![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
116 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a tissue |
Groups of cells with similar structure and function |
|
|
How many kinds of connective tissue are there? (Level 1) |
4 |
|
|
What are the 4 kinds of connective tissue (level 1) |
Proper, bone, cartilage, liquid |
|
|
How many kinds of proper connective tissue are there? (Level 2) |
2 |
|
|
What are the 2 kinds of proper connective tissue? (Level 2) |
Loose and dense |
|
|
How many kinds of loose, proper connective tissue are there? (Level 3) |
3 |
|
|
What are the 3 kinds of loose, proper connective tissue are there? (Level 3) |
Reticulum, adipose, areolar |
|
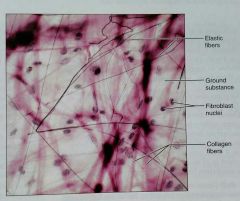
What is this kind of tissue |
Areolar, a loose, proper connective tissue |
|
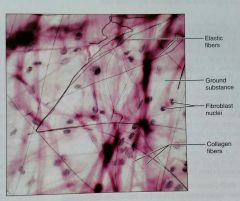
How would you describe this areolar, dense, proper tissue |
Gel-like matrix with all three fiber types (collagen, elastic, reticular) and fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, and some white blood cells |
|
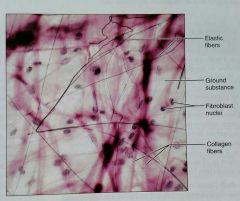
What is the function of the areolar, loose, proper connective tissue? |
Cushions organs, important role in inflammation, holds loose tissue fluid |
|
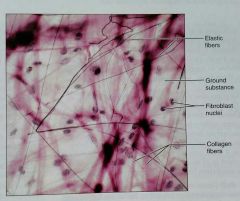
What is the location of areolar, dense, proper connective tissue |
Under epithelia (forms lamina propria), packages organs, surrounds capillaries |
|
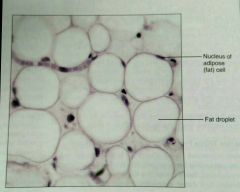
What is this kind of tissue |
Adipose, a dense, proper connective tissue |
|
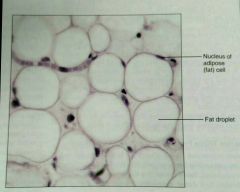
Is there a lot of matrix in the adipose, loose, proper tissue? |
No, there is little matrix because of the closely packed fat cells(adipocytes) |
|
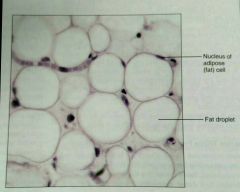
What is the function of adipose, loose, proper tissue? |
Provides reserve food fuel, insulates, supports and protects organs |
|
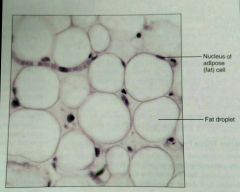
What is the location of adipose, loose, proper tissue |
Under skin, around kidneys and eyes, in abdomen, and breasts |
|
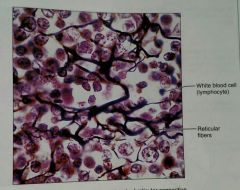
What is this kind of tissue |
Reticular, a loose, proper tissue |
|
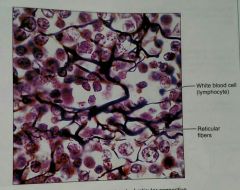
How would you describe a reticular, loose, proper tissue |
Loose network of reticular fibers in a matrix, with lymphocytes floating through |
|
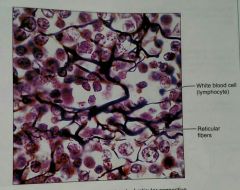
What is the function of a reticular, loose, proper tissue |
These reticular fibers form a soft skeleton that supports other cell types (white blood cells/lymphocytes, mast, and macrophages) |
