![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
126 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Stages of the Canine Cycle
|
Proestrus
Estrus Diestrus (Metestrus) Anestrus |
|
|
In the bitch __________ is a very distinct entity unlike in the cow/mare/other spp.
|
Proestrus
|
|
|
Proestrus
|
initiation of overt activity
|
|
|
Estrus
|
Time the bitch will stand (time for breeding)
|
|
|
Stages of the Canine Cycle
|
Proestrus
Estrus Diestrus (Metestrus) Anestrus |
|
|
Diestrus (Metestrus)
|
pregnancy or pseudo-pregnancy
-will be the same length whether pregnancy or pseudo-pregnancy |
|
|
Estrus
|
Time the bitch will stand (time for breeding)
|
|
|
physical changes in proestrus in the bitch
|
turgid swelling of vulva, hemorrhagic discharge from vulva
|
|
|
vaginal cytology in proestrus
|
cornification of squamous epithelium lining of vagina
|
|
|
what does the vaginal cytology tell you
******************************************** NEED TO KNOW!!! |
1. is she under the influence of estrogen or not
2. does she have inflammation or no |
|
|
what is the bitch's behavior in proestrus?
|
non-acceptance of the male dog
|
|
|
What hormone dominates during proestrus in the bitch?
|
Estrogen
|
|
|
Estrogen has influence on the epithelium of the vagina. When she is not under the influence of estrogen ___________. When she is under he influence of estrogen _______________.
|
the vaginal epithelium doesn't have many layers ............... the vaginal epithelium has many layers
|
|
|
What is the function of extra layers in the vagina that are found when the bitch is under the influence of estrogen?
|
They help protect against trauma
|
|
|
What type of cells do you expect to find in vaginal cytology during proestrus in a bitch?
|
cornified epithelial cells (cornflakes)
red blood cells (do to diapedesis from uterus) white blood cells/PMNs (variable in number; decreasing amount over time) debris in the background |
|
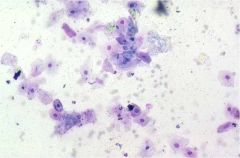
What stage of the bitch's cycle does this vaginal cytology come from?
|
Proestrus
|
|
|
What is the behavior of the bitch in early, middle, and late proestrus?
|
Early - non-acceptance of the male dog
Middle - negative responses - growling, snapping, aggression (eat his face !!!) Late - passive responses - sits down when dog attempts mounting, tucks tail |
|
|
What is the hormone profile of the bitch during proestrus?
|
Estrogen dominates
Gonadotopins - LH and FSH low Progesterone low - (<1 ng/ml) |
|
|
What is the duration of proestrus in the bitch?
|
Avg duration - 7-9 days
Range - 2-21 days Take home message: must remain flexible when managing individual bitches for breeding |
|
|
What are the general physical changes during estrus in the bitch?
|
softening of vulvar swelling, less blood in discharge
|
|
|
What is the general hormone actions during estrus in the bitch?
|
Progesterone rising
Estrogen falling LH and FSH peaks |
|
|
What is the appearance of vaginal cytology in the bitch during estrus?
|
> 90% cornified epithelium cells (cornflakes)
No WBCs Few RBCs Little or no debris on background of the slide |
|
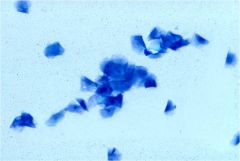
What stage in her cycle is this bitch?
|
Estrus - note large numbers of cornified epithelial cells (cornflakes) with no nuclei, no RBCs or WBCs and little/no background debris
|
|
|
What is the behavior of the bitch during estrus?
|
definition: stands to be mounted
Tail deviated to the side and elevated Muscles around vulva contract and raise vulva - (helps with alignment of penis) stiffening of back legs rolling of skin on back |
|
|
What are the hormone profiles of the bitch during estrus?
|
estrogen begins to fall
progesterone starts to rise - (first rise of P4 is correlated with LH peak) ***estrogen and progesterone are necessary for standing behavior LH and FSH both peak at onset of estrus - may need both for ovulation |
|
|
__________ and ____________ hormones are necessary for standing behavior in the bitch to occur.
|
Estrogen and Progesterone
|
|
|
What is the duration of estrus in the bitch?
