![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is TOGAF?
|
TOGAF is an architecture framework — The Open Group Architecture Framework.
|
|
|
|
What does TOGAF Provide?
|
provides the methods and tools for assisting in the acceptance, production, use, and maintenance of an enterprise architecture.
|
|
|
|
How does the ISO/IEC 42010: 2007 defines ‘‘architecture’’?
|
‘‘The fundamental organization of a system, embodied in its components, their relationships to each other and the environment, and the principles governing its design and evolution.’’
|
|
|
|
What is the TOGAF Definition of "Architecture"?
|
A formal description of a system, or a detailed plan of the system at component level to guide its implementation
The structure of components, their inter-relationships, and the principles and guidelines governing their design and evolution over time. |
- Formal description
- Structure Components |
|
|
Blank
|
blank
|
/
|
|
|
What kind of Architecture does TOGAF deal with? (4)
|
1. Business Architecture
2. Data Architecture 3. Application Architecture 4. Technology Architecture |
4 types of architecture.
|
|
|
What is Business Architecture?
|
defines the business strategy, governance, organization, and
key business processes. |
BPM, stategy, Key Business Processes
|
|
|
What is Data Architecture?
|
describes the structure of an organization’s logical and physical data assets and data management resources.
|
logical and physical
|
|
|
What is Application Architecture?
|
provides a blueprint for the individual application systems to be deployed, their interactions, and their relationships to the core business processes of
the organization. |
blueprint, deployed, interactions, relationship
|
|
|
What is Technology Architecture?
|
describes the logical software and hardware capabilities that are required to support the deployment of business, data, and application services
|
Capabilities
|
|
|
What does Technology Architecture include?
|
This includes IT infrastructure, middleware, networks, communications, processing,
standards, etc |
communications, processing, network
|
|
|
What does the TOGAF Architecture Development Method (ADM) provide?
|
a tested and repeatable process for developing architectures.
|
tested, repeatable
|
|
|
What does the ADM include?
|
The ADM includes establishing an architecture framework, developing architecture content, transitioning, and governing the realization of architectures
|
|
|
|
All of these activities are carried out within an _____ ______ continuous architecture definition
and realization |
iterative cycle
|
|
|
|
The ADM allows organizations to ______ their ________ in a _______ manner in
response to business goals and opportunities. |
1. transform
2. enterprises 3. controlled |
|
|
|
What are the phases of the ADM?
|
1. The Preliminary
2. Phase A: Architecture Vision 3. Phase B: Business Architecture 4. Phase C: Information Systems Architectures 5. Phase D: Technology Architecture 6. Phase F: Migration Planning 7. Phase G: Implementation Governance 8. Phase H: Architecture Change Management 9. Requirements Management |
|
|
|
What is the The Preliminary of ADM?
|
Phase describes the preparation and initiation activities required to prepare to meet the business directive for a new enter prise architecture, including the definition of an Organization-Specific Architecture framework and the definition of principles.
|
|
|
|
What is the Phase A: Architecture Vision?
|
describes the initial phase of an architecture development cycle. It includes information about defining the scope, identifying the stakeholders, creating the Architecture Vision, and obtaining approvals.
|
Stakeholders, vision, approvals
|
|
|
What is the Phase B: Business Architecture?
|
describes the development of a Business Architecture to support an agreed Architecture Vision.
|
Business Vision
|
|
|
What is the Phase C: Information Systems Architectures?
|
describes the development of Information Systems Architectures for an architecture project, including the development of Data and Application Architectures.
|
Data and Application
|
|
|
What is Phase D: Technology Architecture?
|
describes the development of the Technology
Architecture for an architecture project. |
Hardware, Virtualization
|
|
|
What is Phase E: Opportunities & Solutions?
|
conducts initial implementation planning and the identification of deliver y vehicles for the architecture defined in the previous phases.
|
Planning and deliver
|
|
|
What is Phase F: Migration Planning?
|
addresses the for mulation of a set of detailed sequence of transition architectures with a supporting Implementation and Migration Plan.
|
Transition Architectures
|
|
|
What is Phase G: Implementation Governance?
|
provides an architectural oversight of the
implementation. |
Oversight
|
|
|
What is Phase H: Architecture Change Management?
|
establishes procedures for managing change to the new architecture.
|
Transition, change management
|
|
|
What is Requirements Management?
|
examines the process of managing architecture requirements throughout the ADM.
|
Requirements
|
|
|
What are the three categories to describe the type of Architectural Work?
|
1. A deliverable
2. An artifact 3. A building block |
|
|
|
What is a deliverable?
|
a work product that is contractually specified and in turn formally reviewed, agreed, and signed off by the stakeholders.
|
|
|
|
Deliverables represent ?
|
the output of projects and those deliverables that are in documentation form will typically be archived at completion of a project, or transitioned into an Architecture Repository as a reference model, standard, or snapshot of the Architecture Landscape at a point in time.
|
|
|
|
Deliverables represent the output of projects and those deliverables that are in _________ ________.
|
documentation form
|
|
|
|
A Deliverable will typically be archived at _______ __ ___ __________ or transitioned into an _________ ___________ as a reference model, standard, or snapshot of the _______ _________ at a _______ ___ _______.
|
1. completion of a project.