|
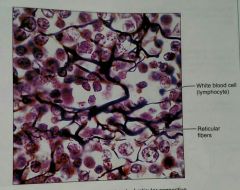
What is the location of reticular, loose, proper tissue |
Lymph organs |
|
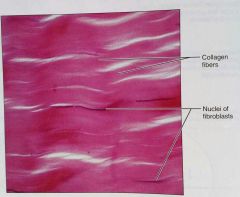
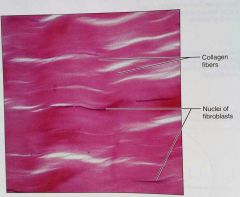
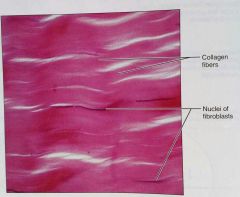
What is this kind of tissue |
Regular, a dense, proper tissue |
|
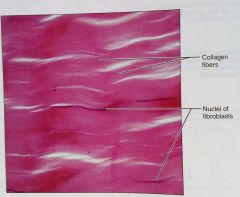
How would you describe regular, dense, proper tissue |
Parallel collagen fibers, some elastic fibers, and the main cell type is fibroblasts |
|
What is the function of regular, dense, proper tissue? |
Attaches muscles to bone or other muscles, can handle great stress if pulls in one direction |
|
What is the location of regular, dense, proper tissue |
Tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses |
|
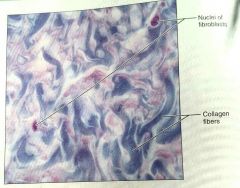
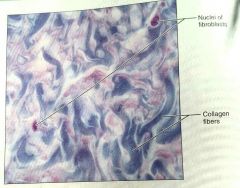
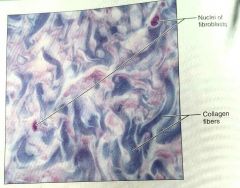
What is this kind of tissue |
Irregular, dense, proper tissue |
|
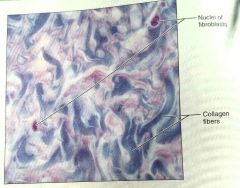
How would you describe irregular, dense, proper tissue |
Collagen fibers, some elastic fibers, with fibroblasts as the major cell type |
|
What is the function of dense, irregular, proper tissue |
Withstands tension from many directions, structural strength |
|
What is the location of irregular, dense, proper tissue? |
Fibrous capsules, dermis, submucosa of the digestive tract |
|
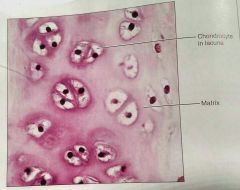
What kind of tissue is this |
Hyaline, a cartilage tissue |
|
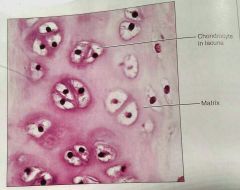
How would you describe hyaline cartilage |
Amorphous, firm matrix, collagen fibers, chondroblasts produce the matrix |
|
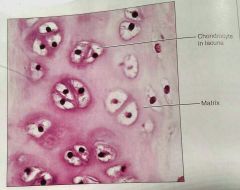
What is the function of hyaline cartilage |
Supports and reinforces, resilient cushion |
|
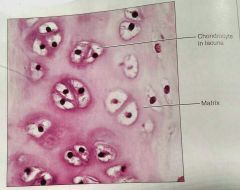
What is the location of hyaline cartilage |
Embryonic skeleton, covers long bones in joint cavities, costal cartilage, cartilage in nose, trachea, and larynx |
|
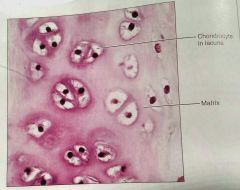
Where are the chondrocytes located in hyaline cartilage |
The lacuna |
|
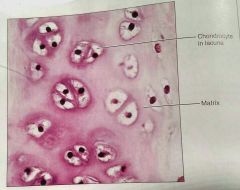
What fiber network is almost invisible in hyaline cartilage |
Collagen |
|
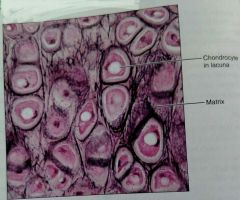
What kind of tissue is this |
Elastic cartilage |
|
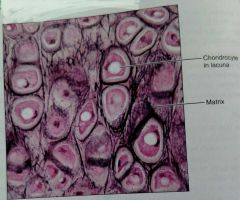
How would you describe elastic cartilage |
Similar to hyaline but more elastic fibers in the matrix |
|
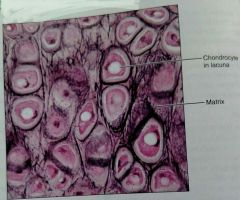
What is the function of elastic cartilage |
