![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
288 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the met-Hb formers
|
COPPER
Napthaline (moth balls) Chlorates Nitrocresols Nitrate/nitrite ACETAMINOPHEN |
|
|
what causes apparent recovery
|
Paraquat
Ethylene Glycol Acetominophen iron |
|
|
what metal causes transient glycosuria?
|
lead
|
|
|
what are CS of acetaminophen toxicity?
|
cyanosis, facial and paw edema, depression, dark choc. Colored urine
Cyanosis due to methemoglobinemia |
|
|
what is the antidote for acetaminophen toxitcity?
|
methylene blue
|
|
|
what is the tx for acetaminophen
|
n-acetylcysteine (mucomyst)
|
|
|
what do aminoglycosides do that is bad to the kidneys
|
renal tubular necrosis, proteinuria, reduced GFR
|
|
|
what do cephalosprorins do to the kidneys that are bad?
|
reduction in transport and gluose production, raised BUN
|
|
|
what do NSAIDs do that is bad to the kidneys, not anything to do with BP
|
renal papillary necrosis
|
|
|
what is the biggest source for lead
|
old batteries being thrown wherever and old ass buildings that have lead paint
|
|
|
how much lead is absorbed in the body?
|
2-10% (50% in neonates)
|
|
|
who absorbs lead better, monogastrics or ruminants
|
monogastrics
|
|
|
where is lead excreted
|
bile, urine, milk
|
|
|
how is lead transported in the body?
|
in the RBC's
|
|
|
where is lead stored in the body?
|
in the bones and replaces Ca2+
|
|
|
can lead cross the placenta
|
yes and it can cause defects, abortion, stillbirth
|
|
|
what effects will copper have on the body
|
lower heme sythesis
|
|
|
what does lead do to the body
|
lowers heme synthesis
direct action on enzyme via a -SH group. ALA dehyrase- most sensitve to bone marrow cerebral edema and blindness potent inhibitor of NMDA receptor-SEIZURES decreases selenium |
|
|
what are CS from lead (CNS and GIT)
|
colic, vomitting, constipation
encephalopathy, anemia, proteinuria |
|
|
what happens to cattle with lead poisoning?
|
blindness, headpressing, excitement, hyperesthesia (senstive to stimuli), muscle spasms
|
|
|
what CS do calves have with acute lead poisoning?
|
bellowing, blepharospasm, ataxia, tetany, convulsions and death
|
|
|
what CS do cattle have with subacute lead poisoning?
|
colic, teeth grinding, coughing, dyspnea, laryngeal paralysis, CNS behabioral changes, mania.
|
|
|
what CS do sheep get with lead tox?
|
its rare so forget it!
|
|
|
what CS do horses get from lead poisoning?
|
GIT (colic) and CNS
BLINDNESS, roaring, paralysis of limbs, muscle fasiculations, SEIZURES |
|
|
what CS do pigs have with lead tox?
|
blindness, melena, head pressing, salivation, excitability
|
|
|
what CS do dogs have with lead tox?
|
GIT first masseteric paralysis, megaesophagus, behavioral changes, seizures, transient glycosuria, wasting
|
|
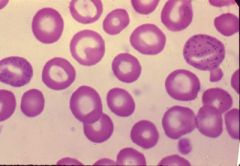
what the hell is this?
|
basophillic stippling from lead poisoning
|
|
|
so what are you going to see on labwork with a patient with lead tox
|
mild anemia with regeneration
basophilic stippling intranuculear inclusion bodies transient glycosuria with porphyrins in urine increase ratio density of LB NRBC may be seen w/o anemia in small animals |
|
|
what are treatment options for lead tox
|
EDTA-chelation therapy mobilizes lead and promotes excretion
Dimercaprol (BAL) D-penicillamine "Cuprimine"-expensive, vomitting, anorexia, CNS signs DMSA (Dimercaptosuccinic acid) supportive-gastric lavage w/ Na sulphate or Mg sulphatewhot |
|
|
who gets arsenic more common from greatest to least, eg. pigs, cows, cats
|
cats>horse>cattle>sheep>pigs
|
|
|
how much arsenic can be in sheep dips?
|
up to 20%
|
|
|
what does arsenic like to associate itself with in the body?
|
RBC
|
|
|
where is arsenic stored in the body?
|
bones, teeth, liver, kidney
|
|
|
for excretion of arsenic how long does it take and where it is excreted
|
rapidly excreted in urine, feces, sweat and milk
|
|
|
whats the MOA of arsenic with cellular resp.
|
blocks cell metabolism and cell resp- leads to depleted cell energy
|
|
|
which -SH compounds does arsenic inhibit?
|
glutathione and oxidases
|
|
|
which tissues does arsenic affect?
|
rapidly dividing tissues, GIT, kindey, liver,lungs, skin
|
|
|
which blood vessels does arsenic like to affect ?
|
splanchnic capillary beds- tranudattion, hypovolemic shock and circulatory failure
|
|
|
can arsenic cross the placenta
|
yes
|
|
|
where is arsenic found in milk in high doses
|
when cows are eating treated herbage
|
|
|
with inorganic arsenic cmpds, are the effects acute or subacute
|
they can be either
|
|
|
what are CS of arsenic poisoning?