2. Architecture Repository 3. Architecture Landscape 4. point in time |
|
|
|
What is an Artifact?
|
a more granular architectural work product that describes an architecture from a specific viewpoint
|
Viewpoint
|
|
|
What are some examples of an artifact?
|
a network diagram, a server specification, a use-case specification, a list of architectural requirements, and a business interaction matrix.
|
|
|
|
Artifacts are generally classified as?
|
catalogs (lists of things), matrices (showing relationships between things), and diagrams (pictures of things).
|
|
|
|
An architectural deliverable may contain many _____ and ______ will form the content of the Architecture _________.
|
1. artifacts
2. artifacts 3. Repository |
|
|
|
What is a building block?
|
represents a (potentially re-usable) component of business, IT, or architectural capability that can be combined with other building blocks to deliver architectures and solutions.
|
|
|
|
Building blocks can relate to ‘‘________’’ or ‘‘________’’.
|
1. architectures
2. solutions |
|
|
|
What are the two types of Building Blocks?
|
1. Architecture Building Blocks (ABBs)
2. Solution Building Blocks (SBBs) |
|
|
|
What is an Architecture Building Blocks (ABBs)?
|
typically describe required capability and shape the specification of Solution Building Blocks (SBBs).
|
|
|
|
What is Solution Building Blocks (SBBs)?
|
represent components that will be used to implement the required capability.
|
|
|
|
What is an Enterprise Continuum?
|
a view of the Architecture Repository that provides methods for classifying architecture and solution artifacts as they evolve from generic Foundation Architectures to Organization-Speific Architectures.
|
|
|
|
What are the two complementary concepts of the Enterprise Continuum?
|
1. Architecture Continuum
2. Solutions Continuum. |
|
|
|
What is the Architecture Repository?
|
1. supports the Enterprise Continuum
2. it can be used to store different classes of architectural output at different levels of abstraction, created by the ADM |
|
|
|
By means of the ________ _________ and __________ __________, architects are encouraged to leverage all other relevant architectural resources and assets in developing an ________-________ ___________.
|
Enterprise Continuum
Architecture Repository Organization-Specific Architecture |
|
|
|
What are the major components within an Architecture Repository?
|
1. The Architecture Metamodel
2. The Architecture Capability 3. The Architecture Landscape 4. The Standards Information Base (SIB) 5. The Reference Library 6. The Governance Log |
|
|
|
What is the Architecture Metamodel?
|
describes the organizationally tailored application of an architecture framework, including a metamodel for architecture content.
|
|
|
|
What is the Architecture Capability?
|
defines the parameters, structures, and processes that support governance of the Architecture Repository.
|
Parameters, structure, processes, Govenance
|
|
|
What is the Architecture Landscape?
|
shows an architectural view of the building blocks that are in use within the organization today
|
|
|
|
What is the Standards Information Base (SIB)?
|
captures the standards with which new architectures must comply, which may include industry standards, selected products and services from suppliers, or shared services already deployed within the organization.
|
|
|
|
What is the Reference Library?
|
provides guidelines, templates, patterns, and other forms of reference material that can be leveraged in order to accelerate the creation of new architectures for the enterprise.
|
|
|
|
What is the Governance Log?
|
provides a record of governance activity across the enterprise.
|
|
|
|
In order to carry out architectural activity effectively within an enterprise, it is necessary to put in place an appropriate business _______ for architecture, through organization __________, _________, __________, _______, and ___________.
|
1. capability
2. structures 3. roles 4. responsibilities 5. skills 6. processes |
|
|
|
enterprise architecture practice should establish capabilities in the following areas:
|
1. Financial Management
2. Performance Management 3. Service Management 4. Risk Management 5. Resource Management 6. Communications and Stakeholder Management 7. Quality Management 8. Supplier Management 9. Configuration Management 10. Environment Management |
|
|
|
What are the benefits of architecture governance include:
|
1. Increased transparency of accountability, and informed delegation of authority
2. Controlled risk management 3. Protection of the existing asset base through maximizing re-use of existing architectural components 4. Proactive control, monitoring, and management mechanisms 5. Process, concept, and component re-use across all organizational business units 6. Value creation through monitoring, measuring, evaluation, and feedback 7. Increased visibility supporting internal processes and external parties’ requirements; in par ticular, increased visibility of decision-making at lower levels ensures oversight at an appropriate level within the enterprise of decisions that may have far-reaching strategic consequences for the organization 8. Greater shareholder value; in particular, enterprise architecture increasingly represents the core intellectual property of the enterprise — studies have demonstrated a correlation between increased shareholder value and well-governed enterprises 9. Integrates with existing processes and methodologies and complements functionality by adding control capabilities |
|
|
|
the TOGAF document is categorized according to the following four categories:
|
1. TOGAF Core
2. TOGAF Mandated 3. TOGAF Recommended 4. TOGAF Supporting |
|
|
|
the Architecture Repository that provides methods for classifying _______ and _______ artifacts as they evolve from _________ _________ Architectures to _____________--________ Architectures.
|
1. architecture
2. solution 3. generic Foundation 4. Organization-Speific Architectures |
|
|
|
The relationships between deliverables, artifacts, and building blocks.
|
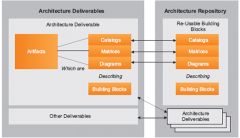
|
|
|
|
What is the Architecture Definition Document?
|

|
|