Maintains shape of structure but with great flexibility |
|
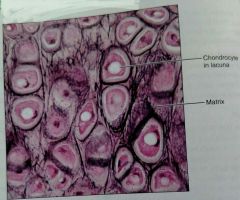
What is the location of elastic cartilage |
External ear, epiglottis |
|
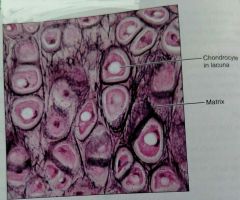
What are two defining characteristics of elastic cartilage |
Has more chondrocytes and elastic fibers can be seen under a microscope |
|
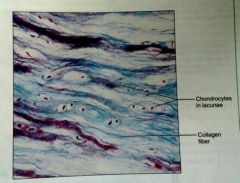
What is this kind of tissue |
Fibrocartilage |
|
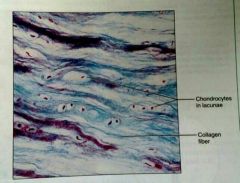
How would you describe fibrocartilage |
Matrix similar to hyaline, but less firm, predominate collagen fibers |
|
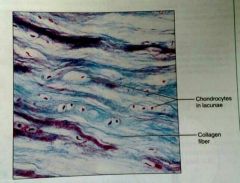
What is the function of fibrocartilage |
Absorption of comprehensive shock |
|
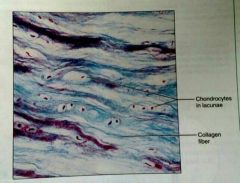
What is the location of fibrocartilage |
Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of knee joint |
|
|
What is the order (from least to most) in terms of the amount of collagen fibers in cartilage? |
Hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage |
|
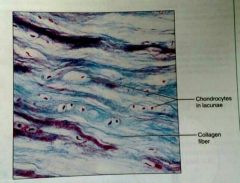
What is the defining characteristic of fibrocartilage |
Prominent collagen fibers |
|
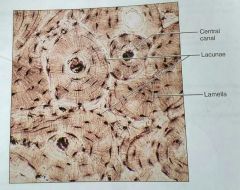
What kind of tissue is this |
Compact bone |
|
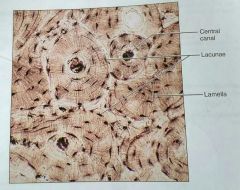
How would you describe compact bone |
Calcified matrix with many collagen fibers, osteocytes lie in lacunae, well vascularized |
|
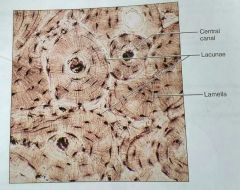
What is the function of compact bones |
Supports and protects, stores calcium and other minerals, core used in lymphocyte formation |
|
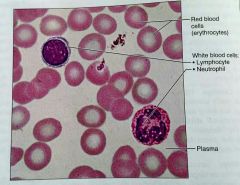
What is this kind of tissue |
Blood |
|
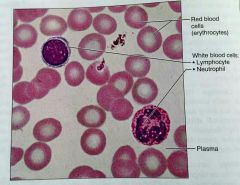
What is the matrix in blood called |
Plasma |
|
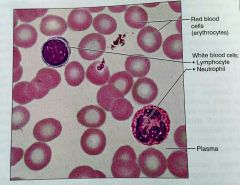
Where is blood hopefully located |
Within blood vessels |
|
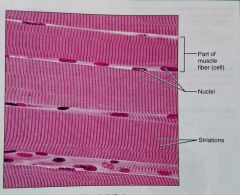
What is this kind of tissue |
Skeletal muscle |
|
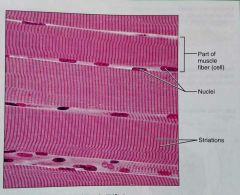
Is skeletal muscle tissue a kind of connective tissue |
Nope |
|
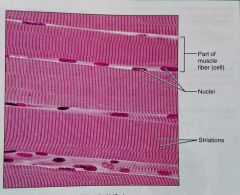
How would you describe skeletal muscle tissue |
Long, cylindrical, multinuclear cells, obvious striations |
|
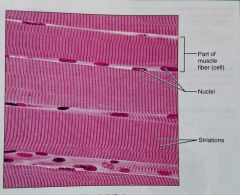
What is the function of skeletal muscle tissue |
Voluntary movement |
|
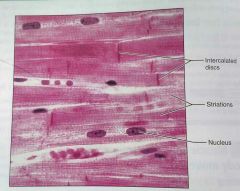
What is this kind of tissue |
Cardiac muscle tissue |
|
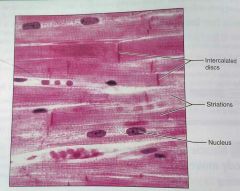
How would you describe cardiac muscle tissue |
