![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
(Thorax -> Lumbar) transitional anatomy?
|
1. Loss of stabilizing costal ligaments
|
|
|
Denis Three Column Model?
|
1. Ant Column -- ALL to half vertebral body
2. Middle Column -- half vertebral body through PLL 3. Post Column -- anything post to PLL |
|
|
Where do compression fractures occur?
|
In the anterior column.
|
|
|
Location of burst fractures?
|
Due to failure of both the anterior and middle columns.
|
|
|
Which column determines stability?
|
Middle column, especially with respect to the PLL integrity.
|
|
|
Chance fracture?
|
Often due to MVA without shoulder belt:
1. Compression: anterior column 2. Distraction: middle + posterior columns |
|
|
Orientation of thoracic facet joints?
|
Frontal/Coronally orientated facet joints.
|
|
|
Orientation of lumbar facet joints?
|
Sagittally orientated facet joints.
|
|
|
Do curves of the spine help absorb/dissipate axial loads?
|
Yes.
Therefore, the straight thoracolumbar junction is uniquely susceptible to axial load fractures. |
|
|
Radiograph of compression fracture?
|
1. Wedge shaped vertebra
2. Posterior vertebral angle <100° (3. PVA >100° a/w unsable burst fracture) |
|
|
Denis Compression Fractures?
|
Type A: failure of sup+inf end plates
Type B: failure of sup end plate Type C: failure of inf end plate Type D: failure of vertebral body |
|
|
Most common Denis compression fracture?
|
Type B.
|
|
|
How to calculate the percentage of vertebral height loss?
|
1 - (ant vertebral height/post vertebral height)
|
|
|
Cobb's Angle?
|
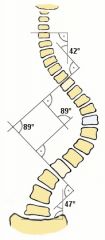
|
|
|
Where is back pain usually in kyphosis?
|
At apical segment or caudad.
|
|
|
Kummell's Disease?
|
Delayed post-traumatic osteonecrosis, may be AVN.
|
|
|
Mechanism of burst fractures?
|
Supraphysiological axial load drives surrounding tissue into the vertebral body, fracturing bone in process.
|
|
|
Denis classification of burst fractures?
|
Type A: failure of sup+inf end plates.
Type B: failure of sup end plate. Type C: failure of inf end plate. Type D: axial load + rotation Type E: axial load + lat flextion |
|
|
Most common Denis burst fracture?
|
Type B.
|
|
|
What portion of vertebral body compresses spine in burst fractures?
|
Typically bone from sup end plate.
|
|
|
Complications of chance fractures?
|
1. High rate if intra-abdominal injuries (45%).
2. 15% rate of neurologic involvement. |
|
|
Special consideration in tx of chance fracture?
|
Obtain CT of middle column.
Reduction of Chance fracture requires compression of middle/posterior columns. This could be hazardous in the setting of comminuted fractures of the middle column. |
|
|
What columns are involved in a fracture dislocation?
|
All three Denis columns.
|
|
|
Which column has the highest rate of neurological injury?
|
Fracture-dislocation.
|
|
|
Frankle Classification of neurological injury?
|
Class A: No motor or sensory
Class B: No motor, some sensory Class C: unuseful motor, some sensory Class D: useful motor, some sensory Class E: normal motor, normal sensory |
|
|
ASIA Impairment Scale?
|
Class A: No motor or sensory
Class B: No motor, some sensory Class C: motor in less than half the muscle groups, some sensory Class D: motor in more than half the muscle groups, some sensory Class E: normal motor, normal sensory |
|
|
CT measurements of spinal column for potential neuro compromise?
|
Ratio of midsagital:transverse diameters.
Elevated ratios correlated with increased risk of neuro involvement. |
|
|
What kind of injury if air in posterior subcutaneous tissue or within spinal elements?
|
Possibly flexion-distraction.
|
|
|
How to treat stable compression fractures?
|
Orthosis brace for 12 weeks.
|
|
|
How to treat pure Chance fracture?
|
If only damage to the boney parts:
1. Hyperextended position 2. Orthosis |
|
|
How to treat Chance fracture with soft tissue involvement?
|
Will not heal predictably, therefore surgery is required.
|
|
|
When to do spinal surgery?
|
There is no substantial difference in outcome between early and late surgical decompression and stabilization.
|
|
|
Holdsworth's model of the spinal column?
|
A two column model.
Anterior Column: PLL and anterior Posterior Column: Posterior to PLL |
|
|
Benefit of Holdsworth's model?
|
The majority of stability providing resistance to progression to kyphosis comes from the posterior column -- aka the middle is redundant.
|