|
GIT and shock bright red gums
|
|
|
CS of peracute arsenic tox?
|
death, cardiovascular collapse
|
|
|
CS of acute arsenic tox
|
salivation, vomitting (except ruminants and horses)
|
|
|
cs of subacute arsenic tox
|
hemorrhage, gastroenteritis (HGE), diarrhea (black and bloody),
|
|
|
what are CS of arsenic tox in pigs?
|
hematuria/ dermatitis
|
|
|
what will be seen with labs of arsenic tox?
|
reddening and edema of gastric mucosa
|
|
|
how do you diagnose arsenic tox?
|
CS, history, PE
predominately GIT signs garlic odor to breath and GIT contents |
|
|
D/DX for arsenic tox
|
lead but lead has CNS signs
|
|
|
tx for arsenic tox
|
BAL
sodium thiosulfate (provides sulfur for the arsenic) DMSA |
|
|
what is the prognosis for arsenic tox
|
poor
|
|
|
which animals do organoarsenicals affect mostly
|
pigs and poultry
animals fed on dry rations |
|
|
what does organoarsenicols affect
|
PNS- causes demyelination and nerve damage
|
|
|
CS in pigs with organoarsenical tox
|
mainly PNS
ataxia, goose-stepping dog sitting- paralysis/ lat recumbency remain alert and eating |
|
|
what kind of lesions does organoarsencials cause?
|
none
|
|
|
dx of organoarsenicals
|
hypovitaminosis B (demylination)
salt |
|
|
d/dx for organoarsenicals
|
hypovitaminosis B (demyelination)
salt poisoning, foot problems, spinal trauma |
|
|
tx for organoarsenicals
|
remove the source, increase water intake, possible diuretic
|
|
|
how common is mercury tox
|
rare
|
|
|
how can mercury get into the body
|
through skin/ resp. route, cross placenta, slow excretion (retention in tissues)
|
|
|
MOA of mercury
|
mercury inhibits enzymes with SH groups
interferes with ribosomes- protein synthesis- cell death |
|
|
clinical signs of inorganic mercury
|
CNS, GIT
GIT- vomitting, diarrhea stomatitis- through cycling of mercury through saliva acute npetritis with oliguria, azotemia (urea accumlates in blood) and hematuria skin lesions with chronic cases |
|
|
CS of organic mercury tox
|
2-3 weeks post ingestion. lacrimation CNS
|
|
|
what is the predominant CS of mercury tox in sheep?
|
GIT
|
|
|
what is the predominant CS of mercury tox in cattle
|
CNS
|
|
|
what is the predominant CS of mercury tox in dogs
|
blindness, convulsions, involuntary chewing
|
|
|
dx of mercury tox
|
history, CS, histo
|
|
|
tx of mercury tox
|
sodium thiosulfate
DMSA succimer- inorganic mercury |
|
|
what is the prognosis for mercury tox
|
guarded, the CNS lesions are irreversible
|
|
|
so what kind of manifestation does copper tox have?
|
acute manifestation of a chronic poison
|
|
|
how do animals get acute copper tox
|
its rare but in feed additives, cattle and pig feeds fed to sheep can cause this and some injectable solns
|
|
|
how does chronic copper poisoning occur?
|
molybdenum deficiency leads to copper toxicitiy.
inherited in Bedlington terrier, westie, skye terrier |
|
|
what pathologies can occur with mercury poisoning?
|
MetHb former!
brown blood and urine accumulates in liver RBCs- hemolytic crisis-ACUTE DEATH renal failure due to debris Hb and kidney copper levles liver damage by HELIOTROPES accumulates copper- jaundice |
|
|
what are acute CS of copper tox
|
nausea, vomitting (green-blue vomitus possible)
diarrhea (maybe hemorrhagic) dehydration shock Hburia (subacute) |
|
|
what are chronic CS of copper tox in sheep
|
its occurs in sheep mainly
Hbemia and Hburia shock |
|
|
what are CS of chronic copper tox in pigs
|
skin signs in pigs with parakeratosis
death in 24-48 hours |
|
|
what is copper carried in ?
|
RBC's
|
|
|
what do sheep and goats have that make them more susceptible to copper poisoning?
|
low glucose-6-phospahte dehydrogenase activity which makes them more susceptible to hemolysis
|
|
|
what is the MOA for copper toxicity
|
accumulation by the liver lysosomes lead to dysfunction of biochemical parameters in serum (LD, SGOT). It also accumlates in the RBC's
|
|
|
what can you find copper in?
|
foot baths, molluscicide for flukes
|
|
|
when can you start to see copper in the urine after copper tox?
|
appears in urine 24 hours before the crisis
|
|
|
does glutathione decrease or increase as the RBC ages?
|
decreases
|
|
|
during free radical formation from copper toxicity, what enxymes are inhibited
|
cholinesterase, opf the pyruvate and the alpha ketoglutarate systems
|
|
|
why do the kidneys fail from copper toxicity?
|
free radicals, debris, hemoglobin, iron release and kidney copper levels. Animals that survive the hemolysis may die of uremia
|
|
|
subacute copper toxicity
|
hemagloinuria
|
|
|
what might you see on autopsy of an animal that had copper poisoning?
