![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
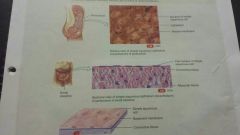
Epithelial-Simple Squamos |
-squamos -Single layer of flat cells -blood vessels, heart lining, peritoneum -filtration,diffusion,osmosis,& secretion in serous membrane |
|
|
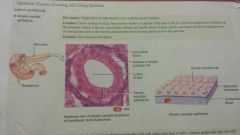
Epithelium- Simple Cuboidal |
-Cuboidal -single layer of cube-shaped cells -pancreas, surface of ovary, kidney tubules -secretion and absorption |
|
|
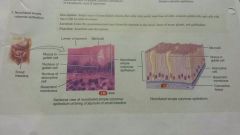
Epithelial- nonciliated Simple columnar |
-columnar -single layer of nonciliated column like cells -lines gastrointestinal tract, ducts of many glands, & gallbladder -secreation and absorption |
|
|
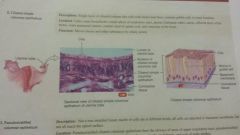
Epithelial-ciliated Simple columnar |
-columnar -single layer of ciliated column cells -uterine tube, uterus, brain, testes, spinal cords -moves mucus and other substances by ciliary action |
Hairy bridge |
|
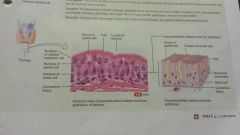
Epithelial- pseudostratified Simple columnar |
-columnar -not a true stratified tissue -respiratory tract, glands, epididymis, male urethra, trachea -secrerion and movement of mucus by ciliary action (ciliated), absorption and protection (nonciliated) |
|
|
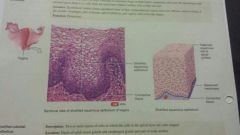
Epithelial-stratified squamos |
-squamos -several layers of cells -vagina, mouth, esophagus, larynx, tongue -protection |
|
|
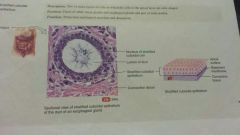
Epithelial-stratified cuboidal |
-two or more layers of cells -adult sweat glands, esophagus glands, and male urethra -protection and limited secretion and absorption |
|
|
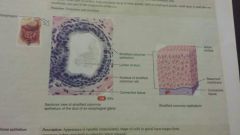
Epithelial-stratified columnar |
-columnar -several layers of irregular shaped cells -urethra, large excretory ducts of some glands, esophagus -protection and secretion |
|
|
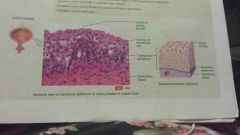
Epithelial-transitional |
-appearance is variable, squamos (stretched), cuboidal (relaxed) -urinary bladder and portions of uterters and urethra -permits distension |
|
|
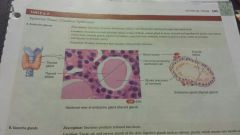
Epithelial- endocrine glands |
-secretory products diffuse into blood after passing through interstitial fluid -pituitary gland and pineal gland in brain, thyroid, parathyroid near larynx, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thymus -produce hormones that regulate various body activities |
|
|
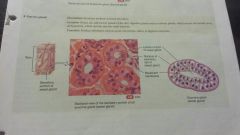
Epithelial- exocrine glands |
-secretory products released into ducts -sweat oil, earwax, digestive, skin -produce substance like sweat, oil, earwax,saliva or digestive enzymes |
Pineapple |
|
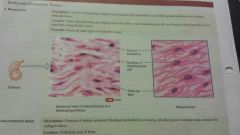
Connective-embryonic mesenchyme |
-consists of irregular shaped mesenchyme cells -embryo, under skin -forms all other types of conncective tissues |
|
|
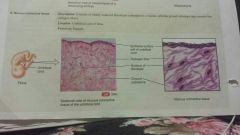
Connective-embryonic mucous |
-consists of widely scattered fibroblast embedded in a viscous, jelly like ground substance that contain fine collagen fibers -umbilical cord of fetus - support |
|
|

Connective-loose areolar |
-consists of fibers, several kinds of cells embedded in a semifluid ground substance -subcutaneous layer on skin, papillary region of dermis of skin, lamina of mucous, blodd vessles, nerves, and body organs -strength, elasticity and support |
Freeway |
|
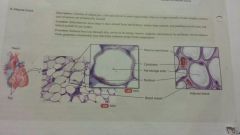
Connective-loose adipose |
