![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Methods of obtaining semen samples
|
-artificial vagina
-manual stimulation into receptacle -electroejaculation |
|
|
Artificial vagina
-used for what animals |
-stallion
-trained bull |
|
|
Artificial vagina
-interior compartment |
-filled with warm water because the stallion is a temperature sensitive ejaculator
|
|
|
Artificial vagina
-provides what |
-temperature stimulation
-pressure stimulation |
|
|
Manual stimulation into a receptacle
-animals |
-dog
-boar |
|
|
Manual stimulation into a receptacle is for what kind of ejaculator
|
-pressure sensitive
|
|
|
Electroejaculation
-animals |
-bull
-billy/ram (sedated) -wildlife 9anesthetized) |
|
|
Things that corrupt collection of a representative semen sample
|
-first part of the sperm rich fraction in the epididymis with sexual rest may be abnormal
-fecal contamination, urine, water, soap, and blood can adversely effect motility and make it difficult to do a good sperm morphological exam -high and low environmental temperatures can affect sperm motiility |
|
|
Are the volume of ejaculate, sperm density, and gross characteristics good predictors of fertility?
|
-NO
|
|
|
Methods of assessing sperm motility
|
-gross motility
-individual motility |
|
|
Semen motility
-minimum recommended motility |
-30% or fair
|
|
|
Sperm motility
-very good rating (gross, individual) |
-gross: rapid swirling
-individual: >70% |
|
|
Sperm motility
-good rating (gross, individual) |
-gross: slower swirling
-individual: 50-69% |
|
|
Sperm motility
-fair rating (gross, individual) |
-gross: generalized oscillation
-individual: 30-49% |
|
|
Sperm motility
-Poor rating (gross, individual) |
-gross: sporadic ascillation
-individual: <30% |
|
|
Does sporadic oscillating semen mean there is a problem?
|
-Not necessarily
-sample can be very dilute and would need to be re-evaluated |
|
|
Why should latex gloves not be worn when handling semen?
|
-latex is spermicidal
|
|
|
Warming plate should be used for:
|
-slides
-stains -coverslips -semen *keep warm at all times and prevent cold shock |
|
|
Examination of gross motility
-procedure |
-place drop of semen on a warmed slide and observe under 100x (low) magnification
|
|
|
Examination of individual motility
-procedure |
-assess under bright-field or phase-contrast microscopy at 400x
|
|
|
Individual motility examples
-dilution |
-sodium citrate
or -skim milk based semen extender or -physiological sterile saline (if exam done promptly) |
|
|
Differential counts of normal and abnormal sperm are generally assessed by:
|
-phase-contrast microscopy using samples fixed in formalin-buffered-saline or PBS-gulteraldehyde
-bright field microscopy of stained smears |
|
|
Morphological exam
-magnification |
-1000x
|
|
|
Evaluation of semen morphology
-stains |
-nigrosin-eosin
-williams stain -modified giemsa -DifQuik -India ink |
|
|
Morphologic evaluation
-how to stain |
-1 drop semen mixed with 1 drop nigrosin-eosin and the mixture is spread over the surface of a glass slide and allowed to dry
-vary smear thickness |
|
|
Morphological evaluation
-requirement for bull to pass BSE |
-al least 100 random sperm need to be observed and at least 70% of observed cells need to be normal
|
|
|
If a particular semen sample has a high number of abnormalities, what may be necessary?
|
-counting 500 or more sperm
|
|
|
Sperm
-viability stain |
-Eosin or Propidium iodide
-relies on a permeable plasma membrane to define a non-viable sperm |
|
|
Why is a viability stain not very well correlated with fertility?
