![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
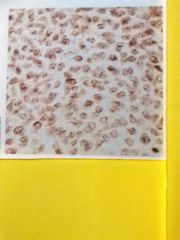
Mesenchyme connective Mesenchymal cells Almost no visible fibers in matrix |
Located in embryos, umbilical cord |
|
|
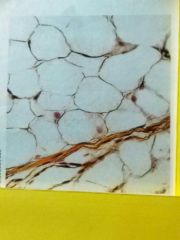
Adipose Adipocytes (marshmallows) with no space No visible fibers Matrix (fat inside cells) Function is storage of fat, cushioning, and insulation. |
Located Hypodermis (beneath skin), mammary glands, behind eyes, around kidneys. |
|

|
Reticular connective Widely scattered reticulocytes Scattered and somewhat cross hatching bundles of fibers Provides structure to soft organs and makes space for other cells to function |
Found in spleen and liver |
|

|
Areolar connective Widely scattered fibroblasts of varying size and shape Loosely arranged fibers arranged almost randomly in a semi solid ground substance Holds organs together in a flexible and elastic manner |
Found in lining in the urinary bladder |
|
|
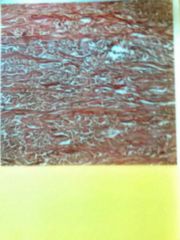
Dense irregular connective Scattered fibroblasts deadly packed by collagen fiber bundles that run parallel to each other, done run in different directions Provide strong yet flexible covering of organs that allow pressure in multiple directions with little stretching |
Located in dermis layer of skin, joint capsules, and organ covering (periosteum) |
|
|
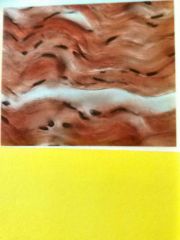
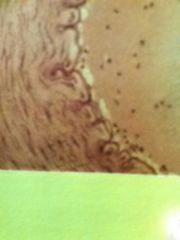
Dense regular connective Scattered fibroblasts surrounded densely by collagen fiber bundles that run parallel to each other but present wavy pattern Provide strong connection between other structure with strength in only one direction |
Located in tendons (connecting muscle to bone), ligaments (connecting bone to bone) |
|
|
Elastic connective Scattered fibroblasts surrounded by densely packed elastic fiber bundles Fiber bundles run parallel to each other with some small spaces between them They provide a stretchable wrapping to organs that must rapidly change size under pressure |
Aorta |
|

|
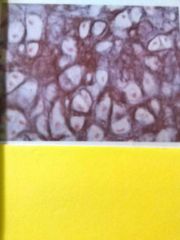
Hyaline cartilage Scattered chondrocytes somewhat resemble eyes Matrix with no visible fibers Provide rigid but lightweight support, provide south articulate surfaces |
Found in trachea, ribs, articular surfaces of bones |
|
|
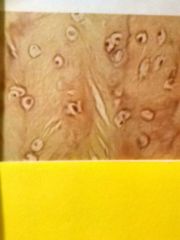
Elastic cartilage connective Scattered chodrocytes somewhat resemble eyes Matrix has large numbers elastic fibers that are not much longer than cells are wide Provides elastic shape to organs |
Found in ears, epiglottis (under tongue) |
|
|
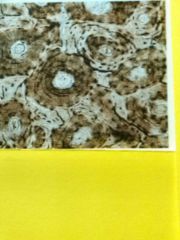
Fibro-cartilage connective Scattered chondrocytes resemble eyes Matrix has large number of collagen fibers that are much longer than cells are wide Provide shock absorption |
Found in intervertebral discs between vertebrae,menisci of knees |
|
|
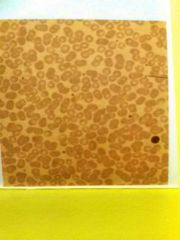
Bone connective Multiple concentric rings around central canal with scattered osteocytes. Shattered glass look. Matrix has collagen fibers embedded in calcium salts Provide strong, hard support and protection |
Located in bones |
|
|
Blood connective Large number of erythrocytes (small round cells with no nuclei), with few larger leukocytes (white blood cells that look red) Surrounded by fluid matrix (plasma) Carries oxygen and other nutrients through body |
Found inside blood vessels |
|