|
Avg duration: 7-9 days
Range - 2-21 days Take home message: must remain flexible when managing individual bitches for breeding |
|
|
How does diestrus in the bitch begin?
|
with change in behavior -- non-acceptance of the male
|
|
|
What hormone in the bitch dominates diestrus?
|
Progesterone dominated - luteal phase
|
|
|
What is the duration of diestrus in the bitch?
|
length of pregnancy = pseudopregnancy is normal in the bitch
|
|
|
What is the origin of diestrus in the bitch?
|
wolf (canis lupis) -- (dogs are the same species they are Canis lupis subspecies familiaris)
|
|
|
What physical changes occur during diestrus in the bitch?
|
vulvar swelling decreases
vulvar discharge disappears - sometimes see scant purulent discharge during the early portion (this is normal) |
|
|
What is the appearance of the bitch's vaginal cytology during diestrus?
|
abrupt change to non-cornified cells
influx of neutrophils |
|
|
What hormone peaks at 3 weeks during diestrus in the bitch?
|
Progesterone
|
|
|
Prolactin is ___________.
|
luteotrophic
|
|
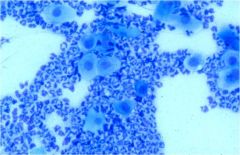
What stage is this bitch in based on the vaginal cytology shown?
|
Diestrus - note the disappearance of cornified epithelial cells and the influx of neutrophils
|
|
|
Felines are ____________ breeders. Meaning _________ daylight hours are necessary for cycling to occur.
|
seasonal breeders
long daylight hours |
|
|
Felines are _________ ovulators.
|
induced
|
|
|
Feline Reproductive Cycle
|
seasonal breeders - must have long daylight hours for cycling to occur
induced ovulators February - November Inside queens exposed to light may cycle year round |
|
|
What are the stages of the feline reproductive cycle?
|
Proestrus - not as defined as in bitches
Estrus- acceptance of mating Post-estrus (interestrus) - no luteal phase if not induced to ovulate Diestrus - when ovulation has occurred |
|
|
Proestrus in the Queen
|
increased activity, vocalization, increased affection towards people
estrogen levels rising vaginal cytology undergoing similar changes as the bitch - (not routinely done) |
|
|
Estrus in the Queen
|
vocalization, rolling behavior, assuming the breeding position, treading with hind legs
estrogen is high when breeding takes place, reflex release of LH from pituitary 4 or more breedings = 100% ovulation |
|
|
Cat copulation diagram
|
|
|
|
Post-estrus in the queen
|
non-ovulatory cycle
no luteal tissue on ovary - no progesterone avg duration - 8-10 days no sexual receptivity |
|
|
Diestrus in the queen only occurs when....
|
ovulation has been induced by breeding or other means (hormonal or mechanical)
|
|
|
What is the length of the luteal phase in pregnancy (diestrus) in the queen.
|
9 weeks in length
|
|
|
What is the length of the luteal phase in pseudopregnancy in the queen?
|
40-45 days in length
|
|
|
Anestrus in the queen
|
classic winter anestrus of the seasonal breeder
no cycling activity seen during this time October/November - January |
|
|
What are infectious reproductive diseases seen in canines and felines?
|
Brucella canis
Canine herpes virus Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP) Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV) Feline Panleukopenia |
|
|
What organism causes canine brucellosis and how?
|
Brucella canis
-contagious through mucous membrane contact with the organism |
|
|
What are the signs of canine brucellosis and how is it treated?
|
- Abortion due to placentitis ***
- Orchitis/Epididymitis*** - Erythritol in placenta and epididymes - essentially non-treatable for breeding stock |
|
|
How do you diagnose Canine Brucellosis?
|
Absolute confirmation - culture of organism
Rapid Slide Agglutination Test - excellent screening test Tube Agglutination Test - diagnostic laboratories - titers Agar Gel Immunodiffusion Test - cell surface and cytoplasmic antigens tested |
|
|
When would you get false negatives when testing for canine brucellosis?
