![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Air Pressure Systems |
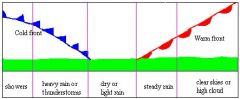
A high pressure system is a whirling mass of cool, dry air that generally brings fair weather and light winds.
A low pressure system is a whirling mass of warm, moist air that generally brings stormy weather with strong winds. Ex- Low pressure system brings cold weather to Austin. |
|
|
Continental Climate |

A measure of the degree to which the climate of a region typifies that of the interior of a large landmass. Ex- The continental climate of Greenland is cold and icy. |
|
|
Continentality (placement on continent) |
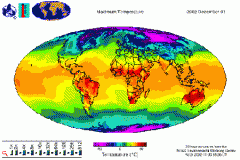
The difference between continental and marine climates characterized by the increased range of temperatures that occurs over land compared with water. Ex- Hawaii has a low continentality, since it is surrounded with water. |
|
|
Convection |
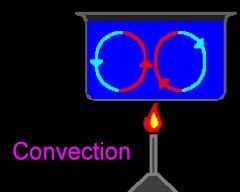
The heat transfer by mass motion of a fluid such as air or water when the heated fluid is caused to move away from the source of heat, carrying energy with it. Ex- Convection currents in ocean |
|
|
Convergent- Collision |

When two plates collide with each other, creating mountains, such as the Himalayas. Ex- The Himalayas |
|
|
Convergent- Subduction |
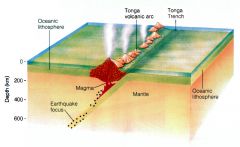
When two plates collide, but one of them goes (subducts) under the other, creating volcanoes. Ex- Yellowstone Caldera in Yellowstone National Park |
|
|
Divergent Boundary |
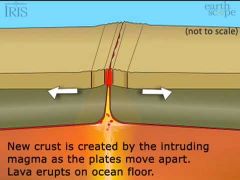
When two plates move away from each other, creating trenches (mainly in ocean) and rifts by letting new crust form. Ex- Marina's Trench |
|
|
Elevation |
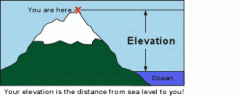
The height above a given level, especially sea level. Ex- Elevation of Denver, CO is very high. |
|
|
Erosion |

Taking away rock from one location. Ex- Water moving sediments from a beach |
|
|
GIS vs GPS |

GIS (Geographic Information Systems)- Uses technology to locate objects or events on the Earth's surface, used to solve problems. GPS (Global Positioning System)- Creates maps, determines/provides directions, and tracks resources. Ex- Phone GPS locating a Starbucks or GIS finding where to build it.
|
|
|
Latitude (climate process) |
-Biggest impact on climate. -Tilt+revolution= seasons –Equator = direct rays = warmer –Poles = indirect rays = colder Ex- The poles are the coldest places on Earth. |
|
|
Leeward vs Windward |
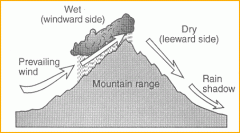
-Leeward= Drier side of mountain, not much rain, causes rain shadow.
-Windward= Wet side of mountain, more rain and vegetation. Ex- Windward Islands, Leeward Islands and Leeward Antilles (in the Lesser Antilles)
|
|
|
Mountain Barriers; Orographic Precipitation/Rain Shadow |

-Rain Shadow Effect - mountains block wind and rain. Ex- The Tibetan Plateau
|
|
|
Patterns |

Asks the "Who? What? When?" and "Where?" of geography. Ex- Pattern of where on Earth people tend to live most. |
|
|
Polar (High Latitudes) |

In the high latitudes on Earth, freezing cold all year. Some bimes include the tundra and coniferous forests. Ex- North Pole |
|
|
Processes |

Asks the "Why?" and "How?" of geography. Ex- The process of certain people's traditions (how they came to be) |
|
|
Rain shadow |
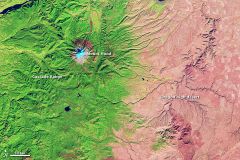
An area of dry land that lies on the leeward (or downwind) side of a mountain. Ex- The Atacama Desert in Chile is the driest desert on Earth because it is blocked from moisture on both sides (because of the Andes Mountains to the east and high pressure over the Pacific at a latitude which keeps moisture from coming in from the west).
|
|
|
Soil deposition—delta |
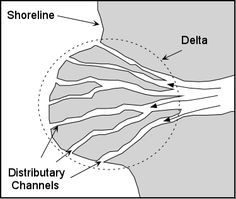
A landform that forms at the mouth of a river, where the river flows into an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, or reservoir. Deltas form from deposition of sediment carried by a river as the flow leaves its mouth. Ex- Nile River Delta |
|
|
Spheres of the earth (4) |

The four spheres that make up Earth: The Atmo, Litho, Hydro, and Biosphere. Ex- The Hydrosphere is all out water on Earth + the water cycle. |
|
|
Temperate (mid-latitude) |
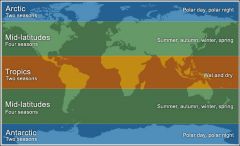
The changes in these regions between summer and winter are generally relatively moderate, rather than extreme hot or cold. Ex- California |
|
|
Transforming (faulting) |
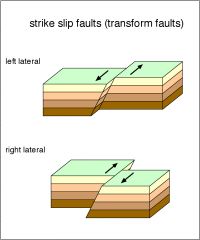
The landform that is created by transforming boundaries. Ex- San Andreas Fault |
|
|
Tropical (low latitudes) |
A region of the Earth surrounding the Equator, and it is hot all year. Ex- Africa (The part near equator) |
|
|
Weathering |

The process of breaking down rock. Ex- Weathering of rock with water that breaks off small particles |
|
|
Wind & ocean currents (climate) |
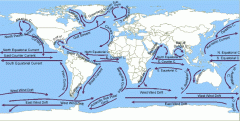
Currents flow around due to convection (warmer waters go from equator to the poles, then it cools, then it goes back to the equator), and circulate Earth. Ex- Convection pushing warm waters down to poles |