|
Simple squamous epithelium Thin layer allows for rapid exchange, smooth surface reduces friction |
Found lining internal spaces like alveoli of the lungs, glomeruli of the kidneys, inside blood vessels |
|
|
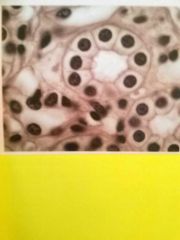
Simple cuboidal epithelium Function is secretion or absorption |
Found lining the tubules of the kidneys, lining various thyroid glands, lining various glandular ducts |
|
|
Simple columnar epithelium Function is secretion/absorption and protection May have goblet cells, May have cilia. |
Found lining intestines, lining stomach, gallbladder, and collecting ducts of kidney |
|

|
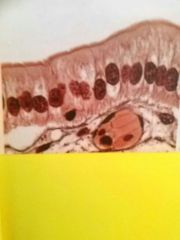
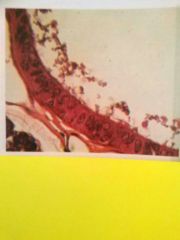
Stratified squamous epithelium Typically more than ten layers, deepest cells often more cuboidal while surface cells flattened. Thick layer provides protection from abrasion, May restrict fluid loss |
Epidermis of skin, lining esophagus |
|
|
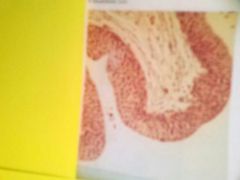
Stratified cuboidal epithelium Typically 2 layers rounded/cuboidal cells. Function is primarily secretion |
Found lining swear gland ducts |
|
|
Stratified columnar epithelium Protection |
Rare in humans, found in small regions male urethra |
|
|
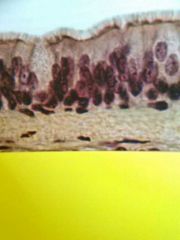
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium Single layer columnar cells with varying levels of nuclei Gives appearance of being stratified when it's not Often has cilia, then it's Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium (PSCC) Primarily provides protection but also secretion of mucous by goblet cells, cilia helps move mucous. |
Lining the respiratory tract |
|
|
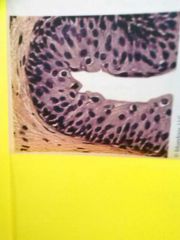
Transitional epithelium Multiple lattes of cells whose shapes vary as the organ they are in changes |
Found lining urinary bladder |
|

|
Skeletal muscle Very long fibers with perpendicular striations, multiple nuclei, very little space between fibers Provides connection to cause movement of bones |
Found in skeletal muscles such as biceps brachii |
|

|
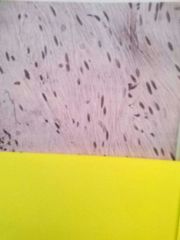
Cardiac muscle short fibers with perpendicular striations and occasional branching. Thicker perpendicular intercalated discs at ends of fibers, slight spaces between fibers. Contracts to cause pumping of blood |
Located in the heart |
|
|
Smooth muscle Short fibers with very noticeable large nuclei and no striations. Very little space between fibers. Provides contraction/relaxation to control shape of organs/diameter of openings |
Found in walls of multiple organs such as stomach and vessels. Found in skin, attached to hair follicles as arrector pilli muscle |
|
|
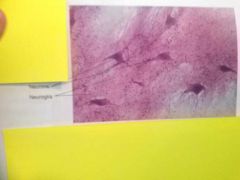
Nervous tissue Cells are neurons, neuroglia are non conductive cells that support neurons. Many more neuroglia than neurons |
Found in brain and spinal cord |

