|
|
What is phlegmasia cerulea dolens
|
this is when there is such profound venous thrombus that it prevents arterial inflow
|
|
|
What is post phlebitic syndrome
|
this is damage to the vein from the presence of a thrombus (why we do thrombolysis in younger patients)
|
|
|
What is the technique for iliofemoral thrombolysis
|
popiteal vein access with US
catheter directed rt-TPA infusion with mechanical thrombectomy as indicated |
|
|
When is venous PTA and stenting used
|
May Thurner
|
|
|
What are the treatment complications of iliofemoral thrombolysis
|
bleeding (arterial, vein)
re-thrombosis |
|
|
What is superior vena cava syndrome
|
this is partial or complete obstrucion of the SVC
|
|
|
What are the etiologies of SVC syndrome
|
neoplasm or adenopathy
inflammation infection chronic CVC chronic dialysis via AVF or graft |
|
|
What are inflammatory causes of SVC syndrome
|
fibrosis mediastinitis from cocci or histo
|
|
|
What thoracic neoplasms may cause SVC syndrome
|
bronchogenic CA
lymphoma sarcoma |
|
|
What is responsible for up to 80% of SVC syndrome
|
bronchogenic carcinoma
|
|
|
What are the SS of SVC syndrome
|
facial edema and flushing
headache dyspnea and cough upper ext edema pain dysphagia syncope |
|
|
What is the treatment of SVC syndrome
|
treat the underlying cause
anticoagulate percutaneous recanalization via PTA or stent |
|
|
What are the complications of treatment of SVC syndrome
|
vein rupture
bleeding stent migration |
|
|
What is the standard treatment for DVT
|
anticoagulation
|
|
|
When is a filter recommended
|
contriindication, complication or failrue of anticoagulation
|
|
|
When is anticoagulations considered a failure
|
enlarging DVT or a PE
|
|
|
If a pt who is not on anticoagulaiton has a massive PE and has an ongoing DVT and therefore at risk for additional PE should get a stent
|
yes
|
|
|
What are 5 indications of a filter for a DVT
|
the last 3 slides (make 2 ...relook at them)
3-free floating iliofemoral or IVC thrombus 4-DVT in the setting of severe cardiopulmonary disease 5-Poor compliance with anticoagulation |
|
|
If a patient has a DVT in the setting of severe Cardiopulmonary disease does he need a filter
|
yes
|
|
|
Is a lazy piece of shit who is not willing to take care of them self need a filter
|
yes
|
|
|
What are relative indications for IVC filter
2 |
-prophylatic for trauma patients
-high risk patients |
|
|
What are considered high risk patients for DVT and PE
|
longterm immobilization
pre-operatively prior to immobilization hypercoaguable pt with or without DVT (malignancy) |
|
|
What are some filters that are avaible
|

|
|
|
What are advantages of the titanium greenfield filter
|
MRI OK
Low IVC thrombosis rate easy to place |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of the greenfield filter
3 |
Difficult placement form left femoral or left jugular approach
max caval diameter of 28cm needed tilting leg asymmetry |
|
|
What is the prototypical umbrella type filter
|
the greenfield filter
|
|
|
Do they make a stainless steel greenfield filter
|
yes and there is more artifact
|
|
|
What happens if a filter tilts when in the cava
|
it does not function as well.
