![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
109 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 3 layers of a blood vessel
|
intima
media adventitia |
|
|
Where is the vasa vasorum located
|
within the adventitia
|
|
|
What is responsible for repair of cells
|
endothelium (lining inside of intima)
|
|
|
Where is the smooth muscle located
|
media
|
|
|
Name the 8 basic angiographic findings
|
stenosis
aneurysm dissection extravasation psuedoaneurysm AV fistula in situ thrombosis embolism |
|
|
What does a normal renal artery look like
|
smooth walls
will taper from proximal to distal |
|
|
What is the MC vascular finding
|
stenosis
|
|
|
What should aspects of a blood vessel should be evaluated when looking at a stricture
5 |
length
severity concentric vs eccentric calcification collaterals |
|
|
What is the 2nd MC finding on an angiogram
|
aneurysm
|
|
|
What should aspects of a blood vessel should be evaluated when looking at a aneurysm
3 |
size
eccentricity concominant dz |
|
|
What is the MC 2ndary cause of htn
|
RAS
Accounts for 1-4% of all patients with hypertension |
|
|
Where are the MC locations for FMD in upper and lower extremities
|
Most common upper extremity artery: Brachial; also seen in subclavian, and axillary arteries
Most common lower extremity artery: External iliac; also seen in femoral, popliteal, and tibial arteries |
|
|
What is the cause of FMD
|
Noninflammatory, nonatherosclerotic arterial disease of unknown etiology
|
|
|
Where are the 2 MC locations of FMD overall
|
Renal is most common 60-70%
Internal carotid 20-30% |
|
|
What is the classic imaging appearance of FMD
|
"String of beads" appearance on diagnostic imagin
|
|
|
Why is angiography the gold standard for treatment of FMD
|
"Gold standard" offers simultaneous therapeutic interventions: Percutaneous revascularization with balloon angioplasty and/or stenting
|
|
|
What is the classic angiographic appearance of FMD
|
Classic "string of beads"
Diameter of beading larger than diameter of normal artery |
|
|
What are the hallmark features of dissection
3 |
intimal flap
compression of true lumen delayed filling of false lumen |
|
|
Can it be difficult to differentiate a dissection from an aneurysm if intimal flap is not seen
|
yes
|
|
|
What is a pseudoaneurysm
|
confined collection of contrast that is restrained by adventitia or periadventitial tissue
|
|
|
Are AVF often assoicated with pseudoaneurysms
|
yes
|
|
|
What is a common cause of an AVF
|
penetrating trauma or aneurysmal rupture
|
|
|
What are 3 causes of in situ thrombosis
|
aute response to vessel injury
trauma hypercoaguable states |
|
|
Where are embolisms most commonly seen
|
bifurcation
|
|
|
What does an embolism look like on angiography
|
a filling defect
|
|
|
Does an embolism have assoicated colleterals
|
no, it is acute
|
|
|
What 2 vessels are prone to embolism
|
RA and SMA
|
|
|
What are the 4 general sizes of blood vessels
|
large (aorta and great vessels)
medium (renal, carotid, sma) small (tertiary segmental branches) arterioles |
|
|
Are arterioles and capillaries visible on angiography
|
no
|
|
|
Are the arterioles affected in wegners
|
yes
|
|
|
What size vessels are affected in takayasu arteritis
|
large
|
|
|
What size vessels are affected in FMD
|
medium
|
|
|
What size vessels are affected in polyarteritis nodosa
|
small
|
|
|
Why is takayasu referrred to as pulsless disease
|
bc it affects the great vessels and thoracic aorta and may result in occlusion of these arteries and loss of pulse
|
|
|
Does polyarteritis nodosa cause aneurysms of small vessels
|
yes
|
|
|
What part of the body is affected by burgers disease
|
lower extremities
|
|
|
What vascular disease occurs in children
|
kawasakis
|
|
|
What age group tends to get Buergers and leriche
|
early middle age
|
|
|
What is the ddx of common arterial vascular disorders
5 |
atherosclerosis
FMD embolic dz intimal hyperplasia traumatic vascular injury |
|
|
What is the ddx of not so common arterial vascular disorders
5 |
inflammatory vasculitis
physiologic disturbance AVM neoplasia congenital/metabolic |
|
|
What is a fibrofatty plaque
|
this is a lesion with a fatty core and is covered by a fibrous plaque
|
|
|
What is a atheroma
|
this is a complex fibrofatty plaque with calcification, ulceration, hemorrhage
|
|
|
What are the complications of fibrofatty plaques/atheromas
|
stenosis, aneurysm, embolization
|
|
|
Where do aneurysm MC occur as a result of atherosclerosis
|
infrarenal
|
|
|
What is a major clue of stensosis on angiographic imaging
|
collaterals
|
|
|
What is blue toe syndrome
|
this is embolization from atherosclerotic disease that causes distal occlusions
|
|
|
What tissue is replaced in fibrodysplasia
|
although fibroous medial dysplasia is most common this can occur in the intima, media or adventitia
|
|
|
What is the MC location of fibrousdysplasia
|
medial
|
|
|
What is the MC location of fibroous dysplasia
|
right renal artery
|
|
|
What location within the renal artery is most common
|
