![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
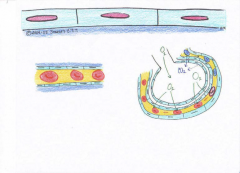
Simple Squamos
Functions: *very thin and permeable Location: *lines the inside of all blood |
|
|
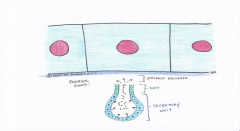
Simple Cuboidal
This tissue is a big secretor! It makes up all types of glands |
|
|
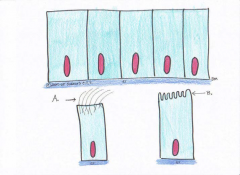
Simple Columnar
This tissue is a big absorber! Just look for the microvilli.
|
|

|
Psuedostratified Colimnar (false)
This tissue is ONLY found lining the upper respiratory |
|
|
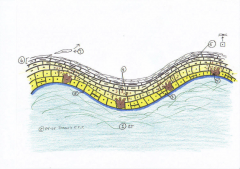
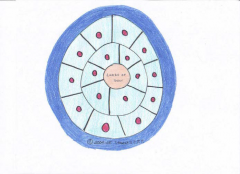
Stratified Squamous
This is the body’s WEAR-N-TEAR tissue This process is known as |
|
|
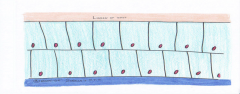
Stratified Cuboidal
This tissue secretes and is usually found in sweat glands and larger glands |
|
|
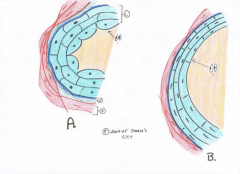
Stratified Columnar
This tissue isn’t located in too many places in the body. The main |
|
|
Transitional Epithelium
bladder |
|
|
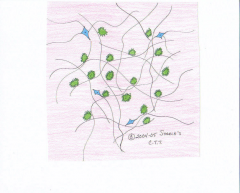
Loose Areolar
This is a common CT found under skin because of its vascularity and high nutrient content |
|
|
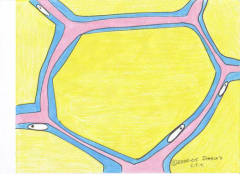
Loose Reticular CT
This tissue makes up the framework of non-hollow organs such as the spleen, This is a picture of a lymph node. |
|
|
Adipose- Our Friend Fat
This tissue is very vascular. |
|

|
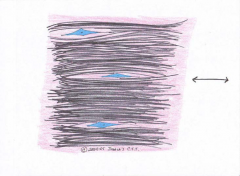
Dense Irregular CT
This tissue is found wrapping around bone The fibers run in ALL directions, which give this tissue strength in ALL |
|
|
Dense Regular
This tissue only makes up tendons, ligaments, and fibrous membranes that increase surface areas of the body. |
|

|
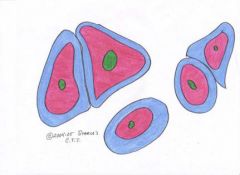
Dense Elastic
This tissue is mainly found under the transitional epithelium (urinary bladder), wall of respiratory pathways, and wall of blood vessels. |
|
|
Hyaline Cartilage
This tissue can be found at the ends of bones at joints where there is movement, nose, trachea and bronchiole tubes, and connects the ribs to the sternum |
|
|
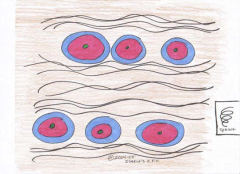
Fibrocartilage
This alternating rows of cells, matrix, and fibers creates a tissue that can take |
|
|
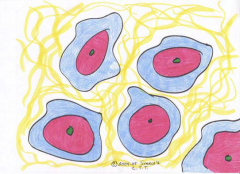
Elastic Cartilage
This cartilage is strong like hyaline, but because of the elastic fibers it is able to return to its original shape after extreme bending. |
|
|
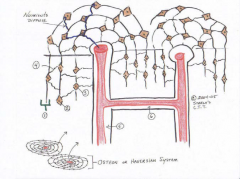
Bone (Osseous) Connective Tissue
The gel-like matrix of the cartilage has calcium salts added. This causes the matrix to harden.Very vascular! Large nerve supply.The matrix has a high amount of collagen fibers for strength |
|
|
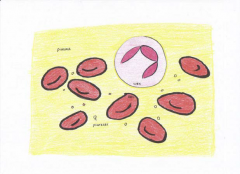
Blood (Connective Tissue)
Matrix is a fluid known as plasma. Fibers are used for blood clotting. Cells all originate from the red bone marrow |
|
|
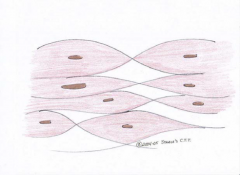
Smooth Muscle Tissue
involuntary muscles |
|
|
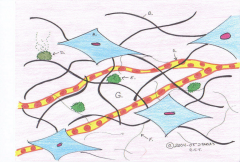
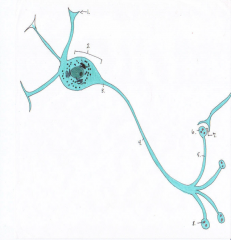
Nervous Tissue
|

