![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Energy |
The capacity to do work. |
|
|
Radiant energy |
Solar energy, that comes from the sun. |
|
|
Thermal energy |
Associated with random motion of atoms. |
|
|
Chemical energy |
Energy that is stored within the structural units of chemical substances. |
|
|
Potential energy |
Energy available by virtue of an object's position. |
|
|
Law of conservation of mass |
Total quantity of energy in the universe is assumed constant (Matter can't be created or destroyed). |
|
|
Heat |
The transfer of energy between two bodies that are at differwnt temperatures. |
|
|
Thermochemistry |
The study of heat change in chemical reactions. |
|
|
System |
Specific part of the universe that is of intrest to us. |
|
|
Surroundings |
The rest of the universe outside the system. |
|
|
Open system |
Can exchange mass and energy, usually in the form of heat with its surroundings. |
|
|
Closed system |
Allows transfer of heat but now mass. |
|
|
Isolated system |
Doea not allow the transfer of either mass or energy. |
|
|
Exothermic process |
Any process that gives off heat, that transfers thermal energy to the surroundings. |
|
|
Endothermic process |
Heat has to be supplied to the system by the surroundings. |
|
|
Thermodynamics |
The study of the interconversion of heat and other kinds of energy. |
|
|
State of a system |
The value of all relevant microscopic properties(composition, energy, temperature, pressure, and volume). |
|
|
State functions |
Properties that are determined by the state of the system, regardless of how that condition was achieved. |
|
|
First law of thermodynamics |
Energy can be converted from one form to another, but cannot be created or destroyed. |
|
|
Work |
Work = Force × Distance. (w = f × d) |
|
|
Calorimetey |
The measurment of heat changes. |
|
|
Specific heat |
Amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of the substance by one degree Celsius. |
|
|
Heat capacity |
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a given quantity of the substance by one degree Celsius. |
|
|
Standard enthalpy of formation |
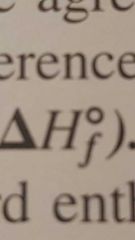
By convention, the standared enthalpy of formation in its most stable form, is zero. |
|
|
Standard state |
Substances are in the standard state at 1 atm. |
|
|
Standard enthalpy of reaction |
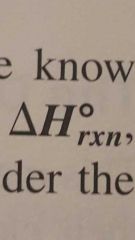
The enthalpy of a reaction carried out at 1 atm. |
|
|
Hess' law |
When reactants are converted to products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps. |
|
|
Heat of solution (Enthalpy of solution) |
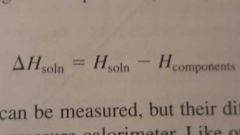
The heat generated or absorbed when a certain amount of solute dissolves in a certain amount of solvent. |
|
|
Latrice energy (U) |
The energy required to completley seperate one mole of a solid ionic compound into gaseous ions. |
|
|
Heat of hydration |
The enthalpy change associated with the hydration process. |
|
|
Heat of dilution |
The heat change associated with the dilution process. |
|

Key Equations |

|
|
|
Thermochemical equations |
Show the enthalpy changes as well as the mass relationships. |

