![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List three procoagulant complexes in the coagulation pathway
|
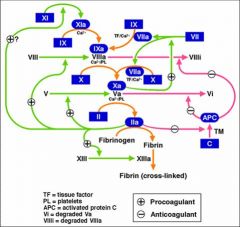
Two xases
TF/VIIa/PL IXa/VIIIa/PL Xa/Va/PL - ptothrombinase |
|
|
Which system is in place to inhibit the coagulation cascade and prevent formation of the pathological thrombus?
|
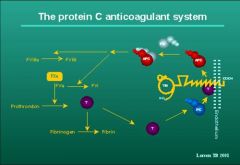
Protein C and cofactor protein S - inactivate VIIIa and Va
Antithrombin III - inactivate IIa and Xa Both prevent thrombus formation in the venous system |
|
|
What markers can be used to detect hypecoagulable states?
|
Fibrinopeptide A
Fibrinopeptide B D-D dimers |
|
|
The two mahor plasminogen activators are:
|
Tissue plasminogen activator TPA and
Urokinase Plasminogen activator uPA |
|
|
Inhibitors of plasminogen activation:
|
Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor -I (PAI-I)
Antiplasmin Thrombin Activatable Fibrinolysis Inhibitor (TAFI) |
|
|
Virchow's triad of thrombotic disorders:
|
Blood Stasis
Blood abnormality Blood vessel wall abnormality |
|
|
Factors that suggest spontaneous thrombosis in adults:
|
Major surgery
Malignancy Immobilization Pregnancy & post-partum oral contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy Myeloproliferative disorders Advancing age |
|
|
Factors that suggest need for laboratory evaluation of inherited prothrombotic disorder
|
Family hx
Age <40 Arterial thrombus Elevated PTT More than one thrombus |
|
|
Thrombophilia
|
Increased tendency to form clots either in veins or arteries. A complex trait - a polygenic disorder
|
|
|
Thrombosis in children:six major issues
|
1. DVT/PE treatment: LMWH
2. catheter-related (PICU, NICU, CA, TPN) 3. L-asp in leukemia 4. anti-phospholipid antibodies 5. cardiovascular, especially CHD 6. congenital prothrombotic disorders |
|
|
Difference between arterial thrombosis and venous thrombosis
|
Arterial thrombosis is due to pathology of platelets whereas venous is due to pathology of coagulation and anticoagulation factors
|
|
|
Difference btw primary and secondary thrombocytosis seen in arterial thrombosis:
|
Primary thrombocytosis, as occurs in the myeloproliferative syndromes, has been implicated in thrombosis - many more platelets presennt.
Secondary thrombocytosis occurs in malignancies, post-splenectomy, iron deficiency and sepsis. |
|
|
Three components required for normal hematopoiesis:
|
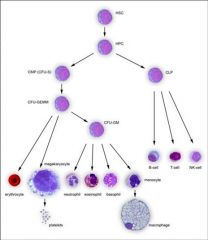
Multipotential hematopoietic stem cells (SEEDS)
Stromal cells & ECM (SOIL) Growth Factors (Manure). |
|
|
Where does hematopoiesis take place:
By third week of embryogenesis At the end of the first month of gestation During embryonic life When does the bone marrow become the main site of hematopoiesis |
By third week of embryogenesis - yolk sac
At the end of the first month of gestation - liver During embryonic life - spleen When does the bone marrow become the main site of hematopoiesis - at the fourth month of gestation |
|
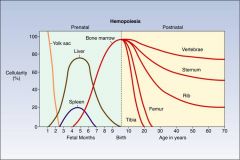
As bone grows, hematopoiesis shifts from ________ to ______
|
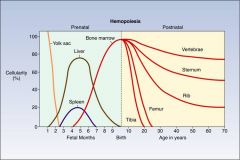
From long bones to axial skeleton
|
|
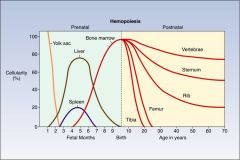
As bone grows, hematopoiesis shifts from ________ to ______
|
From long bones to axial skeleton
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of a blast cell?