|
jaundice, friable yellow or copper-colored liver, distended gall bladder, enlarged, mottled grey to blue-black friable kidneys, enlarged brown to black spleen. This is from all the methemogloin collecting in the organs
|
|
|
how do you treat copper toxicity
|
molybendum salt licks
chronic- ammonium molybdate acute- sodium thiosulfate penicillamine in dogs |
|
|
what is the prognosis of copper toxicity
|
grave once hemolysis occurs
|
|
|
what is the level of copper in the blood to be diagnostic for toxiticy
|
>1.35 ppm
|
|
|
so which element has an inverse relationship with copper?
|
molybdenum
|
|
|
so if you increase molybdenum what will you decrease
|
increase molybdenum will decrease copper
|
|
|
which animal is most senstive to molybdenum toxitiy
|
ruminants
|
|
|
where does molybdenum bind to ?
|
proteins and RBC's.
|
|
|
where is molybdenum excreted?
|
bile, urine, milk
|
|
|
why might molybdenum cause diarrhea
|
complexes with catechols
|
|
|
how does molybdenum cause bone defects
|
collagen defects via lysyl oxidase and via competing with phosphours in bone
|
|
|
when do CS appear with molybdenum tox?
|
8-10 days just know its not acute can happen up to 6 wks later
|
|
|
CS of molybendum tox
|
persistent severe, malodorus green scouring with gassy bubbles. Anemia, depigmentation of the coat around the eyes forming spectacles. Weight loss, stiff gait, posterior ataxia. decreased fertility, j
|
|
|
with the chronic form of molybedum tox what will you see
|
joint pains, rickets. osteoporosis and exostosis, beading of ribs, fractures, overgrowth of long bones; epiphysal dystrophy
|
|
|
what is the treatment for molybdenum toxicity
|
copper sulfate
|
|
|
what is salt poisoning also known as
|
water deprivation toxicosis or sodium ion toxicosis
|
|
|
what animals commonly get salt poisoning
|
pigs and poultry
|
|
|
what is the MOA of salt poisoning
|
relative lack of water, plasma and CNS sodium levels increase. The high CNS levels of sodium inhibit anaerobic glycolosis which in turn decreases the sodium pump energy
|
|
|
what are clinical signs of salt toxicosis in pigs
|
depression of appetite, thrist, salivation, wandering, pruritis, shivering, abnormal gait, arched back, BLINDNESS, head pressing, circling (pivoting), ears and skin feel cold. tonic and clonic convuslions, recumbency and terminal paddling of feet, DEATH IN THREE DAYS backing up and SITTING DOWN
|
|
|
what is the pathonomic lesion of salt poisoning?
|
eosinophillic menigoencepalitits in the early stage
|
|
|
what is the treatment of salt poisoning
|
give drinking water, sparingly 0.5% BW q 60 min.
|
|
|
what is the prognosis of salt poisoning
|
poor
|
|
|
how much iron is in hemoglobin and how much in myoglobin of the body?
|
70% in hemoglobin and 5-10% in myoglobin
|
|
|
what happens with free iron in the GIT
|
cause lipid peroxidation which directly damages epithelial cells by lipid peroxidation
|
|
|
what are cardiovascular effects of iron poisoning
|
increased capillary permeability, extravasation, and cardiovascular collapse. This results in LACTIC ACIDOSIS
|
|
|
what do you have to remember about the onset of CS of iron toxicity
|
may be delayed so ingestion may not be seen.
|
|
|
following oral ingestion of iron, within 6 hours, what CS will you see?
|
drowsiness from the acidosis, depression, vomitting (brown to bloody), colic, dysentery.
|
|
|
after 6 hours of oral ingestion of iron, what CS will you see
|
if there is no death within 6 hours, apparent improvement followed (12-24 hours) by recurrence of diarrhea with dehydration, liver necrosis, shock, acidosis, and coma. fatty degenration of myocardium, increased capillary permability, decreased CO, cyanosis, pallor.
|
|
|
what are some clincial pathology findings you might see with iron toxicity from oral ingestion
|
acute hemolytic anemia, jaundice, hemoglobinemia, and coagulopathy
|
|
|
what does iron toxicity do pathologically to the GIT
|
its corrosive to the GIT, vomitting, and hematemesis
|
|
|
what is considered a high iron diet
|
>5,000 ppm
|
|
|
what does iron interfere with in growing animals?
|
phosphate absorption and lead to growth retardation and rickets
|
|
|
what are the two syndromes followed by an overdose of an iron injection
|
1. severe depression, shock, and acidosis due to circling excess (hypovolemic, hypotensive shock due to extravasation)
2. peracute rxn like anaphylaxis immediately after injection. |
|
|
orally, what pathologies can occur from lead toxicity?
|
mucosal necrosis +/- erosions, fluid to bloody intestinal contents (HGE). congestion of liver, kideny, and splanchnic vessles. liver necrosis, icterus
|
|
|
what can chronic mucosal ulcers lead to
|
stenosis and scarring
|
|
|
what pathology can be caused by injectable iron?
|
yellow brown discoloration of tissues and edema near injection site and drainage of lymph nodes. cardiovascular collapse from all that increased capillary leakage and hypovolemia
|
|
|
what are treatment options for iron toxicity?