|
-we have no idea how viable the unstained sperm are, we just know that they are viable
|
|
|
Rather than different insults causing different morphological abnormalities, ______________
|
a number of different insults cause stress which results in specific abnormalities to germ cells in specific phases of development/maturation
|
|
|
Inherited sperm abnormalities
-why rarely seen |
-cause infertility
|
|
|
Inherited sperm abnormalities
-effects |
-knobbed defect
-dag defect -tail stump defect -azoospermia/oligospermia -decapitated defect -rolling head/nuclear crest/giant head syndrome |
|
|
Sperm cell morphological classification systems
|
-based on origin (testicular, extra-testicular)
-based on significance (major/minor) -based on functional contribution to fertility (compensable/uncompensable) |
|
|
Sperm Morphology based on origin
|
Primary abnormalities
-arise during spermatogenesis in seminiferous tubules due to pathological processes in the seminiferous epithelium -abnormal head, abnormal midpiece, proximal cytoplasmic droplet, etc. Seconday abnormalities: -arise after sperm cells had left testis such as abnormal epididymal function -bent tails, coiled tails, etc. |
|
|
Sperm morphology based on significance
|
Major abnormailites
-correlated to impaired fertility Minor abnormalities -minor importance *difficult to figure out |
|
|
Sperm morphology based on functional contribution to infertility
|
Compensable abnormalities
-defects that cause an affected sperm cell to fail to reach and fertilize the ovum -sperm can induce zona reaction -increasing the dose of sperm (A.I.) will result in more total normal sperm and improved fertility -ex) tail problem that precludes forward motility Uncompensable abnormalities -defects that don't prevent a sperm from reaching the ovum but prevent normal development of the embryo -sperm can't induce zona reaction -increasing sperm dose A.I. will result in same percentage of abnormal sperm and hence same fertility |
|
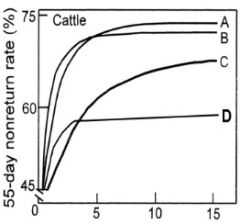
What is it?
-describe |
-Fertility Dose-Response Curve
-Fertility plateaus at 5-10 million sperm cells -Bull C has compensable sperm abnormalities -Bull D has non-compensable traits |
|
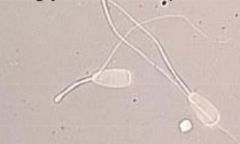
Describe abnormality
-type of abnormality |
Strongly folded midpiece
-Major/Primary abnormality |
|
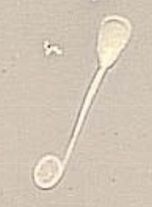
Describe abnormality
-type of abnormailty |
Coiled tail
-Minor/Secondary abnormality |
|
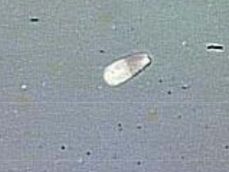
Describe abnormality
-Type of abnormality |
Detached head
-Minor/Secondary abnormality *not uncommon to find in a normal semen sample |
|
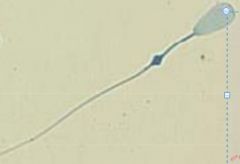
Describe abnormality
-type of abnormality |
Distal droplet
-Minor/Secondary abnormality *not abnormal |
|
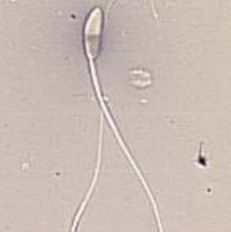
Describe abnormality
-type of abnormality |
Elongated head
-Major/Primary abnormality |
|
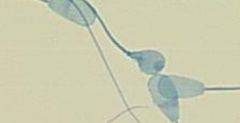
Describe abnormality
-type of abnormality |
Misshapen head
-Major/Primary abnormality |
|
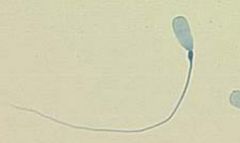
Describe abnormality
-Type of abnormality |
Proximal droplet
-Major/Primary abnormality |
|
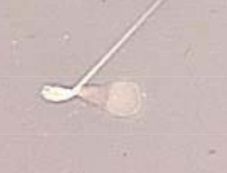
Describe abnormality
-type of abnormality |
Pyriform head and bend midpiece
-Major/Primary abnormality |
|
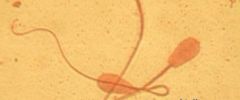
Describe abnormality
-Type of abnormality |
Reversed tail
-Minor/secondary abnormality *probably human error from cold shock if a C-shaped bend is present in the tail |
|

Describe abnormality
-Type of abnormality |
Medusa cell
-unknown |
|
|
Presence of spermatogenic epithelial cells (spheroids) in the semen suggests what?