-consists of adipocytes, cells specialized to store tryglycerides as a large centrally located droplet -subcutaneous layer deep to skin, around heart and kidneys, yellow bone marrow, and padding around joints and behind eyeballs in eye socket -reduces heat loss, energy reserve, support and protects. |
|
|
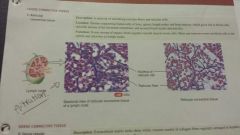
Connective-loose reticular |
-networkof inter lacing reticular fibers and reticular cells -stroma of liver, spleen, lymph nodes -filters and removes worn out blood cells in the spleen and microbes in lymph nodes |
|
|
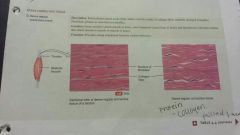
Connective- dense regular |
- extracellular matrix looks shiny white, collagen fibers regularly arranged in bundles, fibroblast presents in rows between bundles -tendons, ligaments, aponeuroses -provides strong attachment between various structures |
Picasso ocean |
|
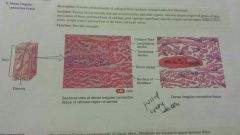
Connective-dense irregular |
-consist predominantly of collagen fibers randomly arranged and a few fibroblasts - dermis of skin -provides strength |
|
|
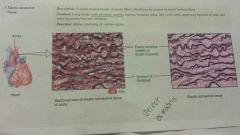
Connective-dense elastic |
-consists of predominantly elastic fibers -lung tissue, walls of elastic arteries, trachea, bronchial tubes, vocal cords, between some ligaments, suspensory lifament of penis -allows stretching of various organs |
|
|
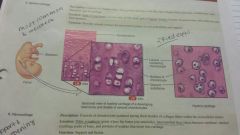
Cartilage-hyaline |
-consists of bluishwhite shiny ground substance with thin, fine collagen fibers and many chondrocytes, most common and weakest - ends of long bones, larnyx, trachea - provides smooth surfaces for movement at joints as well as flexibility and support |
|
|
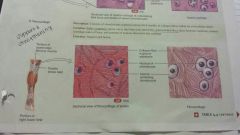
Cartilage-fibrocartilage |
-consists of chondrocytes scattered amoung thick bundles of collagen fibers within the extracellular matrix - pubic symphysis, intervertebral discs, knee cap -support and fusion |
Spagetti and fried eggs |
|
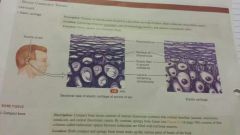
Cartilage- elastic |
Consists of chondrocytes located in a threadlike network of elastic fibers within the extracellular matrix -epiglottis, ear -gives support ans maintains shape |
|
|

Bone tissue- compact |
-Consists of osteons containing lamellae, lacunae, osteocytes, canaliculi, and central canals - bones - support, protection, storage, houses blood forming tissue, enable movement
|
|
|
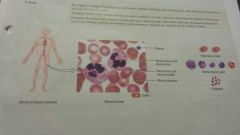
Connective- Liquid blood |
- red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets -with in blood vessels,and chambers of heart -red transport oxygen and carbon dioxide, white carry phagocytosisand allergic reaction and immune response, platelets essential for clottung of blood |
|
|
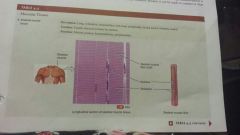
Muscular-skeletal |
-Long, cylindrical, striated fibers -bones by tendons -motion, posture,heat production,and protection |
|
|
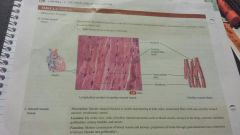
Muscular-cardiac |
-Branched, involuntary control - heart wall - pumps blood to all parts of the body |
|
|
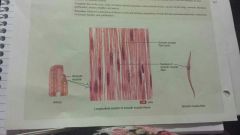
Muscular-smooth |
-spindle-shaped, involuntary control -artery walls, iris of eye, airways to lungs, stomach, intestines, gallbladder, urinary bladder and uterus -motion |
|
|
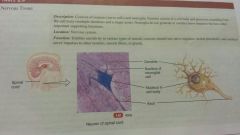
Nervous |
-neurons and neuroglia -netvous system -exhibits sensitivity to various types of stimuli converting into nerve impulses and conducts nerve impulses to other neurons, muscle fibers or glands |
|