|
early in the disease process - < 4-6 weeks
after treatment |
|
|
Why would you get false positives when testing for canine brucellosis?
|
lack of specificity of tests
Cross-reactivity with other antigens |
|
|
Interpretation of canine brucellosis tests
|
slide test - good screening test (in house)
Tube agglutination (titers)- < 1:50 = non-significant titer AGID - rule out false positives - tests for cell surface vs cytoplasmic antigens Culture - absolute confirmation |
|
|
Plan for Brucella canis
|
if positive results in routine screen - AGID to rule out false positive
If positive with clinical signs - blood or discharge cultures if negative on routine screen - no other test needed if negative with clinical signs - 3 monthly tests required to rule out false negatives |
|
|
Canine herpes virus
|
Neonatal deaths primarily - (experimentally: placentitis, abortion, stillbirths)
temperature sensitive virus - replicates in oronasal pharynx ubiquitous - high morbidity no illness in animals over three weeks of age |
|
|
What is the critical time frame for canine herpes virus in the naive bitch (no previous exposure)?
|
the critical window - last three weeks of pregnancy and first three weeks of neonatal life
|
|
|
When is canine herpes virus exposure no problem?
|
if exposed during breeding
if exposed after 2-3 weeks post-partum (past poikilothermic period) |
|
|
What are the clinical signs for canine herpes virus?
|
fading puppies - crying, greenish stool, abdominal pain
high mortality in an affected litter - near 100% all subsequent litters normal Necropsy - petechial hemorrhages in kidney, liver, lung, spleen. INIB on histopathology sections |
|
|
Feline Infectious Peritonitis
|
"kitten mortality complex"
repeat breeders abortion - stillbirths Fading kittens difficult to dx unless they have fulminant clinical disease even with positive titer b/c it is hard to know if it is a x-reaction with another virus |
|
|
Feline leukemia virus
|
fetal resorption
|
|
|
Feline Panleukopenia
|
cerebellar hypoplasia in kittens - these kittens will have intention tremors b/c cerebellum is responsible for coordinated movement
|
|
|
Abdominal palpation for pregnancy diagnosis in small animals
|
21-28 days - "string of pearls" - difficult after day 35
|
|
|
Using radiography in pregnancy diagnosis for small animals
|
Safe after day 40 - but it is best done in the last week of gestation due to calcification - this allows you to count the number of fetuses
-you can get in the ball park of figuring out if there will be dystocia due to size of pup (measure size of skull/size of pelvic opening) |
|
|
Using ultrasound in pregnancy diagnosis for small animals
|
confirms pregnancy
fetal viability information inaccurate to count (typically end up with an under-count) |
|
|
How is relaxin used for pregnancy dianosis in canines?
|
Canine ONLY
comes from the placenta - measurable in serum after day 21-28 this is the only hormone that we have been able to detect in the pregnant bitch that is different from the pseudo-pregnant bitch |
|
|
When there is a lower than ___________ fetal heart rate, we know they are being stressed.
|
200bpm
|
|
|
Pregnancy management
|
generally - as long as she did it before she was pregnant, she can do it during pregnancy
regular exercise - fewer dystocias weight control - fewer dystocias |
|
|
Pregnancy Management: nutrition
|
last trimester - increase 50% (gradually increase)
multiple small meals - b/c she doesn't have a lot of room in abdomen growth formulation - 28-30% protein Fish oil - omega 3's are beneficial AVOID all other supplements |
|
|
what is necessary/needed in a whelping/queening area?
|
must be out of traffic patterns
whelping box w/ pig rails acclimate 1 week prior to due date washable bedding - need good footing (don't want slippery surface) |
|
|
When is a singlet puppy a problem?
|
It isn't necessarily a problem - Typically more of a problem in large breed dogs (get a little worried when there are less than 3 puppies)
|
|
|
How do you predict that whelping is soon to occur?
|
body temp drops ~ 24 hours prior to whelping ( usu. drops to 98 or below)
indicates a drop in progesterone - (progesterone is thermogenic) Transient drop - take temperature twice daily - if she hasn't whelped in 48 hours since temp drop, take her to vet |
|
|
What is the gestation length in the bitch?