distal aspect (
|
|
|
Does fibrous medial dysplasia occur more commonly in men or woment
|
women
|
|
|
what side for FMD is morre common
|
right
|
|
|
What other arteries are affected by FMD
|
carotid and external iliac
|
|
|
Where do 85% or thromboembolism originate
|
heart
|
|
|
What predisposes a patient to thromboembolism from the heart
|
recent MI or a-fib
|
|
|
Where do 10% of thromboembolism come from
|
aneurysms (aorto-iliac region or femoral-popiteal)
|
|
|
What are atheroemboli
|
this is distal arterial aneurysm (cause blue toe syndrome)
|
|
|
Do emboli commonly occur in the SMA
|
yes
|
|
|
What is a cause of intimal hyperplasia
|
vascular injury (platelets aggregate and stimulate smooth muscle cells)
|
|
|
Does initmal hyperplasia sometimes result from the trauma of intravascular surgery
|
yes
|
|
|
Does intimal hyperplasia occur on the inside of a stent
|
yes it can
|
|
|
What are 4 possible results of vascular trauma
|
occulsion
dissection pseudoaneurysm AV fistula |
|
|
What is the pathophysiology of inflammatory vasculitis
|
infitration of the media by histocytes
|
|
|
What are the angiographic manifestations of inflammatory vasculitis
|
stenosis
thrombosis vessel rupture pseudoaneurysm aneurysm |
|
|
What are the etiologies of inflammatory vasculitis
3 |
infection
radiation idiopathic |
|
|
Are mycotic aneurysm usually eccentri or concentric
|
they are usualy eccentric
|
|
|
Is kawaskis usually post viral
|
yes
|
|
|
What vessels does kawasakis typically affect
|
the coronary arteries
|
|
|
Where does polyarteritis nodosa typically affect
2 |
kidneys
pancreas |
|
|
What are the findings of polyarteritis nodosa
|
microaneursyms
|
|
|
Where does temporal arteritis typically affect
2 |
temporal artery
arch vessels |
|
|
What is the result of temoral arteritis
|
stenosis or occlusion
|
|
|
Where does takayasus disease affect
3 |
aorta, arch, pulmonary artery
|
|
|
What is the result of takayasyu
|
stensosis or occlusion
|
|
|
What is the result of buergers disease
|
segmental occlusion
|
|
|
Where does buergers disease typically occur
|
peripheral vasculature
|
|
|
What are the locations of the idiopathic arteritis
|

|
|
|
Can polyarteritis lead to rupture
|
yes
|
|
|
Does polyarteritis cause microaneurysm
|
yes
|
|
|
In addition to the temporal artery and the aortic arch where else does temporal arteritis occur
|
the upper extremity vessels (this can cause an upper extremity occlusion)
|
|
|
Can takayasu disease cause a mid aortic stenosis
|
yes
|
|
|
What is the hallmark feature of buergers disease
|
cork screw collaterals
|
|
|
What are physiologic causes of vascular abnormalities
|
extrinsic compression
drug induced vasospasm |
|
|
What are 3 types of extrinsic compression
|
popiteal entrapment
thoracic outlet syndrome median arcuate ligament compression |
|
|
Which way is the popiteal artery deviated in popiteal entrapment syndrome
|
medially
|
|
|
When does the occlusion occur the axillary artery in thoracic outlet syndrome
|
during abduction
|
|
|
What secondary injury may occur to the subclavian/axillary artery as a result of thoracic outlet syndrome
|
aneurysms
|
|
|
What does median arcute ligament compression syndrome look like
|
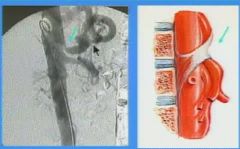
|
|
|
What does the median arcuate ligament compress
|
the celiac artery
|
|
|
What is the cause of AVM
|
congenital aberration of embryonic development at 4-10 wks
|
|
|
Where is the MC location of an AVM
|
pulmonary
|
|
|
What are the findings of pulmonary AVMs
|
lower lobe
enlarged PA branch tangle of vessels early draining veins |
|
|
What is the MC syndrome associated with AVM
|
osler webber rendu
|
|
|
What is the big difference between an AV fistula and AVM
|
there is a tangle of vessels (nidus) with an AVM
|
|
|
What is the MC cause of AV fistula
|
trauma
|
|
|
What neoplasms that are associated with vessels
|
hemangioma
hemangiosarcoma pericytoma |
|
|
Are hemangiosarcoma and pericytoma malignant
|
yes
|
|
|
Where are the MC locations of hemangiomas
|
skin, liver, spleen, pancreas
|
|
|
What are the findings of a hemangioma
|
large feeding vessel, densley staining mass
|
|
|
What are some predisposing substances to vascular neoplasm
|
arsenic
thorotrast PVC |
|
|
What does balloon dilation look like
|
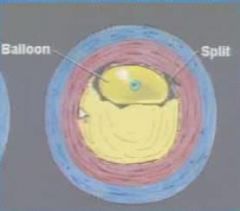
|
|
|
What happens to the intima during balloon dilation
|
it tears
|
|
|
Is an angioplasty balloon compliant or non-compliant
|
non-compliant
|
|
|
What does non-compliant mean
|
it will not increase beyond a certain size despite increased pressure
|
|
|
What happens as result of angioplasty
|
loss of vessel recoil
|
|
|
Do you ever do angioplasty in an asymptomatic patient
|
no
|
|
|
What are some clinical SS that warrant angioplasty
|
claudication
rest pain non-healing ulcer htn and renal failure (renal artery) |
|
|
What are examples of underlying pathology that may require angioplasty
|
atherosclerosis
FMD post operative stenosis |
|
|
What is almost always the reason we do angioplasty
|
atherosclerosis
|