|
|
|
Can a birds nest filter be placed in a larger IVC than a greenfield
|
yes, that is one of its advantages (it can accomidate a IVC up to 40mm in diameter)
|
|
|
Is the birds nest MRI friendly
|
no, it is a nest of wires
|
|
|
What is does a vena tech filter look like
|
umbrella filter with vertical struts
|
|
|
What are advantages of the vena tech filter
|
bidirectional placement
|
|
|
What happens if there is more metal involved with a filter
|
more thrombogenic
|
|
|
Is the vena tech filter MRI friendly
|
yes
(it can also fit larger IVC upto 35mm) |
|
|
What is the Simon Nitinol filter
|
it has a 2 tier configuration that conforms to a predetermined shape at a specific body temperature
|
|
|
What does nitinol allow to happen
|
conforms to a predetermined shape at a specific body temperature
|
|
|
Does the trap ease filter have a questionable increase in IVC thrombosis
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the recovery filter
|
the first filter that was FDA to be removed
|
|
|
Is the gunther tulip filter retrievable
|
yes
|
|
|
Do retrievable filters generaly have an umbrella configuration
|
yes
|
|
|
Which way must a gunther tulip filter be retrieved
|
it can be placed both ways but must be retrieved by the jugular approach because it has a hook at the top
|
|
|
What is the advantage of the Opt Ease filter
|
this is a nitinol filter that can be retrieved from the femoral approach
|
|
|
What must be done when checking for an insertion site of a filter q
|
confirm patency with an ultrasound
|
|
|
If it is decided to insert via the femoral approach what should be done
|
perform iliac and IVC venogram
|
|
|
What should be evaluated with a venogram of the femoral approach
4 |
DVT
anomalies level or renal veins caval diameter |
|
|
What is important to do if you decide to insert the filter via the jugular or brachial vein
|
EKG to look for a LBBB since you will go through the right atrium
|
|
|
Is a venogram done for both femoral and jugular approaches
|
yes
|
|
|
If you discover a renal vein thrombosis where should the filter be deployed
|
supra renal
|
|
|
What are some indications of a suprarenal IVC filter deployment
|
renal vein thrombosis
IVC above the renal veins thrombus extending above the previous infrarenal filter filter placement during pregnancy |
|
|
Where do filters placed during pregnancy go
|
above the renal veins
|
|
|
What are 2 additional reasons for placement of an IVC filter above the renal viens
|
-PE secondary to a gonadal vein thrombosis
-Anatomic variants |
|
|
What are 2 anatomic variants that may require a suprarenal IVC filter
|
duplicate IVC
low insertion of renal veins |
|
|
What are inferior vena cava anomalies to be aware of
|
duplicate
lef sided IVC IVC with azygous interruption circumaortic left renal vein retroaortic left renal vein |
|
|
What do you want to be sure to do if a patient has a circumaortic left renal vein
|
place the filter below the lower most vein
|
|
|
What does a circumaortic left renal vein look like
|
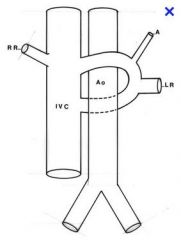
|
|
|
Filter types
|
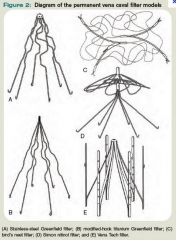
|
|
|
Why does the filter need to be placed below a circumaortic left renal vein
|
clot can extend into the circumaortic left renal vein and by pass the filter
|
|
|
What are indications for temporary filters
4 |
-short term protection during fibrinolysis of a caval or iliac thrombi
-before surgery in a pt with DVT -During pregnancy in a pt with a DVT -after PE in a patient with short term CI to anticoagulation |
|
|
What are the FDA approved retrievable filters
|
Bard recovery filter
gunther tulip filter (cook) Opt ease (cordis) |
|
|
Does the Barb recovery filter have its own retrieval device
|
yes
|
|
|
Does the gunther tulip (cook) filter have a hook at its apex
|
yes
|
|
|
Where is the hook of the opt ease filter
|
the inferior aspect
|
|
|
Is the opt ease approved for retrieval
|
no,
|
|
|
What most be done prior to retrieval of the filter
|
a venogram to make sure there is no clot
|
|
|
If the filter is full of clot do we retrieve it
|
no, it becomes permanent
|
|
|