|
if recent digestion < 4 hours apomorphine
oral washing soda as an emetic gastric lavage, plus saline purgative milk of magnesia to precipitate insoluble iron hydroxide. oral desferroxamine will bind to iron to reduce absorption. fluids chleation therapy- desferroxamine . have to be careful with IV because of histamaine release ascorbic acid enhances iron excretion |
|
|
what will the urine look like with an animal that is excreting iron?
|
red-brown
|
|
|
where is selenium found and where is there a risk for toxicity?
|
in the soil and risk areas are those that have 1-6 ppm or more
|
|
|
can plants accumulate selenium ?
|
yes, some can have up to 1,000-15,000 ppm
|
|
|
are seleniferous plants palatable?
|
no, but they are a little better when they wilt.
|
|
|
do horses aviod seleniferious plants
|
surprisingly yes, they try for once not to die
|
|
|
what are other ways animals can get selenium toxicity?
|
iatrogenic (inj. from stupid farmers), selenium med's (selsun shampoo), ceramics and glass, environiumnment- waterfowl may get this from leached water/run offs from fields
|
|
|
what does selenium do when it gets into the body
|
the soluble salts and seleno-amino acids get rapidly absorbed from the small intestine and are distributed on plasma proteins to the liver, spleen, and kidneys, later on the hooves. also crosses the placenta
|
|
|
what can complex with selenium in the body and reduce their indivual toxicities
|
selenium and mercury
|
|
|
what can complex with selenium to increase tissue levels but somehow reduce toxicitiy?
|
cadmium
|
|
|
what is the proposed mechanism of how selenium causes bad shit to happen in the body
|
it may replace sulfur in amino acids and therefore cause fucked up proteins in the hooves and hair. It can inhibit enzymes and decrease ATP and oxygen utilization
|
|
|
how can selenium interfere with anti-oxidants?
|
via the -SHG group in gluathione and glutathione peroxidases. therefore peroxidases can more readily damage cells, reduces vit C as well
|
|
|
can selenium cause cancer?
|
possibly by seleno-proteins
|
|
|
is it common for animals to go and eat selenium rich plants
|
no they taste like shit
|
|
|
who out of our brilliant farm animals will go and eat shit tasting selenium rich plants
|
cattle and sheep
|
|
|
how long will it take for animals who eat this shitty tasting selenium rich plants to die
|
hours to days
|
|
|
what are CS of eating selenium rich plants
|
irritancy to mucous membranes, rapid weak pulse, mydriasis, pyrexia, dyspnea, cyanosis, bloat, colic, polyuria, dark watery diarrhea, unsteady gait, death due to resp. failure usually before dx. lung edema, bloody froth from the nose
|
|
|
what will you find on post mortem from an animal with selenium toxicity
|
hemorrhage in lungs and abdominal organs. Ascites, hydrothorax. renal necrosis. Atony of smooth muscle. GIT contents may SMELL LIKE ROTTEN GARLIC. capillary damage.
|
|
|
in the paralytic syndrome of selenium toxicity what might you find on post mortem exam
|
focal poliomyelomacia in lumbar ventral horns.
myocardial necrosis |
|
|
how do you diagnose selenium toxicity?
|
signs, history, lab results
tissues levels blood plasma GLUTATHIONE PEROXIDASE activity is REDUCED |
|
|
what is the subacute form of selenium toxicity also called
|
blind staggers- which can also be due to sulfate
|
|
|
who has the paralytic syndrome "blind staggers" of selenium toxicity been reported in
|
pigs who are alert, afebrile, recumbent that squeak if distrubed. Standing pigs use the snout for support due to anterior paresis. Incoordination, lameness. Normal appetite.
posterior paralysis or even quadriplegia |
|
|
what are clinical signs of subacute selenium toxicity "blind staggers"
|
weight loss, staring coat, isolation from herd, staggering gait, impairment of vision, anorexia, depression, circling, aimless wandering, anterior paralysis. later- salivation, lacrimation, cloudy cornea, colic, paresis of mm of swallowing of tongue, lethargy, rapid resp, hypothermia, collapse and death
|
|
|
what will you see on post mortem exam of an animal that died of selenium toxicity
|
degeneration, of the liver and spleen (necrosis, atrophy, and cirrhoiss)
ascites, congestion, hemorrhage, edema, malacia in the brain. possibly splenomegaly |
|
|
what are CS of chronic selenium toxicity aka Alkali disease
|
loss of long hair from mane and tail of horses and the switch of cattle. rough and dull coat. emaciation and depraved appetite. decrease bld circulation= cold extremities. rings below the coronary band. hoof may slough in horses. in the cattle hoof becomes deformed. lameness and stiff gait due to arthritis.
|
|
|
what are some other CS of alkali dz, think birds, prego
|
low hemoglobin, fetal abnormalites, teratongeic effects, underdeveloped feet, and legs in waterfowl. malformed eyes and beak. decreased fertility
|
|
|
PM of alkali dz
|
atrophy of heart, atrophy of liver and cirrhosis, pulmonary edema, gastro-enteritis and nephritis. vacuolation in brain stem
|
|
|
how can you diagnose selinium tox
|
blood analysis to evalute intake levels > 5 ppm
|
|
|
treatment for selenium toxicity
|
symptomatic
O2 for dyspnea arsenic to change excretion from the lungs to bile copper high protein diets may protect increase sulfur containing proteins in diet acetylcysteine |
|
|
what could blind staggers also be due to instead of selenium tox?