|
-poor health of the seminiferous tubules
|
|
|
Breeding soundness exam
-limitations |
-only reflects breeding soundness on the day tested
-sperm cells seen today were begun weeks ago -does not predict ability to cause conception in the future -better for identifying subfertile males than highly fertile females |
|
|
Breeding soundness exam
- strengths |
-guarantees that sub-fertile males are not used for breeding
-removes subfertile males from the genetics of the herd and breed -over time herd and breed fertility are increased |
|
|
Breeding soundness exam
-interpretation |
-good at IDing poor performing males
-bell shaped curve does not allow us to predict how males that pass BSE will perform |
|
|
Ultrasound
-use |
-evaluate/detect fibrosis
-soft areas -spermatoceles |
|
|
Thermography
-use |
-check thermoregulation of testes
-if scrotal surface temp is high or displays little decrease as one moves from the top to the bottom of the scrotum there are: more abnormal sperm, fewer pregnancies |
|
|
Computer Aided Sperm Analysis (CASA)
-equipment |
-software that utilize video capture from microscope video recorded
-phase contrast or darkfield microscope |
|
|
Computer Aided Sperm analysis
-motility can be altered by |
-dilution of semen
-image settings -semen viscosity and ionic composition -temp extremes |
|
|
Evaluation of frozen semen
-preferred values |
> 50% linear motility (slower motility)
|
|
|
Evaluation of frozen sperm
-when to evaluate |
-thaw
-2 hours post thaw |
|
|
If AI uses fewer sperm cells and many are damages, how do we get cows/mares/b!tches pregnant?
|
-deposit semen in uterus rather than vagina
|
|
|
Evaluation of sperm quality has arisen because:
|
-our desire to predict fertility
*goal has not been achieved |
|
|
Role for in vitro evaluation of sperm quality
|
-predicts male will be less fertile than average males
-can predict that a given sample has a high probability of providing similar to that he has achieved in the past (if males with known fertility had semen characterized in the past) |
|
|
What can't be done with in vitro evaluation of sperm quality?
|
-can't take a male with unknown fertility and predict that his fertility will be greater than the mean for fertile males
|
|
|
CASA
-measured characteristics |
-Percent motility
-Velocity curvilinear -Velocity average path -Velocity straight line -Linearity -Wobble -Progression |
|
|
Attributes of sperm essential for fertility
|
-acceptable morphology
-maturation of spermatozoa within the proximal epididymis -maturation of membrane lipids -maturation of membrane proteins -activation of integral enzymes associated with fertilization -upon exposure to the micro-environment of the oocyte -upon exposure to the cytopplasm of the oocyte |
|
|
Frozen semen
-chemical and physiological shanges that occur during freezing and thawing |
-partial dehydration
-cryprotectant penetration of cells -reorganization of membrane lipids and proteins -exposure to high salt concentrations -exposure to inter and intracellular ice crystals |
|
|
Evaluation of frozen semen
-purpose of evaluation post-thaw |
-evaluate degree of sperm damage inflicted by crypreservation feature
|
|
|
Diadem Crater Defect
-induced by |
-pyrexia
-ethylene dibromide -sulfasalazine -corticosteroids -low testosterone -viruses |
|
|
Midpiece defect
-induced by |
-Gossypol
-Ethylene dibromide -Genetics -Respiratory disease |
|
|
Gossypol
-effects on bull repro tract |
-degeneration and reduction of spermatogenesis
-damage to the basement membrane of spermatogenic tubules -increase in abnormal sperm |