What is the rate of PE after filter placement
|
2-7%
|
|
|
Can a PE result from a thrombosed filter
|
yes, an you may have to place a suprarenal filter at that point
|
|
|
Do patients who have a filter have a higher incidence of recurrent DVT
|
yes, but the PE rate is decreased. Nevertheless the patient should be placed on anticoagulation also
|
|
|
What is the 1 year primary patency of an AVF
|
60-80
|
|
|
What is the 2 year primary patency of an AVF
|
50-70
|
|
|
What percent of vascular access for hemodialysis are AVF
|
25%
|
|
|
What percent of vascular access for hemodyalisis are grafts
|
75%
|
|
|
What are 2 types of grafts used for hemodialysis
|
prosthetic and non-prosthetic
|
|
|
Where are the 2 MC sites for direct AVF
|
distal forearm and AC
|
|
|
What is anastomosed in the distal forearm
|
the radial artery with the cephalic vein
|
|
|
What is anastomosed in the AC
|
brachial artery to cephalic vein
brachial artery to the basilic vein |
|
|
What are 3 types of interposition grafts
|
polytetrafluorethylene graft
Bovine carotid artery heterograft homologous saphenous vein graft (rare) |
|
|
Name 3 interposition graft sites
|
brachial artery to basilic vein
radial artery to cephalic vein axillary artery to axillary vein |
|
|
Why would a necklace AV graft be used
|
if there is no access sites left...so important not to use all sites
|
|
|
What are the non-hemodynamic problems with AVF
|
infection
CHF pulmonary embolism |
|
|
When is infection more common
|
synthetic (why AVF is preferred)
|
|
|
What are the flow related complications of hemodialysis
6 |
stenosis
thrombosis venous aneurysm varicosities venous or graft pseuodaneurysm arterial steal |
|
|
Why are venous graft pseudoaneurysms an issue
|
they may result in impairment of flow through the fistula
|
|
|
What is graft related arterial steal
|
this is a condition where the flow to the distal arm is diverted to the graft. It is associated with reversal of diastolic flow distal to the graft.
|
|
|
What parameters are used to determine patency of a graft
|
measuring venous pressures
urea recirculation duplex doppler |
|
|
When is venous pressure increased
|
if there is an outflow problem
|
|
|
When is urea increased
|
if there is an inflow problem
|
|
|
Where are the common locations of stenosis of a dialysis graft
|

|
|
|
Where do 85% of dialysis graft stenosis occur
|
around the venous anastamosis site
|
|
|
What percent will occur at the venous anastomosis
|
47% the rest (35%) are either up or down stream from the anastomotic venous site
|
|
|
Where does stenosis occur in AVF
|
at the radiocephalic anastomosis (distal arm) it will occur at the AV anastomosis
At an upper arm (brachiocephalic) anastomosis the stenosis will occur at the proximal, mid or distal cephalic vein with equal likelihood |
|
|
Can stensosis occur prior to the venous insertion site of the graft, at the anastomosis, or down stream
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the treatment for dialysis fistula stensosis
|
surgical revision
balloon dilation endoluminal stenting atherectomy |
|
|
What is better PTA or surgical revision for immediate and longterm patency of occluded fisutula
|
PTA
|
|
|
What has a longer average patency period following angioplasty; brachiocephalic or radiocephalic
|
radiocephalic (19months)
brachiocephalic (7months) |
|
|
What are the clinical indications of stenting dialysis fistulas
3 |
stenosis resistant balloon dilation
-treatment of venous dissection or rupture -exclusion of pseudoaneurysm |
|
|
What are the 2 most common hemodynamic complications of fistulas or graft
|
stenosis and thrombosis
|
|
|
What r the tx of thrombosis of a fistula
|
surgical thrombectomy
new fistula or graft fibrinolysis |
|
|
What is done after injecting TPA into the clot
|
balloon catheter, then sweep out debri towards the venous outflow and dilate any stenosis
|
|
|
What are some of the mechanical thrombectomy kits available
5 |
treeretola ptd
amplatz clot buster possis angiojet hydrolyser oasis thrombectomy device |
|
|
What does a treretola PTD
|
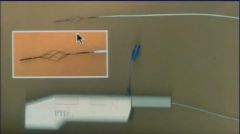
rotating basket catheter
|

