![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where does the capula (pleural cavity) of the lungs extend?
|
In to the neck, above the clavicles
|
|
|
In males, where are the nipples located?
|
4th intercostal space
|
|
|
Where does the liver lie with respect to the diaphragm?
|
The liver lies under the right dome of the diaphragm.
|
|
|
Where does the stomach and spleen lie with respect to the diaphragm?
|
The stomach and spleen lie under the left dome of the diaphragm.
|
|
|
Where does the Left kidney lie with respect to the vetebral column?
|
The left kidney lies anterior to the T12- L3 vertebrae
|
|
|
Where does the right kidney lie with respect to the vertebrae?
|
The right kidney lies one vertebrae lower at T11-L4. It is pushed down by the liver.
|
|
|
Where are the lungs in the thoracic cavity?
|
The lungs are located superior to a horizontal line passing through the nipples.
|
|
|
The thoracic cavity is divided into what three major spaces?
|
Right Pulmonary Cavity, Left Pulmonary Cavity and mediastinum
|
|
|
What encloses the thoracic cavity inferiorly?
|
The diaphragm
|
|
|
What are the components of the sternum?
|
Manubrium
Body Sternal Angle Jugular Notch |
|
|
How many pairs of ribs are there?
|
12 with costal cartilages involving 12 thoracic vertebrae and IV discs
|
|
|
Which ribs are the "True" ribs?
|
The true/vertebral costal are ribs 1-7
They attach directly to the sternum via costal cartilages. |
|
|
Which are the "false" ribs?
|
These are the vertebrochondral, ribs 8-10
|
|
|
The vetebrochondral ribs/false ribs attach to what?
|
They attach to the costal margin attachment
Ribs 8-9-10's cartilage meets up with the cartilage of rib 7= costal margin |
|
|
Which ribs are the floating ribs?
|
Floating ribs are 11 and 12
|
|
|
The articular facets articulate with what vertebra?
a)The vertebrae at the level of the rib and the one below b)The vertebrae at that level and the one above |
A) Articular facets articulate with the vertebrae at the level of the rib and the one BELOW it
|
|
|
What does the tubercle of the rib hold?
|
There is an articular facet in the tubercle for the transverse process of the spine
|
|
|
What is the costal groove?
|
A passageway in the bending rib for blood vessels
|
|
|
The first rib has how many articular facets on its head?
|
One
|
|
|
Ribs 10-12 have how many articular facets on their head?
|
Singular articulate facets
|
|
|
Where do ribs 11 and 12 end?
|
Muscular Abdominal Wall
|
|
|
What spinous process is at the superior angle of the scapula?
|
T2 spinous process is at the superior angle of the scapula
|
|
|
What spinous process is the inferior angle of the scapula?
|
T7 is the inferior angle of the scapula
|
|
|
What vertebral body level is the jugular notch?
|
Jugular notch is T2 vertebral body
|
|
|
The Sternal Angle is where what costal cartilages attach?
|
Sternal angle is where 2nd costal cartilages attach
|
|
|
The sternal angle is at the level of what IV disc
|
The IV disc between T4 and T5
|
|
|
What is the space that allows for movement of the breast?
|
Retromammary Space
|
|
|
Mammary glands are modified from what type of glands?
|
Sweat Glands that form lobules
|
|
|
The breast is situated over which ribs?
|
2nd -6th
|
|
|
The Sternal Angle of the scapula is where which costal cartilages attach?
|
2nd costal cartilages
Level is IV disc between T4 and T5 |
|
|
What is the main arterial supply of the breast? (3)
|
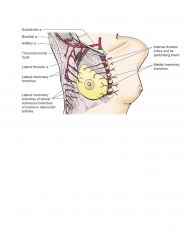
LIP
Lateral Thoracic (lateral Mammary branches) Internal Thoracic (medial mammary branches) Posterior intercostal arteries (2nd, 3rd and 4th intercostal spaces) |
|
|
What is the venus drainage of the breast?
|
Ax In Az
Lateral mammary veins Axillary Vein Medial Mammary Veins into Internal thoracic Azygous system via intercostal veins |
|
|
What is the innervation of the breast?
|
2nd to 6th intercostal cutaneous branches of intercostal nerves
|
|
|
What nerve innervates the nipple?
|
4th intercostal Nerve
|
|
|
Where does most lymph in the breast drain?
|
Laterally and superiorly to the Axillary Nodes
|
|
|
CC:
During Radical Masectomy, what nerve is often damaged resulting in winged scapula? |
Long Thoracic Nerve
|
|
|
What two muscles overlying the thoracic wall help in forced respiration?
|
Pec Major and Minor
|
|
|
External Intercostals are membraneous on which side(s)?
|
Anteriorly
|
|
|
Internal intercostals are membraneous on which side(s)
|
Posteriorly
Blood vessels run behind |
|
|
Innermost intercostals are membraneous on which side(s)?
|
Anteriorly and Posteriorly.
