![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

this is an anterior anal grove. what genus is it ?
what genus would it be if it had an posterior anal grove or no anal grove |
Ixodes.
posterior- haemaphysalis none-dermacentor |
|
|
|
what acarines are of vet signifiicance?
|
ticks and mites
|
|
|
|
what is the name for a hard tick and a soft tick
|
hard- Ixodes
soft-argas |
|
|
|
What is The difference between a hard tick and a soft tick
|

Hard( Ixodes)-have exoskeleton scutum where as soft ( argas) don't also mouthpart is visible in hard ticks whereas in soft ticks it is not
. also soft ticks feed repeatedly. also mating takes place off the host in soft ticks. also they are resistant to drought |
In the name and the mouth!
|
|
|
name the 3 majour EU species of family Hard ( Ixodes) ticks and what they are associated with
|
Ixodes Canisuga- dog kennels
Ixodes hexagonus- hedge hogs Ixodes ricinus -( aka EU sheep tick)-all mammals and birds ( red water/ tick born fever due to anaplasma seen in all Rum. and dogs/louping ill due to falvi virus seen in sheep, cattle and grouse/ lyme disease due to B.burgdorferi seen in horses, cattle and dogs) |
CHR ( COOL Human Resources!!)
|
|
|
how do you differnetiate between the 3 majour species of the hard tick family ( Ixodes) Canisuga/hexagonus/Richius
|
Ixodes casnisuga- no overlaping spur on 1st coxa
Ixodes Richius- has overlaping spur on 1st coxa- the cool one Ixodes Hexagonus- has spur of 1st coxa but it does not overlap |
think spurs!!- not the football team though!!
|
|
|
what disease is the hard tick Dermacentor reticulatus associated with and where is it found
|
Babesia in dogs.
S.England and Wales |
|
|
|
how do you differentiate between Ixodes V other hard ticks
|
Ixodes- anal grove is anterior
others- haemaphysalis- posterior/ dermacentor -none |
they have their ass in their mouth !! like most important people.
|
|
|
where are the prefered sites of attachment for ticks?
|
thin skin areas- face/ears/axilla/inguinal region
|
thin skinned areas
|
|
|
where do the males and female ticks mate, how long are they on the host before they mate, what are the life stages of a tick, where does the female lay her eggs, how long do the larvae and nymph feed for, how long does the life cycle take and how long is the total time spent on the host
|
mate on host, 14 days during which the female takes a large blood meal to make the eggs, egg-larvae-nymph-adult ( die) , on the ground, around 6 days, 3 years with only 26-28 days spent on the host.
|
|
|
|
what do the females do before mating
|
have a large blood meal for 14 days
|
eat !!!
|
|
|
how does a one host tick lifecycle usually differ from a 3 host cycle like ixodes ricinus
|
larvae nymph and adults will all feed on the same host and as a result the lifecycle is usually faster ( 3 weeks instead of 3 years)
|
|
|
|
describe in detail the lifecycle of ixodes ricinus, beginning with the egg
|
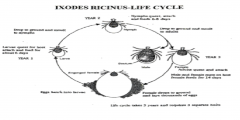
1000's eggs layed on ground by female. ( female dies).
eggs develope into larvae with 3 sets of legs. the larvae quest for a host by climbing to the top of a plant and detecting changes in the light and temp. when attached to the host they will feed on blood for around 6 days (yr 1) nymph then drop to the ground and molt to larvae which have 4 sets of legs. larvae quest for a new host and again feed on blood for around 6-8 days. they then drop of the host and molt to adults ( yr 2) the adults then quest for the final host and when they attach the female will take a large blood meal over 14 days before mating occurs. the blood meal is then converted to eggs. the life cycle takes 3 years and 3 separate hosts and yet only 26-28 days is spent on the host. |
|
|
|
where are ixodes ricinus ticks found and how is this influenced by climate. also what time of year are they usually most active.
|
humidity - need > 90 % to survive.
temp- only quest for host when the average day- night temp is > than 10 degrees. so...... they only survive in wet pasture or deciduous woodland and usually stop questing for hosts in autumn with peak activity being in april - may |
think climate ( humidity and temp)
|
|
|
what is the pathogenic siginificance of ixodes ricinus
|
Ixodes ricinus -( aka EU sheep tick)-all mammals and birds ( red water/ tick born fever due to anaplasma seen in all Rum. and dogs/louping ill due to falvi virus seen in sheep, cattle and grouse/ lyme disease due to B.burgdorferi seen in horses, cattle and dogs)
heavy infestations ( 1000's ) can cause anaemia. Also irritation, hide condemnation and secondary infections eg tick pyaemia seen in lambs due to stap. from skin or blow fly strike seen in sheep. |
|
|
|
ticks can transmit redwater/tick born fever/loupinh ill and lyme disease what sp are these diseases seen in and what causes the disease
|
red water in cattle - B.Divergens
tick born fever in Ruminants and dog - Anaplasma louping ill in sheep cattle and grouse - falvi virus lyme disease in dog, cattle and horse- B. Bergdorferi |
|

