![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe the boarders of the thoracic inlet/Superior thoracic aperture |
Both the right and left ribs create the sides of the inlet, T1 is the posterior border, and the superior end of sternum creates the anterior portion |
|
|
Describe the boarders of the thoracic outlet/Inferior thoracic aperture |
Xiphisternal joint, chondral attachment to sternum, rib 12, T12 note: This is closed b the diaphragm |
|
|
What makes up the sternal region (median anterior wall)? |
-Manubrium -Body of sternum -Clavicular and chondral attachments to sternum -Xyphoid process |
|
|
Where is the midsternal line located? |
Right at the midline; cutting the sternum in half |
|
|
Where is the midclavicular line located? |
in the middle of the clavicle; cutting the clavicle in half |
|
|
Describe the scapular line |
The line is passing through the inferior angle of the scapula |
|
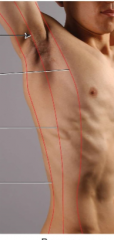
Name the: A-Lateral Line B-Middle line C-Medial line |
A-Posterior axillary line (vertical line dropped at lateral border of axillary fossa) B-Midaxillary line (vertical line through middle of axillary fossa) C-Anterior axillary line (vertical line dropped at lateral border of pectoralis major) |
|
|
Where is the sternal angle located at the vertebral level (at what rib)? |
-Rib 2 -T4 - T5 |
|
|
Where is the root of the spine of the scapular located at the vertebral level? |
Vertebral level of T4, spine of T3 |
|
|
Where is the inferior angle of the scapula located? |
-overlies rib 7, points to rib 8 -vertebral level T8, spine of T7 |
|
|
What kind of joint is the sternoclavicular joint? |
-synovial joint -saddle type |
|
|
What kind of joint is the manubriosternal joint? |
-secondary cartilaginous joint (immovable) |
|
|
What kind of joint is the xiphisternal joint? |
primary cartilaginous joint (immovable) |
|
|
What vertebral level does the manubrium lie? |
it will span between T3 and T4 |
|
|
What vertebral level does the body of the sternum lie? |
T5 to T9 |
|
|
what vertebral level does the xiphoid process usually lie? |
T9 but can come down to T10 |
|
|
What is the function of the thoracic cavity? |
-Protection of thoracic and abdominal viscera -Respiration, resists internal pressures of inspiratory movements -Attachment and support of upper limb -Musculature attachments of upper limbs, neck, abdomen and back |
|
|
What are the true ribs? |
1st through the 7th pair |
|
|
what are the false ribs? |
8th to the 12t pair |
|
|
What are the floating ribs? |
11th and 12th pair |
|
|
Describe the head of the rib |
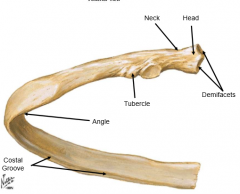
vertebral end of rib; has two facets for articulation with vertebral body of thoracic vertebrae (more specifically, the demifacets) |
|
|
Describe the angle of the rib |
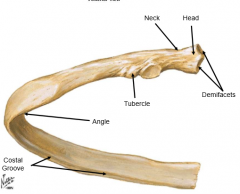
point of greatest curvature |
|
|
What is the costal groove? |
Houses the interscostal neurovascular bundle |
|
|
Pec major: -proximal attachment -distal attachment -innervation -blood supply |
-Prox: Clavicle, sterum, upper 6 costal cartilages -Dis: lateral lip of intertubercular groove -Innervation: medial and lateral pectoral nerves -Blood supply: pectoral branches of the thoracoacrmial trunk |
|
|
Pec minor: -proximal attachment -distal attachment -innervation -blood supply |
prox: 3-5th ribs dis: coracoid process of scapula innervation: medial pectoral nerve blood supply: pectoral branches of thoracoacromial trunk |
|
|
seratus anterior: -Proximal attachment -distal attachment -innervation -blood supply |
prox: Upper 8 or 9 ribs Dis: medial border of scapula Blood supply: lateral thoracic artery innervation: long thoracic nerve |
|
|
How many facets are there on each thoracic vertebrae? List them |
3 -Inferior facet -Superior facet -Transverse costal facet |
|
|
How do the ribs articulate with the vertebrae (how do they align with the vertebrae)? |
The vertebrae of the same number and the vertebrae above it; Rib 4 articulates with T3 and T4 |