|
---gestation length is critical
65 days from LH peak (P4=2ng/ml) 61 days post ovulation (P4=5ng/ml) 61-63 days post breeding date - most inaccurate (range = 55-70 days) 56-57 days after onset of diestrus |
|
|
What is the gestation length of the feline?
|
average 63 days
(Range = 58-70 days) |
|
|
If you see abnormal vaginal discharges during pregnancy...
|
occasional mucus is normal
hemorrhagic- may be normal or may be sign of impending abortion (do vaginal cytology and vaginoscopy) purulent discharge - pyometra or dead fetus antibiotics - only if necessary - rest - supportive therapy as needed |
|
|
Fetal Wastage
|
incidence unknown - prob. 30% of preg. have at least 1 fetal resorption
ultrasonography is best way to confirm causes: trauma, heat stress, luteal insufficiency, viral, bacterial, CEH, protozoa treatment: evacuate her uterine contents if all puppies/kittens are dead (PGF2a) |
|
|
Prolonged gestation in the bitch
|
-must confirm pregnancy (radiographs)
-important info: breeding dates, end of estrus, previous pregnancies - problem w/ singleton puppies, esp in med. to large breed dogs - primary uterine inertia: P4= <2ng/ml ----- no labor u/s : fetal viability, stress c-section if needed |
|
|
uterine torsion in small animals
|
uncommon
clinical presentation: acute abdomen - pain distress; may be asymptomatic until dystocia diagnosis - exploratory laparotomy - you won't know until you get in there |
|
|
What causes the initiation of parturition in small animals?
|
progesterone falls rapidly to initiate parturition: <2ng/ml
transient drop in body temp (take BID) milk evident in glands 1-7 days prior - unreliable in prediction of parturition |
|
|
The first stage of parturition in small animals
|
begins after progesterone drops
-removal of progesterone "block" from the uterus - myometrial activity begins -increase in oxytocin receptor sites -nesting, anxiety, anorexia, vomiting |
|
|
The second stage of parturition in small animals
|
active contractions - fetus in pelvic canal stimulates "urge to push"
Ferguson reflex - oxytocin release and abdominal contractions amnion appears first greatest effort is to deliver the head breech presentations are normal |
|
|
What is the Ferguson reflex and when does it occur?
|
-oxytocin release and abdominal contractions
- occurs during 2nd stage of parturition |
|
|
Continuation of the second stage of parturition
|
greenish black discharge - uteroverdin in canine pregnancies; placental marginal hematomas
dam will eat placentas avg interval: 30 min-1hr |
|
|
What is the intervention criteria in the second stage of parturition in the bitch?
|
active contractions >1hr
rest period >4hrs black, thick discharge w/out fetus |
|
|
What should be done if intervention is necessary?
|
C-section should be considered early (don't do unless you have confirmed fetal presence on radiograph)
U/S to help determine fetal viability radiography to determine presence of additional fetuses oxytocin - if no obstruction present Ca++ if deemed necessary |
|
|
Third stage of parturition in small animals
|
passage of placentas (retention is rare) - consider if purulent discharge occurs post-partum
most are passed immediately following the fetus oxytocin is not necessary if suckling puppies/kittens are present |
|
|
Normal involution in small animals
|
decreases over time - most expelled in first two weeks
changes in color - red (blood) -> brown (old blood) changes in consistency - watery -> mucoid no odor brownish mucoid lochia can be normal for 4-6 weeks post-partum |
|
|
Management of Dam
|
monitor mammary glands and vulvar discharges daily
unlimited food and water (to dam) |
|
|
Weaning (small animals)
|
Start weaning process at 3-4 weeks by offering gruel (complete by 5-8 weeks)
reduce food to dam at weaning the pressure in her mammary glands gives the signal to stop producing milk |
|
|
Care of Newborns (small animals)
|
Need colostrum and daily milk intake (don't get antibodies through the placenta)
eat, sleep, and dream dam stimulates urination/defecation crying indicates a problem poikilothermic for the first 2-3 weeks |
|
|
Hypothermia is critical during the first __________ weeks.