Because of vessels anteriorly and and pleura that is continuous from inside the thoracic cavity |
|
|
What purpose do the subcostal muscles serve?
|
Subcostals are on the Posterior Surface and span 2-3 intercostal spaces
*Strength for where the tubercles attach |
|
|
What muscles are major contributors to respiration?
|
External Intercostals
Internal intercostals Innermost intercostals |
|
|
What are the two main sources of blood to the thoracic cavity?
|
Posterior and Anterior Intercostals
1. Posterior intercostal arteries These originate from thoracic aorta (and the uppermost two originate from the superior thoracic artery, a branch from the costocervical trunk) 2) Anterior Intercostals. From internal thoracic artery, a branch of the subclavian |
|
|
What are the two routes that blood drains from the thoracic cavity?
|
Internal thoracic veins, drain to brachiocephalic veins
Azygous system, drain to superior vena cavae |
|
|
What two muscles overlie the breast?
|
Pec major and serratus anterior
|
|
|
Posterior Intercostal Arteries are which levels?
|
2nd 3rd and 4th intercostal spaces
|
|
|
Most lymph drains to which duct (left side of body)
|
Thoracic (Left)
|
|
|
How does breast cancer spread to the liver and diaphragm?
|
There is some drainage to the subdiaphragmatic nodes & liver
|
|
|
The thoracodorsal nerve innervates what muscle?
|
LatissimusDOrsi
|
|
|
A medical student needs to inject the subcostal space, where does he inject?
|
superior to the rib
|
|
|
Subcostals (back) are part what are a counterpart of what muscles?
|
transversus thoracic muscles
|
|
|
Transversus Thoracic are anterior or posterior
|
Anterior
|
|
|
What passes through the central tendon of the diaphragm at T8?
|
The inferior vena cava
Right phrenic nerve pericardiacophrenic artery pass through the central tendon at vertebral level T8 |
|
|
What travels through anterior to T10 in the diaphragm?
|
The esophagus and vagus nerves pass through the muscular part of diaphragm at vertebral level T10
|
|
|
Where is the hilum of the lung
|
T5-T7
|
|
|
Endothroacic pleura is composed of what type of tissue?
|
Loose CT
|
|
|
What are the contributors to respiration arising from the back?
|
Scalene muscles
Posterior serratus muscles Deep back muscles -->levator costorum, and transverse thoracic muscles |
|
|
Blood drains to the venous system in the thoracic wall via what veins?
|
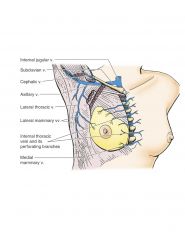
Internal Thoracic Vein
Azygous system- drains superior vena cava |
|
|
What is the name of air in the lungs
|
pneumothorax is air in pleural cavity
|
|
|
What is the name of water in the pleural cavity?
|
hydrothorax
|
|
|
What is the accumulation of blood in the pleural cavity?
|
Hemothorax
accumulation of blood in the pleural cavity |
|
|
What is a PE?
|
Obstruction of a pulmonary artery by a thrombus (blood clot) due to fat globule, air from leg vein
The clot may block blood flow in part or completely – when the embolus is large, patient suffers acute respiratory distress due to a major decrease in the oxygenation of blood & may expire in minutes |
|
|
What is the cardiodiaphragmatic recess?
|
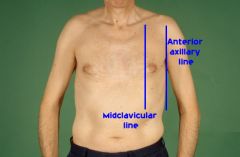
It is located below the 6th rib in the midclavicular line and the 8th rib in the midaxillary line.
|
|
|
What is the Relationship between visceral and parietal pleura?
|
|
|
|
What unites to form the hilum of the lung?
|
Visceral and Parietal layers are continuous
|
|
|
What is the main blood supply of the diaphragm?
|
Abdominal Aorta
|
|
|
What passes through the aortic hiatus at T12?
|
Thoracic duct and thoracic aorta
|
|
|
What passes through the muscular part of the diaphragm at T10?
|
Esophagus and Vagus N
|
|
|
What passes through the central tendon of the diaphragm at T8?
|
Inferior Vena Cava and Right Phrenic Nerve
|
|
|
Is the lung inside or outside the pleural cavity?
|
Outside
|
|
|
What vertebral level is the hilum of the lung formed?
|
T5 to T7
|
|
|
Where is the costal pleura located?
|
Adjacent to ribs and intecostal spaces
|
|
|
What does the pulmonary ligament do?
|
Movement of the lung.
It is an extension of the two pleural layers |
|
|
What is a loose CT layer that separates the parietal pleura from the internal surface of the thoracic wall?
|
Endothoracic Fascia
|
|
|
What is a recess in the lung?
|
Visceral and parietal pleura are separated in regions that are not invaded during quiet respiration
Allows for expansion during forced inspiration (and fluid collection) |
|
|
What is a region of the lung not invaded during quiet respiration?
|
A recess
|
|
|
Where is the costodiaphragmatic recess located?
|
Below the 6th rib in the midclavicular line and the 8th rib in the midaxillary line
|
|
|
How many lobes are in the right lung?
|
3
Separated by a horizontal and oblique fissure |
|
|
How many lobes does the left lung have?
|
2
Oblique fissure separates |
|
|
On the Right Lung, what is the cut edge where the visceral and parietal pleura unite?
|
Pulmonary Ligament
|
|
|
In the right lung, the bronchus is in what position with respect to the pulmonary arteries?
|
Posterior and lateral
|
|
|
On the left lung, the main bronchus is in what position to the pulmonary artery?
|
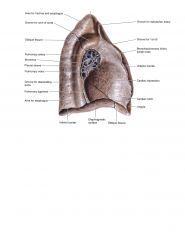
Inferior (note: mediastinal surface)
|
|
|
Each lung has how many bornchiopulmonary segments?
|
10
|
|
|
What is the largest subdivision of the lobe of a lung?
|
bronchiopulmonary segment
|
|
|
What artery supplies the lungs?
|
Bronchial
|
|
|
Why can't blood oxygenation reach 100%?
|
Bronchial veins unite in the lungs with the pulmonary veins.
|
|
|
What does the bronchial vein drain into on the right?
|
Azygous Vein
|
|
|
Blood from the bronchial vein on the left drains into what?
|
hemiazygous Vein
|
|
|
Nerves to the lungs and visceral pleura arise from what?
|
pulmonary plexuses
|
|
|
What is the parasympathetic innervation of the lung and pleura?
|
Vagus (constrict)
|