|
sulfur
|
|
|
what has sulfide been linked to in a feedlot
|
polioencehalomacia
|
|
|
where do these feedlot animals get the sulfur to become toxic with
|
water water water
|
|
|
when you do your labwork for a ruminant with suspected sulfur poisoning what do you want to keep in mind
|
the sulfur levels decrease fast! get them fast
|
|
|
what are acute and subacute signs of sulfur poisoning
|
diarrhea, thick dark ruminal fluid may be related to sulfide fromati
of H2S NOT THIAMINE |
|
|
how long after oral NaS to sheep will PEM occur
|
<1 1 and lesions in <1 day
|
|
|
so what do we cook with allll the time that contains sulfur
|
onions
|
|
|
what are some common things that have zinc in them
|
pennies, batteries, fungicides and medicine, bandaids for wounds, cosemetics, diaper rash products, textiles, rubber good, soaps, printers, ink ;/`
|
|
|
how is zinc carried in the body
|
by carrier mediated process, bound to plasma proteins to sites of deposition
|
|
|
what are sites of deposition of zinc
|
liver, kidney, prostate, muscle and pancreas
|
|
|
where is zinc excreted
|
mostly in feces but also in urine and saliva
|
|
|
how is zinc utilized in the body
|
metalloenzymes
|
|
|
is zinc necessary?
|
yes for reproduction, growth, skeletal development, collagen formation (affects lysyl oxidase), feather formation, and epidermis (wound healing)
|
|
|
what can happen in the body if there is a deficiency of zinc
|
intravascular hemolysis and disseminated intravascular coagulopathy perhaps through affecting enzyme systems
|
|
|
high levels of zinc will compete with what in the body?
|
Ca2+for GIT absorption, zinc may interfere with copper storage in the liver
|
|
|
what may zinc anatagonize in the hemodynamic process
|
zinc may antagonize copper and iron in hemotopoietic processes. It inhibits ALA dehydrogenase. Zinc also affects glutathione reductase and hexose monophosphate enzymes
|
|
|
what are clinical signs of zinc toxicity in dogs
|
GIT, anorexia, and vomitting leading to CNS depression, lethargy and diarrhea (less common). Chronic anemia hemoglobinuira and jaundice. Renal failure - primary sign may be PORT WINE URINE, may die if untreated. Corrosive to GIT, halitosis, lameness PU/PD, exophthalmia and seizures
|
|
|
what are clinical signs of zinc tox in farm animals
|
anorexia, LIGHT GREEN DIARRHEA and lethargy, leading to weight loss
|
|
|
what can happen in the body if there is a deficiency of zinc
|
intravascular hemolysis and disseminated intravascular coagulopathy perhaps through affecting enzyme systems
|
|
|
high levels of zinc will compete with what in the body?
|
Ca2+for GIT absorption, zinc may interfere with copper storage in the liver
|
|
|
what may zinc anatagonize in the hemodynamic process
|
zinc may antagonize copper and iron in hemotopoietic processes. It inhibits ALA dehydrogenase. Zinc also affects glutathione reductase and hexose monophosphate enzymes
|
|
|
what are clinical signs of zinc toxicity in dogs
|
GIT, anorexia, and vomitting leading to CNS depression, lethargy and diarrhea (less common). Chronic anemia hemoglobinuira and jaundice. Renal failure - primary sign may be PORT WINE URINE, may die if untreated. Corrosive to GIT, halitosis, lameness PU/PD, exophthalmia and seizures
|
|
|
what are clinical signs of zinc tox in farm animals
|
anorexia, LIGHT GREEN DIARRHEA and lethargy, leading to weight loss, drop in milk yield, then anemia and jaundice. PU/PD, polyphagia, exophtalmia, convulsions, and paresis
|
|
|
what are CS of zinc tox in foals
|
lameness, epiphyseal swelling, and stiffness. adult horses- unthrifty
|
|
|
what can you see with zinc tox hematology
|
hemolytic anemia, DIC, low PCV, RBC changes may resemble lead (nucleated RBC, basophilic stippling, polychromasia, anisocytosis)/.