|
2-3 weeks (because they are poikilothermic)
|
|
|
Ambient temperatures required by neonates (small animals)
|
1-7 days (85-90 degrees F)
8-28 days (80 degrees F) 29+ days (70-75 degrees F) - can provide heat lamps of heating pads as long as they are able to move away from the heat source |
|
|
Pig piles = __________ babies
|
cold babies
|
|
|
What is the daily weight gain of small animal neonates?
|
10% of birth weight daily
|
|
|
important factors in monitoring neonates
|
hypothermia - most important
hypoglycemia - inadequate caloric intake hypovolemia - dehydration |
|
|
Post partum diseases: Metritis
|
inflammation of ENTIRE uterus (endometrium and myometrium)
systemic illness: fever, depression, purulent vulvar discharge Dx: CBC, vaginal cytology, culture, U/S Treatment: PGF2a to evacuate the uterus; supportive therapy- fluids, antibiotics |
|
|
Post-Partum Diseases: Mastitis
|
Can kill bitches
enlarged, hot painful glands fever, leukocytosis coliforms, strep, staphs hot pack and strip abnormal milk aspirin, antibiotics tends to reoccur w/ subsequent litters or pseudo-pregnancies |
|
|
Post-Partum Diseases: Hypocalcemia (Eclampsia)
|
occurs primarily in small, nervous breeds
can be hereditary in some lines progressive clinical signs: panting, pacing, muscle tremors (trembling), ataxia, hyperthermia (106-108 deg F), tonic-clonic convulsions, death Treatment: give calcium |
|
|
Treatment of Hypocalcemia in Small animals
|
IV calcium gluconate - to effect
Oral calcium supplements for maintenance Weaning: if puppies are old enough; if unable to control clinical signs; re-occurrence of clinical signs |
|
|
Post-Partum Diseases: Subinvolution of Placental Sites - SIPS
|
persistent uterine bleeding (after whelping)
usually identified if bleeding persists after weaning gross lesions: erosions in endometrium Histologic lesions: Multinuclear giant cells = trophoblast cells |
|
|
Treatment and Prognosis of SIPS
|
usually self-limiting
PGF2a Not related to: post-partum metritis or future infertility |
|
|
Estrus control: Ovaban (megesterol acetate)
|
Progestin - only treatment approved for use in breeding bitches (contraindicated in queens -> diabetes mellitus)
daily dosing required proestrus - (1st 3 days) -1mg/lb PO 8 days Anestrus: 0.25 mg/lb PO 32 days |
|
|
Estrus control: Mibolerone (Cheque)
|
Androgenic compound
contraindicated in cats: liver toxicity not approved for use in breeding bitches daily dosing required - oral Must start 30 days prior to next anticipated cycle |
|
|
Estrus control: Testosterone
|
used routinely in racing greyhounds
many start prepubertally Ex. protocol: 20mg aqueous testosterone weekly IM 25 mg methyl testosterone PO twice weekly side effects minimal |
|
|
Estrus Control: Deslorelin- GnRH analogue
|
long acting implants - 6-12 months (not avail.yet in USA)
implants visible by ultrasound so can be removed early if desired downregulates the pituitary-gonadal axis totally safe totally reversible can be used in dogs and bitches |
|
|
Canine Pseudo-pregnancy
|
normal after every estrus in bitches
overt vs covert only in queens that have been stimulated to ovulate (40-45 days) Treatments: testosterone, mibolerone, bromocriptine, time (self-limiting) |
|
|
Mis-mating shots
|
estrogen - within 72 hours of breeding- while still in estrus
causes "tubular lockage" and disrupts/alters uterine environment 25% incidence of pyometra (side effect) client release form signed Estrone |
|
|
Estrogen toxicity
|
bone marrow suppression - dogs and ferrets (not a problem in cats)
lethal and irreversible do not repeat ECP injection more frequently than once every 30 days Pyometra - 25% incidence |
|
|
What are other options to mis-mating shots?