|
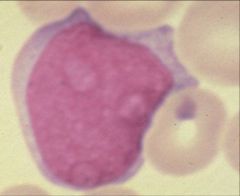
Big
Blue cystoplasm Bloated nuclueas Presence of one or more nucleoli A blast cell is more concenred with dividing than with its own maturation |
|
|
1 - Myeloblast - Big, blue n bloated
2 - Promyelocyte - smaller nucleus 3 - myelocyte - note clumping of chromatin 4 - metamyelocyte - indentation of nuclues and mature cytoplasm 5 - band neutrophil 6 - segmented neutrophil |

Name the cells at the different stages of differentiation of this granulocytes
|
|
|
Name the growth factors that are required by the following lineages:
Myeloid series Granulocytic lineage Monocytic lineage Eythroid proliferation Megakaryocytes |
Myeloid series - GM-CSF
Granulocytic lineage : G-CSF Monocytic lineage: M-CSF Eythroid proliferation: EPO Megakaryocytes: TPO |
|
|
What is the diameter of mature eyrthrocytes?
Size of erythrocytes compared to that of lymphocytes |
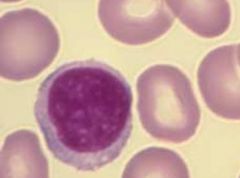
What is the diameter of mature eyrthrocytes? 7um
Size of erythrocytes compared to that of lymphocytes - eyrthocytes are smaller than the nucleus of a lymphocyte |
|
|
What characteristics make the eyrthrocytes deformable?
|
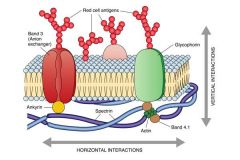
Lipid bilayer memberane and underlying cytoskeleton (consisting of spectrin, actin, ankyrin and band 4.2).
|
|
|
Shift curve to the rise, increase release of oxygen at the tissue level
|
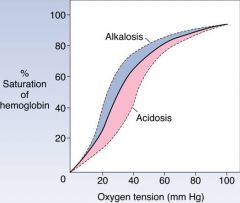
What is the effect of acidic conditions and increased levels of 2,3-DPG have on oxygen release at the tissue level?
|
|
|
List the three normal types of hemoglobin that exist
|
Hg alpha2 beta2 - adults
alpha2 gamma2 - fetus (1% adults) alpha2 delta2 - 2-3% adults |
|
|
Granulocytes - 50 -65% of circulating WBC's
Involved in inflammatory rxns, are phagocytic, contain bacterial killing enzymes Half life - 12hrs Have 3-4 lobes normally |
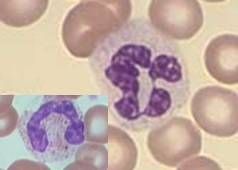
Name the most abundant leukocytes found circulating in blood
What is their main function? t1/2? |
|
|
Lymphocytes
Ctyotoxic lymphocytes ad=nd NK cells - 5 % of lymphocytes with large cytoplasm with granules |
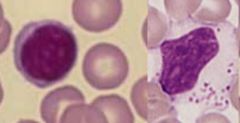
These are the second most abundant WBS's in adults and most abundant in children who are developing an immune system.
The lymphocyte that contains cytoplasmic grnaules make up 5% of this gp of cells and correspond to: |
|
|
Difference between basophils and mast cells?
|
Mast cells are found in tissue whereas basophils circulate ib blood. Their granules both contain histamine
|
|
|
What is contained in the granules of eosenophils?
|
Major basic protein
|
|
|
What is the lifespan of a platelet?
|
7-12 days
|
|
|
List the lab tests done to assess blood cells
|
CBC
Stained blood smear - Wright-Giemsa |
|
|
Define the following terms:
Anisocytosis Poikilocytosis Normocytic Polychromasia |
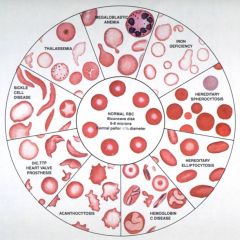
Define the following terms:
Anisocytosis - variations in red blood cell size Poikilocytosis - variation in red cell shape - sickle cell, target cells, spherocytes Normocytic - description related to MCV Polychromasia - increased reticulocyte count |