|
|
|
what other laboratory findings may you see with zinc toxicity
|
azotemia, ECG changes, hepatocellular centrilobar necrosis, hemosiderosis, pancreatic duct necrosis and fibrosis
|
|
|
what do you have to be careful of when taking blood and zinc levels
|
rubber stoppers of blood tubes can sometimes contain zinc
|
|
|
what can intravascular necrosis caused by zinc toxicity cause
|
pre-hepatic bilirubinemia from intravascular hemolysis caues and increase in uncongugated bilirubin and jaundice. Hemoglobinemia and hemoglobinuria, casts in urine
|
|
|
what are treatment options for zinc toxicosis
|
fluid therapy, EDTA, blood transfusion. heparin for DIC, fresh frozen plasma for dogs with DIC or pancreatitis. H2 blockers to reduce acidity and absorption. sucralfate is demulcent
|
|
|
d/dx for zinc tox
|
onion toxicity, auto-immune hemolytic anemai, babesia `
|
|
|
how can animals get fluorine toxicitiy
|
from water, it can naturally reach high levels in water. forages grown on silds with high levels, but mostly fluoride on leaf. industrial contamination. feed and mineral supplements and mineral phospahtes
NaF is an old anthelmintic for pigs and wood preservatives. occasionally in powders and insecticides. |
|
|
who does the acute form of fluorine toxicity occur in
|
pigs 4-5% NaF is fatal
|
|
|
which form of fluorine toxicity is more important
|
chronic form "fluorosis" is more important. tox due to inorganic forms and depends on solubility
|
|
|
which animal is more susceptible than other herbivores and pigs to fluorine toxicity
|
cattle
|
|
|
cs of fluroine tox in sheep
|
teeth and fleece lesions
|
|
|
CS acute form fluroine tox
|
corrisive GIT, salivation, hyperpnea, spasms. vomitting, colic, diarrhea, muscular weakness, convulsions, cardiac failure, collpase and death
|
|
|
PM acute florine tox
|
hemorrhagic gastro-enteritis, congestion of liver and kidneys, NaF delays clotting time and enolase
|
|
|
treatment for acute fluorine tox
|
there isnt one
|
|
|
what are the kinetics of fluorine toxicity
|
absorption may be decreased by aluminum, magnesium, or calcium.
95% accumlation in bones and teeth and thence is slowly redistributed and excreted over months. ` |
|
|
does fluorine cross the placenta ?
|
yes but it doesn't affect the fetus
|
|
|
are milk and meat a hazard when there is flourine toxicity
|
no
|
|
|
what does fluorine affect that will cause remodeling of bone
|
calcium metabolism, osteoblasts, osteoclasts
|
|
|
how are the teeth affected by fluorine toxicity
|
abnormal enamel and dentine aloows pitting and wear. local oxidation leads to discoloratoin
|
|
|
what is the mechanism of fluroine toxiity
|
the flourine replaces the hydroxyl (-OH) groups of hydroxyapatite and delays mineralization. It may also affect enzymes
|
|
|
what vitamin can be affected by fluorine toxicity
|
vitamin C through its balancing of Fe2+ ions which may be tied up with fluorine. can cause scruvy in g.pigs
|
|
|
how long may it take for CS to appear with fluorine toxicity
|
6-12 months
|
|
|
what does fluorosis toxicity severity depend on
|
age, dose, duration of exposure, solubility of the flouride salt and nutritional status
|
|
|
what decreases with fluorine toxicity
|
decrease milk production, decrease appetite, emaciation, decrease bone marrow production
|
|
|
what are some CS of fluorine toxicity
|
painful, stiff, gait, SHIFTING, LAMENESS, DIAGONAL LAMENESS, bony exotoses on legs,enlargement of sternum, spontaneous fracture of bones.
|
|
|
where are CS more prominent in cattle
|
bony lesions.
|
|
|
what are CS that are more prominent in sheep
|
teeth lesions. un-erupted teeth sheep may lap water like a dog. teeth can have mottling, erosions, discolorations (brown to black). Abnormal wear, poor occlusion, gingivitis, and periodontal dz.
|
|
|
what can happen with the skin of sheep with fluorine toxicity
|
dry and less pliable. bleeding may occur
|
|
|
what can be seen on PM with fluorine toxicity
|
exostoses, periosteal hyperostosis, thickened bones (esp. coritices), "chalkiness". porosity. teeth lesions. starts metatarsals later mandible, metacarpals and ribs.
|
|
|
how much fluorine is usually in bones
|
1000 ppm of fluorine in dry weight in bone. Mild cases 3000 ppm, in chornic 15,000-20,000 ppm, urine > 10 ppm (normal 2-6)
|
|
|
how do you dx fluorine toxicosis
|
signs, anamnesis and lesions
bone and urine concentrations >1500 ppm and 10 ppm urine radiology |
|
|
what are treatment options for fluorine tox
|
non specific aim is to prevent
aluminum sulfate may complex F in the diet ensure balanced Ca:P:Vit D change agriculture system pastures vitamin C |
|
|
which breed of cattle is more susceptible to organophosphate toxitcity than bos taurus and why
|
brahmans, because bos taurus have a greater binding to AChE
|
|
|
how are most OP absorbed
|
thorugh the skin because they are lipid soluble
|
|
|
does OP accumulate
|
no but some distrubutes to fat to release later
|
|
|
what can thiophospates be converted into
|
more toxic phosphates. excretion is rapid. The phosphoramidates are polar (N+) and do not readily into the CNS
|
|
|
what is the MOA of OP's
|
an acute poisoning due to inhibition of acetylcholinesterase. The result is potentiation of acetylcholine and reinforcement of parasympathetic effects.
|
|
|
what can cats have in their blood that can cause them to be very susceptible to OP tox
|
pseudochoinesterase
|
|
|
when does the OP-esterase bond become even more stable
|
as it ages. this requires formation of new cholinesterases, hence the need to stare oxime therapy early
|
|
|
what is a major clinical sign of OP tox
|
loss of consciouness followed by convulsions; if no anticonvulsant is given quickly, then irreversible neuronal damage can occur.
|
|
|
what will happen if you don't start treating OP tox with anti-muscarinic drugs
|
lack of tx leads to other neurotrasmitters being involved and then anti-muscarinics durgs will not control the convulsions
|
|
|
what drugs will stop even late stage convulsions of OP tox
|
N-methl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists will stop even late stage convulsions. these drugs are also glutamate receptor blockers. Glutamate will lead to continuous release of acetylcholine.