|
spaying
waiting until day 28-30, U/S - abort pregnancy at that time allowing whelping - euthanasia of pups, placement of pups |
|
|
Prolactin inhibitors
|
Bromocriptine and Cabergoline
dopamine agonists prolactin is luteotropic in bitch and queen during the second trimester CL's lyse in response to lowered prolactin levels progesterone <2ng/ml for 48hrs induces whelping/abortion |
|
|
Prostaglandin
|
multiple small injections will lyse the CL of the bitch or queen
side effects seen w/ smooth muscle contractions but minimize over time Luteolytic dose only 5-fold from LD50 best accomplished during 2nd trimester after pregnancy diagnosis |
|
|
Emerging alternatives to mis-mating
|
GnRH implants- deslorelin
-down regulation of pituitary support results in luteolysis -prolonged release over time GnRH vaccine -anti-GnRH antibodies result in luteolysis Requires 2 injections at 2-4wk interval |
|
|
Vaginitis in the puppy
|
small amount of purulent discharge in the prepubertal bitch
best option - scientific 'neglect' rule out concurrent cystitis postpone spay until resolved goes away w/ first estrus |
|
|
Vaginitis: Adult onset
|
primarily seen in spayed bitches
rule out: skin disease- perivulvar dermatitis anatomic - inverted juvenile vulva urinary tract infections foreign bodies tumors |
|
|
Treatments for adult vaginitis
|
Hormonal: DES to thicken the vaginal epithelium
Surgery: removal of excess skin folds around the vulva; allows freer voiding of urine; only done when problem is serious and refractory to medical treatment |
|
|
Routine Breeding Management of the Bitch
|
identify first day of vulvar discharge: start counting = Day 1
identify first day of standing estrus breed every 2-3 days until no longer stands Avg scenario: breed on day 10, 12, and 14; out of estrus - day 16-18 |
|
|
Blood supply to dog's penis during copulation
|
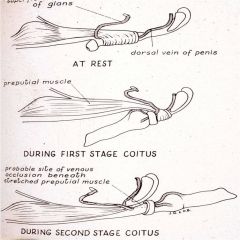
|
|
|
Breeding management: Progesterone
|
modern standard for breeding management
semiquantitative: ELISA quantitative methods preferred: radioimmunoassay, chemiluminescence Sample every other day (M-W-F) principle: 2ng/ml = LH peak 5 ng/ml = ovulation |
|
|
Breeding management: Time frame for using progesterone in the bitch
|
Ovulation begins 24-48 hours after LH peak- or first rise in progesterone (2ng/ml)
ovulation takes 24-48hrs - waves of ovulation over time for multiple follicles two meiotic divisions to take primary oocytes to secondary oocytes (24-48 hours) 3-6 days from LH peak = FERTILIZATION |
|
|
Breeding Management: LH Assays
|
In-house kit available
helpful in breeding mgmt - used in conjunction with progesterone assay more definitive than progesterone disadvantage - must take daily samples gestation length defined = 65 days spayed animals will have high LH - no negative feedback |
|
|
Feline Breeding Management
|
natural breedings are the norm
copulation necessary for ovulation unless GnRH/hCG given multiple breedings ensure complete ovulation bring queen to male's territory - allow time for acclimatization |
|
|
Pyometra
|
diestral disease- occurs during progesterone phase of cycle
seen 60-90 days postestrus in the bitch - anytime in the queen often seen in older individuals medical reason for spaying females not intended for breeding |
|
|
Clinical presentation of pyometra
|
depression - most often seen with toxemia
leukocytosis- may see left shift vulvar discharge - if open cervix PU/PD - endotoxins from E. coli Dx: abdominal palpation, radiograph, U/S** |
|
|
Medical Therapy for Pyometra
|
PGF2a - Lutalyse
causes smooth muscle (myometrial) contractions to evacuate the uterus multiple small injections will lyse the CL - continue until progesterone is baseline Treat "to effect" - until uterine contents are gone per U/S |
|
|
Pyometra: medical therapy considerations
|
culture/sensitivity: appropriate antimicrobial therapy - bacterial showers
side effects of PGF2a: panting, salivation, vomition, defecation, vocalization (queens) - 30-40 min duration Recommendation: breed next occurring estrus - Then spay |

