![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Periodic trends
|
-A trend is a predictable change in a particular direction.
-Trends in the periodic table depend on the electron configurations of the element. |
|
|
|
Trends help us to make predictions about the chemical behavior of the elements.
|
|
|
Ionization energy
|
The ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion.
Li + energy------------->Li + + e- ( neutral atom) (Ion ) |
|
|
Electron shielding
|
The shielding effect describes the decrease in attraction between an electron and the nucleus in any atom with more than one electron shell
|
|
|
Ionization energy in a group
|
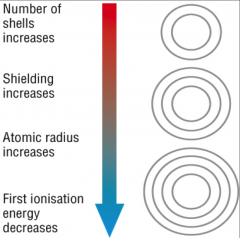
(picture is i.e down a group)
Ionization energy tends to ↑ as you move from left to right across a period. The electrons get added to same shell. Electron shielding effect remains same. |
|
|
Atomic radius
|
-Bond radius is half the distance from center to center of two like atoms that are bonded together.
-The bond radius can change slightly depending on what atoms are involved. |
|
|
Bond length
|
Bond Length is the average distance between nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule.
|
|
|
Trends of atomic radius
|
|
|
|
Electronegativity
|
-The ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons.
-The atom with ↑ E.N will pull the electrons more strongly. |
|
|
|
-Electrons are added to the next shell.
-Electron shielding is high in smaller elements and electrons are attracted by the nucleus more strongly. |
|
|
|
-Electrons are added to the same shell.
-Electron shielding does not change. -Effective nuclear charge increases, electrons are -attracted more strongly. -Electronegativity is ↑. |
|
|
|
An atom loses electron to become ( + )ve ion. ( cation)
An atom gains electron to become ( – ) ve ion. ( anion) -As atomic radius ↑ ionic radius ↑. -Down a group Ionic radius ↑ -Across a period, ionic radius ↓. |
|
|
|
It is the energy change that occurs when a neutral atom gains an electron.
Down a group E.A ↓. Across a period E.A ↑. |
|
|
|
-Melting point – the temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid.
-Boiling point - the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the atmospheric pressure. |
|
|
MP & BP trends
|
In a period, mp & bp ↑ at first and then ↓
Tungsten (W) is the element with ↑mp & bp. Mercury ( Hg) is the element with ↓ mp & bp. |