|
|
|
how do NMDA receptor activators lead neuronal swelling
|
leads to Na+ and water influx= neuronal swelling. calcium ingress will lead to accumulation of calcium and cell metabolism derangement and cell death.
|
|
|
what are some NMDA antagonists
|
ketamine, dextromethophran, and memantime
|
|
|
in addition to the usual acute organophophate anticholinesterease mechanism, what else can the OP's do
|
delayed neurotoxicity or OPIDN (OP induced delayed neurotoxicity)
|
|
|
what do the OP's do to the neurons that cause neurotoxicity
|
neuronal demyelination of motor nerves mainly in mid-neuron which causes a chemical transection of the nerve and axonal degeneration. There is also Schwann cell proliferation. The effects start peripherally and work up the spine (dying back). the results include inability to walk or high-stepping gait ("foot drop") with sensation deficits and pain. Humans are most sensitive and cats less so. Hnes are used as the model. Latency of 1-2 weeks. Hindlimb weakness, ataxia. May progress to forelimbs
|
|
|
do all OP groups cause neurotox
|
no
|
|
|
what can happen to cats wearing flea colors
|
flea collar toxicosis. where muscle wasting occurs similar to that after nerve damage. The dicholorvos group of OP's can form an aged complex with NTE
|
|
|
CS of muscarinic tox
|
salivation, lacrimation, sweating, urination, defecation (SLUD) cough, bradycardia, serous nasal discharge, miosis, vomiting and dypsnea
|
|
|
CS of nicotinic recptor tox from OP
|
fascilution of facial mm, eyelids and tongue, tetany then terminal weakness and paralysis. resp. failure, sometimes sympathetic effects confuse the muscarinic picture (mydriasis, tachycardia, hyperglycemia)
|
|
|
what can happens with NMJ tox from OP
|
fasciculations, tremors, weakness, can occur without CNS or ANS and can be prolonged
|
|
|
what can happen with CNS tox from OP
|
nervousness, apprehension, irritabilty, ataxia, convulsions, coma. Large animals take a saw-horse stance, rarely convulsions, pigs off hindlimbs
|
|
|
how can animals die from OP tox
|
respiratory failure, occasionally resp. failure
|
|
|
what can be seen on PM from OP
|
pulmonary edema, agonal hemorrhages in chest (on heart). edema of organs (including brain). Petechiation of organs e.g. kidney, GIT, dilated with fluid
|
|
|
how can you dx OP tox
|
signs and history
choinesterase levels in blood and brain. use whole blood for AChE in erytrhocytes response to antidotes (atropine) ifheart rate increases and mydriasis occurs then it could be carbamate |
|
|
what are some treatment options for OP tox
|
2PAM (pralidoxime)- acts competitively to break down complex of nicotinic and muscarinic effects.
atropine supportive care diphenhydramine |
|
|
how long does full recovery take for OP tox
|
2-4 weeks
|
|
|
when do you give atropine with OP tox
|
used for hypersecretion, bradycardia, bronchocontstriction, NOT LATER CNS or nitotinic signs
|
|
|
would you give atropine to a cat with OP tox that has cyanosis
|
no
|
|
|
when will you give diphendydramine to a patient with OP tox
|
when they have nicotinic signs
|
|
|
would you give diphenhydramine and atropine together to a patient with OP tox
|
fuck no
|
|
|
what does hypoxia do to cells to cause damage and death
|
reduces ox phos and ATP formation. ATP def. reduces the ATPase mechanism and allows ions to enter the cell and increase its osmolar gradient. drawing water into the cell leads to cloudy swelling, and early mainfestation of cell necrosis. Low ATP reduces other cellular activity. Anaerobic resp leads to lactate build up as the body tries to form ATP from glycogen. Reduced protein sysntehesis. Cell membrane damage, including intracellular membranes (mito)
|
|
|
what happens when the cellular membrane is damaged
|
phospholipids decrease in membranes through activation of phospholipases in response to increased cellular calcium. Intracellular proteases also increase in response to increased intracellular calcium. oxygen free radicals increase and also damage membranes. free fatty acids and other lipid breakdown comps also assault the membranes permeability is altered by toxins bindding to sulfhydral groups -SH in membrane proteins
|
|
|
what happens to free radicals in lipid membranes
|
they turns into peroxidases that fuck up the cell
|
|
|
what do free radicals do to protein
|
oxidize amino acidswht
|
|
|
what do free radicals do to DNA
|
cause breaks in strands by reacting with thymidine
|
|
|
what do antioxidants Vit E, A, C and gluathione GSH do
|
scavenge radicals and reduce formation
|
|
|
how are reactive forms of transition metals dealt with
|
Fe and Cu are minimized by binding the transferrin, ferritin, lactoferrin, and cerulospasmin
|
|
|
what do enzymes do to free radicals
|
scavenge free radicals and destroy oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide (catalase sueproxide dismutase and gluathione peroxidase)
|
|
|
how does oxygen behave in the body
|