Branching, striated, typically uninucleate, connect at specified junctions (intercalated discs) |
|
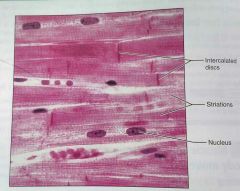
What is the function of cardiac muscle |
Contracts to propel blood into circulation |
|
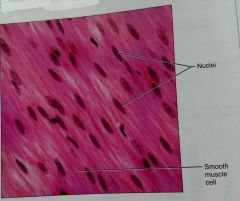
What is this kind of tissue |
Smooth muscle tissue |
|
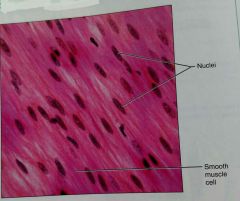
What is another view of smooth muscle tissue |

|
|
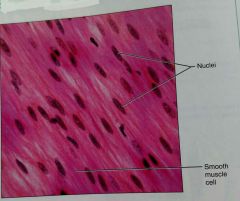
What is the function of smooth muscle tissue |
Propels substances along internal passageways |
|
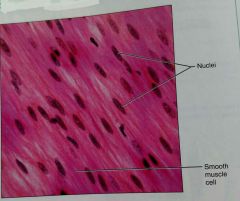
What is the location of smooth muscle tissue |
In the walls of hollow organs (intestines) |
|
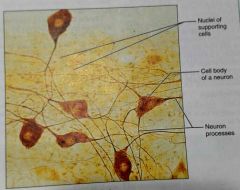
What is this tissue |
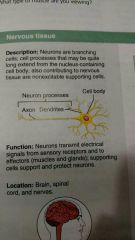
Nervous tissue |
|
|
What are the three kinds of muscle tissues |
Smooth, cardiac, skeletal muscle |
|
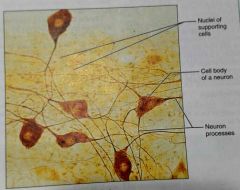
How would you describe nervous tissue |
Branching cells that extend their neural processes (axon), and dendrites to other neural cells |
|
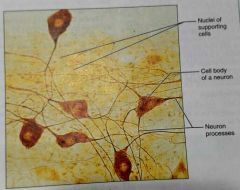
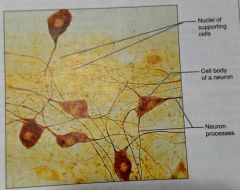
What is another view of neural cells |
|
|
What is the location of neural cells |
Brain, spinal cord, and nerves |
|
|
What are 3 characteristic of proper connective tissue |
Binding tissue, reservoir for salts and water, adipose storage |
|
|
What are 4 types of cells in proper connective tissue |
Fibroblasts, fibrocytes, defense cells, adipocytes |
|
|
What are 2 types of cells in cartilage |
Chondroblasts and chondrocytes |
|
|
What are 2 defining characteristics of cartilage |
Resists compression because of the amount of water held in matrix, acts as a cusion |
|
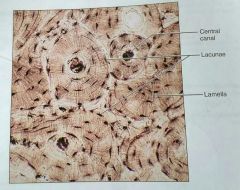
What are 2 types of cells in bones |
Osteoblasts and osteocytes |
|
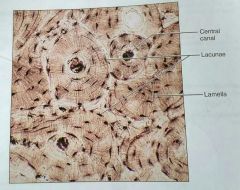
What kind of fibers are contained in bone tissue |
Collagen |
|
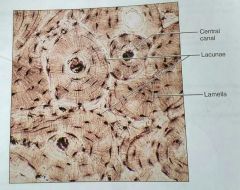
What is the matrix of bone tissue calcified with |
Inorganic salts |
|
|
What is the only tissue without fibers |
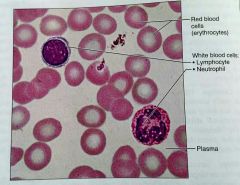
Blood |
|
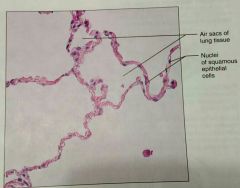
What is this kind of epithelial cell |
Simple squamous |
|
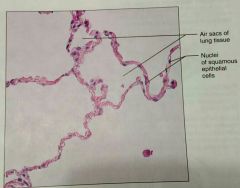
What is a description of a simple squamous epitheium |
Single layer of squamous (disc shaped with central nuclei) |
|
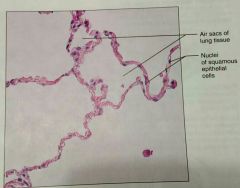
What is the function of simple squamous epithelial tissue |
Allows material to pass through by diffusion and filtration, secretes lubricating substances, not uses in places where protection is important |