|
|
what makes up the costovertebral joint? |
a demifacet on a rib head and a facet on a thoracic vertebrae |
|
|
What makes up the costotransverse joint? |
where the rib meets the transverse process of a a thoracic vertebrae |
|
|
what are the muscles of inspiration? |
Principal: External intercostals; interchondra part of internal intercostals; diaphragm Accessory: Sternocleidomastoid; anterior and middle scalenes; posterior scalenes |
|
|
What are the muscles of expiration? |
Quiet breathing: Expiration results from recoil of lungs and rib cage Active breathing: Internal intercostals (excluding interchondral part); abdominals (rectusd and transverse; oblique muscles (external and internal) |
|
|
What are the intercostal muscles innervated by? |
local intercostal nerves (ventral primary ramus of spinal nerve) |
|
|
How do the fibers run in the external intercostal muscles? |
anteroinferiorly from upper to lower tin |
|
|
How do the external intercostal muscles move the ribs? |
They elevate the ribs (aiding in inhalation) |
|
|
where are the attachments of the external intercostal muscles? |
they start at the costal tubercle and attach to the costochondral junction -Extends to sternum as external (anterior) intercostal membrane |
|
|
How do the internal intercostal muscles function on the ribs? |
Costal portion: depresses ribs (aiding in exhalation) |
|
|
How do the fibers run in the internal intercostal muscles? |
posteroinferiorly from upper to lower rib |
|
|
How do the internal intercostal muscle orient? |
the muscle starts at the lateral border of the sternum and runs to the costal angle -extends to vertebrae as internal (posterior) intercostal membrane |
|
|
what action do the innermost intercostals have on the ribs |
-elevation (aids in inhalation) |
|
|
Where are the innermost intercostals located? |
In the third muscular-layer of the intercostal space |
|
|
Where are the subcostal muscles located? |
internally on the posterior thoracic wall |
|
|
How do the subcostal muscles move the ribs? |
Elevate (aiding in inhalation) |
|
|
Where and how are the subcostal muscles oriented? |
the muscle crosses more than one intercostal space on the posterior thoracic wall |
|
|
Where and how is the transverse thoracis oriented? |
Lower sternum to the internal surface of the 2nd - 6th costal cartilage -Located in the third muscular layer f the intercostal space anteriorly |
|
|
What attachments does the diaphragm have? |
Sternal, costochondral and lumbar |
|
|
How many intercostal spaces are there? |
11 |
|
|
How are the subcostal muscles, transversus thoarcis, and the thoracic diaphragm connected to the parietal pleura? |
They are firmly attached to the internal surface of the thoracic wall by endothoaracic fascia Note: this is the most internal part of the intercostal space |
|
|
Where is the neurovascular bundle housed? |
in the costal groove between the second and third muscular layers |
|
|
What are the intercostal nerves? |
-Thoracic nerves -Thoracoabdominal nerves (subset of thoracic nerves) |
|
|
Where do the thoracic nerves originate? |
T1 - T11 |
|
|
Where do the thoracoabdominal nerves originate? |
T7 - T11 |
|
|
where do the intercostal arteries anastomose? |
within the intercostal space |
|
|
What are the anterior internal thoracic arteries and what do they split into? |
Internal thoracic artery (terminates 6th IC space) Splits into musculophrenic (splits laterally) and superior epigastric (splits medially) arteries |
|
|
What does the musculophrenic artery supply blood to? |
7th-9th space |
|
|
There are no anterior intercostal arteries in spaces ____ and ___ |
10 and 11 |
|
|
What are the posterior interthoracic arteries? |
-Superior intercostal -Thoracic aorta supply spaces 3-11 |
|
|
superior (supreme) intercostal artery is a branch of what? |
the costocervical trunk |
|
|
What spaces does the supreme intercostal artery supply? |
1st and 2nd spaces |

