![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
which cells recognise foreign antigens
how |
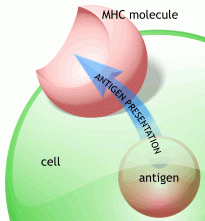
Tcells recognise HLA/MHC molecules
CD8= recognise MHC class 1 CD4= recognise MHC class2 |
|
|
which cells express HLA class 1 on cell surface
|
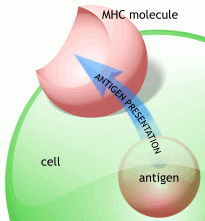
all nucleated cells
|
|
|
which cells express HLA class 2 on their surface?
|
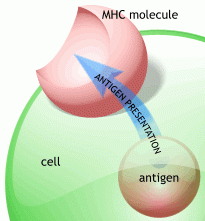
specialised APCs:
- Bcells, dendritic cells, macrophages |
|
|
how many types and variants of each HLA molecule are there?
|
3 types of each HLA class
2 variants of each class (2 HLA classes --> 6 total types --> 12 total variants) |
|
|
how are transplant rejections minimised
|
HLA matching
|
|
|
which HLA classes and types are the most important in matching for transplant
|
class 2 HLA-DR >> class 1 HLA-B >> class 1 HLA-A
|
|
|
wchi are HLA-DR the most important
|
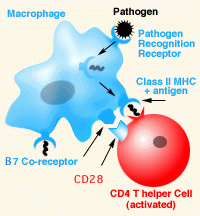
expressed highly on CD4 T helper cells
|
|
|
what 4 functions do activated CD4 T cells bring about
|
produce CYTOKINES
activate CD8 help AB prod recruit PHAGOCYTES |
|
|
what hypersensitivity reaction is ACTE CELLULAR REJECTION
|
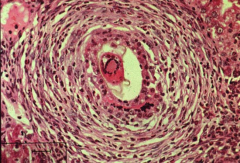
type 4 delayed Tcell-mediated GRANULOMATOUS inflam with NECROSIS & scarring
|
|
|
3 methods of CD8 cytotoxic killing mechanisms
which specific molecules |
TOXIN release- granzyme B
punch holes - perforin apoptotic- Fas-L & Th1 cytokines |
|
|
if T cell activation persists...which other immune component is activated
how |
B cell activation;
- co-stimulatory signals - ab's |
|
|
biopsies of acute cellular rejection show influx of which cells
|
T cells (incl: granzyme B, perforin, Fas-L)
phagocytes B cells NK cells (activated by B cells) |
|
|
4 types of transplant rejection
|
hyperacute
acute cellular acute vascular chronic allograft failure |
|
|
when does each 4 types of transplant rejection occure (time period)
|
hyperacute: mins-hrs
acute cellular: 5-30d acute vascular " " chronic allograft failure: >30d |
|
|
hyperacute transplant rejection:
- pathology - mechanism - treatment |
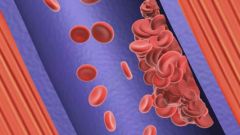
PATH: thrombosis, necrosis
MECH: PREFORMED ab-antigen (prev exposure) Rx: none! |
|
|
acute cellular rejection:
- path - mech - Rxx |
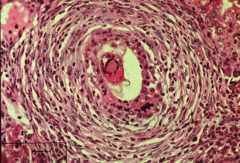
PATH: cellular infiltration (type 4 hypersensitivity)
MECH: CD4&8, B cells, phag Rx: immunosuppression |
|
|
acute vascular rejection
- PATH - MECH -Rx |
PATH: vasculitis
MECH: lymphocytes (T&B) Rx: immunosuppression |
|
|
chronic allograft failure >30d post-transplant
-PATH -MECH -Rx |
PATH: fibrosis, scarring
MECH: immune & non-immunes Rx: minimise drug toxicity, HTN & hyper lipidaemia |
|
|
eg of hyperacute rejection
|
incompatible blood groups (body naturally have ab's to other blood groups)
|
|
|
what happens to blood vessel walls in chronic allograft failure
|

proliferation of smooth muscle--> occlusion of lumen
interstitial fibrosis & scarring |
|
|
indications for lung transplant
|
advanced resp failure
life expectancy <3yrs CF, COPD, restrictive lung disease, a1-antitrypsin def, po HTN FIT for surgery! |