|
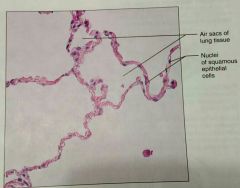
What is the location of simple squamous tissue |
Kidneys, air sacs of lungs, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, lining of ventral body cavity |
|
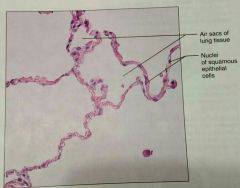
What is another view of simple squamous tissue |

|
|
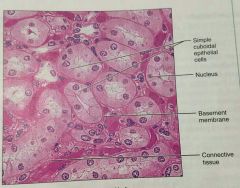
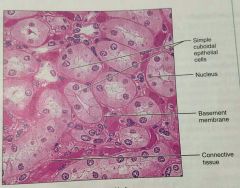
What is this kind of epithelial tissue |
Simple cuboidal |
|
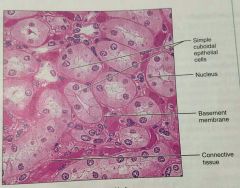
What is the function of simple cuboidal epithelium |
Secretion and absorption |
|
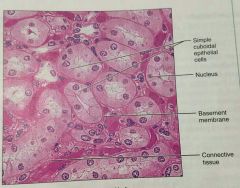
What is the location of simple cuboidal epithelium |
Kidney tubules, ducts of small glands, ovary surface |
|
What is another view of simple cuboidal epithelium |

|
|
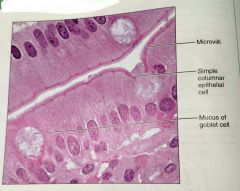
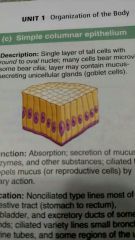
What is this type of epithelial tissue |
Simple columnar |
|
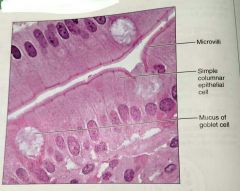
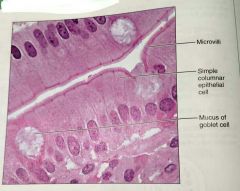
What is the function of simple columnar epithelium |
Absorption, secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances, ciliated type can propel mucus by cillia |
|
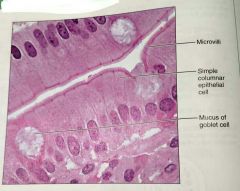
What is the location of simple columnar epithelium |
Noncilliated: digestive tract, gallbladder, excretory ducts of some glands. Ciliated: small bronchi, uterine tubes, some regions of the uterus |
|
What is another view of simple columnar epithelium |
|
|
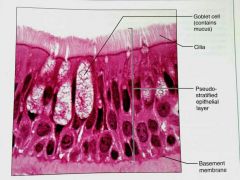
What is this kind of epithelial tissue |
Psudostratified columnar |
|
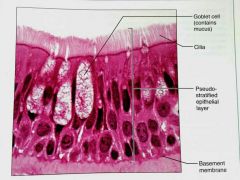
How would you describe Psudostratified epithelial tissue |
A single layer of cells with differing heights that make it look like multiple layers (stratified), may contain cilla |
|
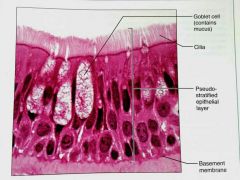
What is the function of Psudostratified columnar epithelial tissue |
Secretes mucus, propels mucus by ciliary action |
|
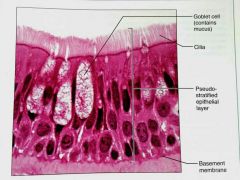
What is the location of Psudostratified columnar epithelium |
Noncilliated in males: in sperm carrying ducts and in large glands, Ciliated: lining of the trachea, most of the upper respiratory track |
|
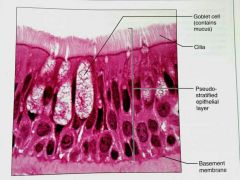
What is another view of Psudostratified columnar epithelial tissue |

|
|
|
How many different types of tissues are there? |
4 |
|
|
What are the 4 types of tissues |
Connective, epithelial, muscle, nerve |
|
|
What are 2 types of epithelial tissue |