oxygen has 2 unpaired electrons. normally atoms join into molecules to pair off their electrons. if not the molecule with the unpaired electron is known as a free radical and is usually short lived as in some chemical reactions
|
|
|
is O2 more or less stable than other free radicals
|
is more stable and less reactive
|
|
|
what is the gluthione redox cycle and what do we need to know
|
it protects against cell damage we need to know
NADPH releases a H+ and causes GSSG to be GSH (g-gylamyl cysteine) via GSH reductase when we have a reactive H2O2 in the body, The GSH goes to GSSG via GSH perioxidase and turns peroxide into two water molecues |
|
|
in the ox phos chain what happens if there are inhibitors
|
the mitochondira has fewer protons and less charge than the other side of the membrane. This leads to a proton gradient with a tendency to leak back. stops the chain
|
|
|
how is ox phos uncoupled
|
dissociate oxiation in the chain from phosphoryloation such that oxygen is still utilized but the engery goes to heat rather than phosphate gonds
|
|
|
what do aminoglycosides do to the kidney
|
reduced GFR. aminoglyocsides fuse to primary lysocome and forms myeloid bodies- this leads to lysosomal enzyme release. acute renal failure can happen in 5-7 days
|
|
|
what can cause hematuria
|
anticoagulant, rodenticides, chlorate, mercury, monesisn, phenylbutazone, braken fern, buttercup, oak, st. johns wort
|
|
|
what can cause hemoglobinuria
|
chlorate, copper, acetaminophen, phenothizines, brassica
|
|
|
what causes brown-black urine
|
acrons, rhubarb
|
|
|
what causes red urine
|
beets, myoglobin, pahtalene
|
|
|
what causes red-brown urine (does not settle on standing)
|
hemaglobinuria-brassica, chlorate, copper, acetominophen (cat), phenothiazine, ibuprofen
|
|
|
what causes red-pink urine (settles on standing)
|
hematuria- anticoagulants; chlorate; mercury; monensin (pig), St. John's wort
|
|
|
what causes reddish- gold urine
|
bilirubin, aflatoxins, blue-green algae, ragwort
|
|
|
what causes yellow urine
|
dinitro components, carrots
|
|
|
what causes orange urine
|
paprikia
|
|
|
what causes green urine
|
propfol
|
|
|
how is most acetaminophen excreted
|
as the glucoronide with some sulfate. this is why there is a greater tox in cats (deficient in glucuronyl transferase) dogs excrete about 50-60% and cats about 3%
|
|
|
acetominophem + p450=
|
hydroxamic acids
|
|
|
hydroxamic acid-> n-acetyl-b-benzo (BAD) + lots of GSH=
|
cell tox
|
|
|
even though n-acetyl-b-benzo reacts with GSH why doesn't the GSH chill the benzo the fuck out
|
the system is overwhelmed the benzo is irreversibly bound to macromolecues via the SH
|
|
|
what do we have to know about acetaminophen tox
|
hematuria
hemoglobinuria apparent recovery methemoglobin former dark chocolate urine face and paw edema N-acetyl cysteine (mucosmyst)- antidote |
|
|
what are some hypericin's that cause an increase of photosensitization
|
st. johns wort, fagopyrin from buckwheat, furocoumarins
|
|
|
what is congenital photosensitization
|
RARE porphyrins accumulate due to disturbances in heme synthesis. signs depend on concentration in skin. occurs in humans, cats, pigs, cattle, fox, squirrel
|
|
|
what is the cause of primary photosensitization
|
due to uptake of compound directly responsible for photosensitizing the animal (St. johns wort, buckwheat)
causes skin damage |
|
|
what is the cause of secondary photosensitzation
|
due to accumulation of photochemicals after excretory distrubances such as bile duct obstruction or liver dysfunction. bighead in sheep
liver damage |
|
|
if you use straight ketamine what can happen
|
excitatory effects
|
|
|
the vomitting central has what kind of synapse
|
dopaminergic
|
|
|
where is the vomitting center
|
in the dorsal lateral reticular system
|
|
|
what is the vomitting center close to that has a cholinergic synpase
|
salivation and respiration centers
|
|
|
which type of alveoli are less sensitive to intoxicants
|
type II (surfacts)
|
|
|
what mainly affects the liver but sometimes the lung
|
cortalaria spp has a reactive pyrrole metabolite that is carried to the lung to cause damage to vascular enodthelium
|
|
|
what does gossypol do
|
its a male contraceptivw
|
|
|
what do locoweed do to cells
|
causes vaculoes in cells
|
|
|
what do lupines do to calves
|
cause crooked calf dz
|
|
|
what does 2,4-D cause in dogs
|
myotnia
|
|
|
why is lead excretion slow
|
because its all up in the bones and is staying there
|
|
|
who are the methemoglobin formers
|
acetominophen
copper |
|
|
what causes wasting in dogs
|
lead tox
|
|
|
what is the antidote for lead
|
EDTA
succimer |
|
|
how do you screen for lead
|
ALA dehydrogenase activity
|
|
|
commonest source of lead tox
|
car battery
|
|
|
tx for arsenic tox
|
succimer (DMSA)
|
|
|
what does organiarsencial mainly affect
|
PNS, GIT
|
|
|
apparent recovery in
|
acetominophen
paraquat |
|
|
what toxicities can you use water as the antidote
|
organoarsenicals
mercury salt |