Covering/lining (on ext and internal surfaces) and glandular (secretory in glands) |
|
|
How many characteristics are there of epithelial cells |
4 |
|
|
What are the 4 epithelial tissue characteristics |
1) apical (upper, free) and basal (lower, attached) surfaces. 2) cells are closely packed. 3) avascular (lack of blood vessels) 4) high rate of regeneration |
|
|
What does apical mean |
Upper, free area of a epithelial tissue. May contain microvilli |
|
|
What does basal mean |
The lower, attached surface on an epithelial tissue |
|
|
How are epithelial cells able to be so tightly compact |
Desmosomes and tight junctions |
|
|
What does avascular mean |
Lacking in vesicles or blood flow, happens in epithelial tissue |
|
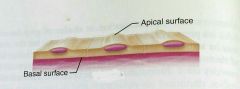
What is this kind of epithelial tissue |
Simple |
|
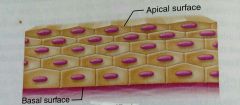
What kind of epithelial tissue is this |
Stratified |
|

What kind of epithelial tissue is this |
Squamous |
|

What kind of epithelial tissue is this |
Cuboidal |
|

What kind of epithelial tissue is this |
Columnar |
|
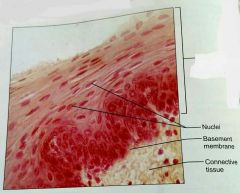
What is this kind of epithelial tissue |
Stratified squamous epithilium |
|
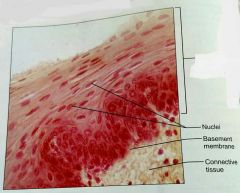
How would you describe the basal surface of stratified squamous epithilium |
Basal: cuboidal or columnar, metabolically active |
|
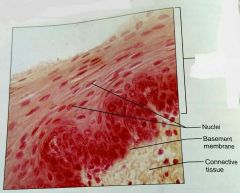
What is the function of stratified squamous epithelial tissue |
Protects underlying tissues that are subjected to abrasion |
|
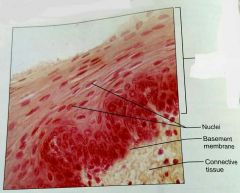
What is the location of stratified squamous epithelial tissue |
Nonkaritinized: moist linings of esophagus, mouth, and vagina. Karitinized: dry membranes of the epidermis |
|
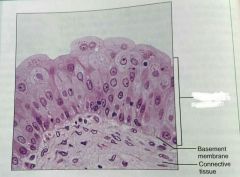
What is this kind of epithelial tissue |
Transitional epithelium |
|
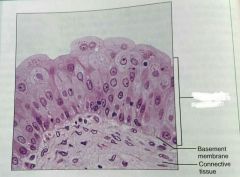
Describe transitional epithelium |
Basal cells are cuboidal or columnar, and apical cells are squamous like |
|
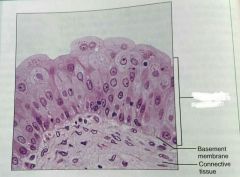
What is the function of transitional epithelial cels |
Stretchy so it can store urine |
|
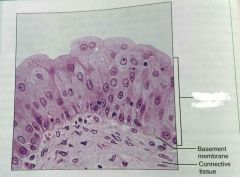
What is the location of transitional epithelium |
Lines ureters, bladder, and part of the urethra |
|
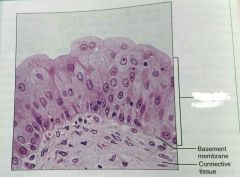
What is another view of transitional epithelium |
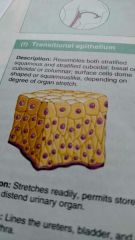
|
|
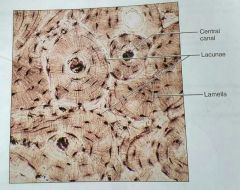
What is the lacuna in a compact bone tissue |
The matrix between the lamellae in an osteon |

